Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?
![Biotin Mouse Anti-Mouse I-A[d]](/content/dam/bdb/products/global/reagents/flow-cytometry-reagents/research-reagents/single-color-antibodies-ruo/550xxx/5505xx/550554_base/550554_AMS321_fig1.png)
![Biotin Mouse Anti-Mouse I-A[d]](/content/dam/bdb/products/global/reagents/flow-cytometry-reagents/research-reagents/single-color-antibodies-ruo/550xxx/5505xx/550554_base/550554_AMS321_fig1.png)

![Biotin Mouse Anti-Mouse I-A[d]](/content/dam/bdb/products/global/reagents/flow-cytometry-reagents/research-reagents/single-color-antibodies-ruo/550xxx/5505xx/550554_base/550554_AMS321_fig1.png)
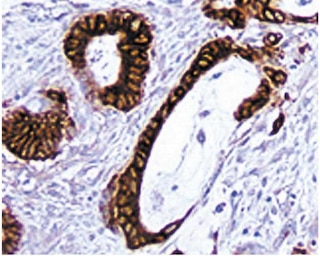
Immunohistochemistry of I-A[d] positive cells. Frozen sections of mouse thymus were reacted with the anti-I-A[d] antibody. Cells expressing the MHC class II molecule I-A[d] can be identified by the intense brown labeling of their cell membranes. Magnification 20x.

![Biotin Mouse Anti-Mouse I-A[d]](/content/dam/bdb/products/global/reagents/flow-cytometry-reagents/research-reagents/single-color-antibodies-ruo/550xxx/5505xx/550554_base/550554_AMS321_fig1.png)
BD Pharmingen™ Biotin Mouse Anti-Mouse I-A[d]

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
Immunohistochemistry: The AMS-32.1 clone reactive against mouse I-A[d] is recommended to test for immunohistochemical staining of acetone-fixed frozen sections. Tissues tested were mouse (BALB/c) spleen and thymus. The antibody stains the I-A[d] molecules found on the surface of cells expressing MHC-II in strains of mice expressing this haplotype. For optimal immunohistochemical staining, the biotinylated antibody should be titrated (1:10 to 1:50 dilution) and developed with Streptavidin-HRP (Cat. No. 550946) together with the DAB detection system (Cat. No. 550880). The clone AMS-32.1 is not recommended for formalin-fixed paraffin embedded sections.
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- This antibody has been developed for the immunohistochemistry application. However, a routine immunohistochemistry test is not performed on every lot. Researchers are encouraged to titrate the reagent for optimal performance.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products



The AMS-32.1 antibody specifically reacts with the I-A[d] MHC class II alloantigen. It crossreacts with cells from mice of the H-2[f], H-2[g7], H-2[i], and H-2[v] haplotypes. Reactivity with other haplotypes (e.g., k, p, q, r, s, u) has not been observed.
Development References (3)
-
Loken MR, Stall AM. Flow cytometry as an analytical and preparative tool in immunology. J Immunol Methods. 1982; 50(3):R85-R112. (Immunogen: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Matsumoto S, Setoyama H, Umesaki Y. Differential induction of major histocompatibility complex molecules on mouse intestine by bacterial colonization. Gastroenterology. 1992; 103(6):1777-1782. (Clone-specific: Immunohistochemistry). View Reference
-
Wall KA, Lorber MI, Loken MR, McClatchey S, Fitch FW. Inhibition of proliferation of MIs- and Ia-reactive cloned T cells by a monoclonal antibody against a determinant shared by I-A and I-E.. J Immunol. 1983; 131(3):1056-64. (Clone-specific). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.