Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
For optimal and reproducible results, BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer should be used anytime two or more BD Horizon Brilliant dyes (including BD OptiBuild Brilliant reagents) are used in the same experiment. Fluorescent dye interactions may cause staining artifacts which may affect data interpretation. The BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer was designed to minimize these interactions. More information can be found in the Technical Data Sheet of the BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer (Cat. No. 563794).
Product Notices
- This antibody was developed for use in flow cytometry.
- The production process underwent stringent testing and validation to assure that it generates a high-quality conjugate with consistent performance and specific binding activity. However, verification testing has not been performed on all conjugate lots.
- Researchers should determine the optimal concentration of this reagent for their individual applications.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,110,673; 8,158,444; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Ultraviolet 395 is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,158,444; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
Companion Products





The 1AH2 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to CD137. CD137 is a member of the TNFR/NGFR superfamily that is likewise known as Tnfrsf9, 4-1BB, Ly-63, or ILA. Monomers or multimeric forms of CD137 are expressed, upon activation, on the surface of splenic T lymphocytes, thymocytes, intestinal intraepithelial T lymphocytes (IEL), and some T cell lines and clones. While stimulating T cells by IL-2, IL-4, or anti-CD28 alone does not result in the expression of CD137; addition of IL-2, IL-4, anti-CD28, or syngeneic accessory cells to splenic T cells stimulated via TCR/CD3 can result in a high level CD137 expression. CD137 is also reportedly expressed on IL-2 activated NK cells, but not on freshly isolated NK cells. CD137 physically associates with p56 [lck] through a Cys-Arg-Cys-Pro binding site in its cytoplasmic domain; the same motif in the cytoplasmic tail of the CD4 and CD8a molecules is responsible for association with p56 [lck]. A signaling function for the CD137 molecule in mouse T cells is indicated by reports in which cross-linking of CD137 with 1AH2 mAb resulted in enhanced proliferation of CD3e-activated splenic T cells and IEL and in enhanced cytolytic activity of IEL in response to immobilized anti-CD3e. In addition to extracellular matrix proteins which bind to CD137, the CD137L (4-1BBL) serves as a ligand for CD137. This molecule has also been detected on LPS-activated macrophages, and anti-IgM antibody-activated splenic B cells. Interaction between T and B cells through CD137/CD137L is reported to play a role in antigen presentation, further supporting a costimulatory role for CD137 in the immune response of T lymphocytes.
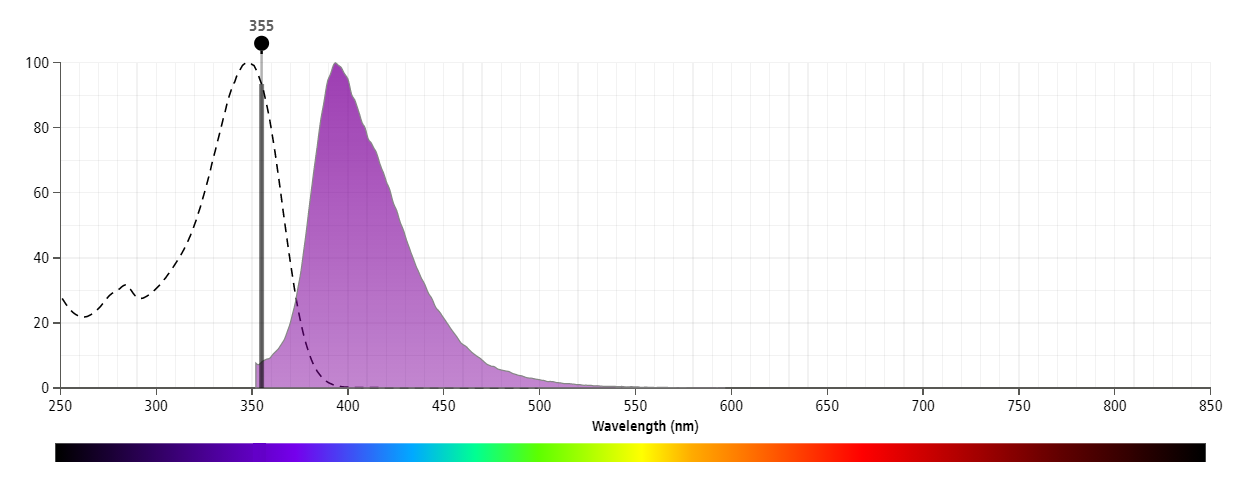
The antibody was conjugated to BD Horizon™ BUV395 which is part of the BD Horizon Brilliant™ Ultraviolet family of dyes. This dye has been exclusively developed by BD Biosciences to have minimal spillover into other detectors, making it an optimal choice for multicolor flow cytometry. With an Ex Max at 348 nm and an Em Max at 395 nm, BD Horizon BUV395 can be excited with a 355 nm laser and detected with a 379/28 filter.
Development References (11)
-
Chalupny NJ, Peach R, Hollenbaugh D, Ledbetter JA, Farr AG, Aruffo A. T-cell activation molecule 4-1BB binds to extracellular matrix proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992; 89(21):10360-10364. (Biology). View Reference
-
DeBenedette MA, Chu NR, Pollok KE, et al. Role of 4-1BB ligand in costimulation of T lymphocyte growth and its upregulation on M12 B lymphomas by cAMP. J Exp Med. 1995; 181(3):985-992. (Biology). View Reference
-
DeBenedette MA, Shahinian A, Mak TW, Watts TH. Costimulation of CD28- T lymphocytes by 4-1BB ligand. J Immunol. 1997; 158(2):551-559. (Biology). View Reference
-
Hurtado JC, Kim SH, Pollok KE, Lee ZH, Kwon BS. Potential role of 4-1BB in T cell activation. Comparison with the costimulatory molecule CD28. J Immunol. 1995; 155(7):3360-3367. (Biology). View Reference
-
Hurtado JC, Kim YJ, Kwon BS. Signals through 4-1BB are costimulatory to previously activated splenic T cells and inhibit activation-induced cell death. J Immunol. 1997; 158(6):2600-2609. (Biology). View Reference
-
Kim YJ, Pollok KE, Zhou Z, et al . Novel T cell antigen 4-1BB associates with the protein tyrosine kinase p56lck1. J Immunol. 1993; 151(3):1255-1262. (Biology). View Reference
-
Pollok KE, Kim SH, Kwon BS. Regulation of 4-1BB expression by cell-cell interactions and the cytokines, interleukin-2 and interleukin-4. Eur J Immunol. 1995; 25(2):488-494. (Biology). View Reference
-
Pollok KE, Kim YJ, Zhou Z, et al. Inducible T cell antigen 4-1BB. Analysis of expression and function. J Immunol. 1993; 150(3):771-781. (Immunogen). View Reference
-
Saoulli K, Lee SY, Cannons JL, et al. CD28-independent, TRAF2-dependent costimulation of resting T cells by 4-1BB ligand. J Exp Med. 1998; 187(11):1849-1862. (Biology). View Reference
-
Takeda K, Oshima H, Hayakawa Y, et al. CD27-mediated activation of murine NK cells. J Immunol. 2000; 164(4):1741-1745. (Biology). View Reference
-
Zhou Z, Pollok KE, Kim KK, Kim YJ, Kwon BS. Functional analysis of T-cell antigen 4-1BB in activated intestinal intra-epithelial T lymphocytes. Immunol Lett. 1994; 41(2-3):177-184. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.