Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?





Analysis of PKA RIIα (pS99) in human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were either treated with 1µM Staurosporine (EMD Biosciences, Cat. No. 569397) for 2 hours at 37ºC (shaded histogram) or untreated (open histogram). The PBMC were fixed (BD Cytofix™ buffer, Cat. No. 554655) for 10 minutes at 37°C, permeabilized with BD Phosflow™ Perm Buffer III (Cat. No. 558050) on ice for 30 minutes, and then stained with Alexa Fluor® 647 Mouse anti-PKA RIIα (pS99, Cat. No. 560164). For data analysis, lymphocytes were selected by their scatter profile. The data demonstrates that the level of phosphorylation of PKA RIIα decreases when protein kinase activity is inhibited by the treatment. Flow cytometry was performed on a BD FACSCalibur™ flow cytometry system.



BD™ Phosflow Alexa Fluor® 647 Mouse anti-PKA RIIα (pS99)

BD™ Phosflow Alexa Fluor® 647 Mouse anti-PKA RIIα (pS99)

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
Either BD Cytofix™ fixation buffer or BD Phosflow™ Fix Buffer I may be used for cell fixation. Any of the three BD Phosflow™ permeabilization buffers may be used.
Product Notices
- This reagent has been pre-diluted for use at the recommended Volume per Test. We typically use 1 × 10^6 cells in a 100-µl experimental sample (a test).
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Alexa Fluor® 647 fluorochrome emission is collected at the same instrument settings as for allophycocyanin (APC).
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- The Alexa Fluor®, Pacific Blue™, and Cascade Blue® dye antibody conjugates in this product are sold under license from Molecular Probes, Inc. for research use only, excluding use in combination with microarrays, or as analyte specific reagents. The Alexa Fluor® dyes (except for Alexa Fluor® 430), Pacific Blue™ dye, and Cascade Blue® dye are covered by pending and issued patents.
- Alexa Fluor® is a registered trademark of Molecular Probes, Inc., Eugene, OR.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products




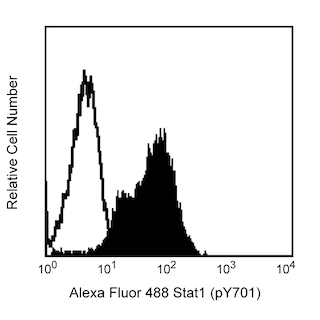
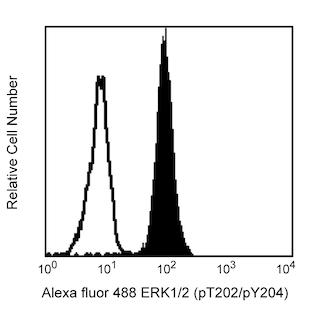
cAMP-dependent Protein Kinase (PKA) is composed of two distinct subunits: catalytic (C) and regulatory (R). Four regulatory subunits have been identified: RIα, RIβ, RIIα, and RIIβ. These subunits define type I and II PKAs. Following binding of cAMP, the regulatory subunits dissociate from the catalytic subunits, rendering the enzyme active. Type I and II holoenzymes have three potential C subunits (Cα, Cβ, or Cγ). Type II PKA can be distinguished by autophosphorylation of the R subunits, while type I PKA binds Mg/ATP with high affinity. The cAMP-dependent autophosphorylation of the human RIIα subunit occurs at Serine 99 (S99) [Entrez Protein Accession #CAA33094]. Most cells express both type I and type II PKAs. Although the Rα isoforms are ubiquitously expressed, the Rβ isoforms are predominantly found in nervous and adipose tissues. In addition to their enzyme regulatory activity, the RIIα and RIIβ subunits determine the subcellular location of the holoenzymes via their interactions with specific intracellular anchoring proteins.
The I65-856.286 antibody recognizes human PKA RIIα phosphorylated at S99.
Development References (2)
-
Francis SH, Corbin JD. Structure and function of cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. Annu Rev Physiol. 1994; 56:237-272. (Biology). View Reference
-
Scott JD, Stofko RE, McDonald JR, Comer JD, Vitalis EA, Magili JA. Type II regulatory subunit dimerization determines the subcellular localization of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1990; 35:21561-21566. (Biology).
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.