-
Reagents
- Flow Cytometry Reagents
-
Western Blotting and Molecular Reagents
- Immunoassay Reagents
-
Single-Cell Multiomics Reagents
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- BD® OMICS-One Protein Panels
- BD OMICS-One™ WTA Next Assay
-
Functional Assays
-
Microscopy and Imaging Reagents
-
Cell Preparation and Separation Reagents
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current location site or be switched to your location?

Compensation and Spectral Unmixing Controls
Compensation or spectral unmixing is critical when setting up flow cytometry experiments to correct fluorescence spillover that can lead to biological artifacts. While single-color stained cells are the preferred controls, microparticles (beads) that bind species-specific antibodies may be used for compensation and spectral unmixing. Beads are especially useful when cell samples are limited, cell population frequency is low, or when markers are lowly or variably expressed. It is important to validate any chosen single-color control to ensure proper fluorescence spill over corrections.
Products for Compensation and Spectral Unmixing
| Product | Reactivity | Format | Light chain recognized |
|---|---|---|---|
| BD™ SpectraComp™ Unmixing and Compensation Particles | Mouse, Rat, Hamster (Armenian, Syrian) | Single vial with both positive and negative beads | Kappa & lambda |
| BD™ CompBeads Anti-Mouse Ig, κ/Negative Control Compensation Particles Set | Mouse | Separate vials for positive and negative beads | Kappa |
| BD™ CompBeads Anti-Rat Ig, κ/Negative Control Compensation Particles Set | Rat | Separate vials for positive and negative beads | Kappa |
| BD™ CompBeads Anti-Rat and Anti-Hamster Ig κ /Negative Control Compensation Particles Set | Rat, Hamster (Armenian, Syrian) | Separate vials for positive and negative beads | Kappa |
| BD™ CompBead Plus Anti-Mouse Ig, κ/Negative Control (BSA) Compensation Plus (7.5 µm) Particles Set | Mouse | Separate vials for positive and negative beads | Kappa |
| BD™ CompBead Plus Anti-Rat Ig, κ/Negative Control (BSA) Compensation Plus (7.5 µm) Particles Set | Rat | Separate vials for positive and negative beads | Kappa |
BD™ SpectraComp™ Unmixing and Compensation Particles
BD™ SpectraComp™ Unmixing and Compensation Particles are a multi-species reference control that can be used for correcting fluorescence spillover. The positive particles have a bright signal, which is well resolved from the negative population.
BD™ SpectraComp™ Unmixing and Compensation Particles:
- Have proven performance in traditional compensation and spectral unmixing
- Simplify setting up controls by having multi-species reactivity to mouse, rat and hamster immunoglobulin light chains in one bottle
- Expand the range of antibodies that can be recognized, binding both kappa and lambda light chain-bearing immunoglobulins
- Are compatible with BD fluorochromes, including BD Horizon RealYellow™ and BD Horizon RealBlue™ Fluorochromes
- Integrate into your workflow as they are compatible with BD Horizon™ Brilliant Stain Buffer and other commonly used lysis and fix/perm buffers
- Are compatible with analyzer and sorter workflows
Examples of how BD™ SpectraComp™ Unmixing and Compensation Particles are used in both conventional and spectral flow cytometry
Identification of differentiated human T cell subsets using BD™ SpectraComp™ Unmixing and Compensation Particles as single-color controls for compensation in traditional flow cytometry
Human whole blood was stained with the BD Horizon™ T Cell Backbone Panel along with four additional drop-in markers to identify and interrogate T cell subsets. Single-color controls were prepared using BD™ SpectraComp™ Unmixing and Compensation Particles and used to generate the compensation matrix. Single-color stained cells were analyzed in a NxN matrix to evaluate the compensation accuracy of the compensation matrix. The T cell subsets were then analyzed based on differential expression of CD45RA and CD197 and showed proper resolution of populations.
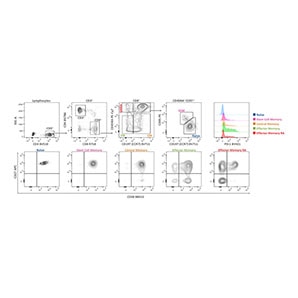
Identification of differentiated human T cell subsets

N×N matrix for single-color cell samples compensated using BD™ SpectraComp™ Unmixing and Compensation Particles.
List of Reagents in a 9-color T cell Panel
| Marker | Clone | Fluorochrome | Cat No. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD3 | UCHT1 | BV510 | 568263 | BD Horizon™ Human T Cell Backbone Panel | |
| CD4 | SK3 | BV786 | |||
| CD8 | RRPA-T8 | R718 | |||
| CD45RA | HI100 | PE-Cy7 | |||
| BCD197(CCR7) | 2-L1-A | BV711 | |||
| CD95 | DX2 | PE | 555647 | ||
| PD-1 | EH12.1 | BV421 | 562516 | ||
| CD27 | M-T271 | APC | 558664 | ||
| CD28 | CD28.2 | BB515 | 564492 |
Human whole blood from a normal donor was stained with the BD Horizon™ Human T Cell Backbone Panel and four drop-in markers to generate the data shown below.
Identification of human B cell, NK cell and dendritic cell populations using BD™ SpectraComp™ Unmixing and Compensation Particles as single-color controls for spectral unmixing of rare cell populations
A 32-color broad immunophenotyping panel was used to stain human PBMCs from a healthy donor. BD™ SpectraComp™ Unmixing and Compensation Particles were used as single-color controls instead of cells for BV605, BV786, BV711 and RY568 due to low cell frequency and variable expression of those markers. Assessment of these fluorochromes in NxN matrices revealed insignificant unmixing errors that did not affect the analysis of the target populations of B cells, NK cells and dendritic cells.
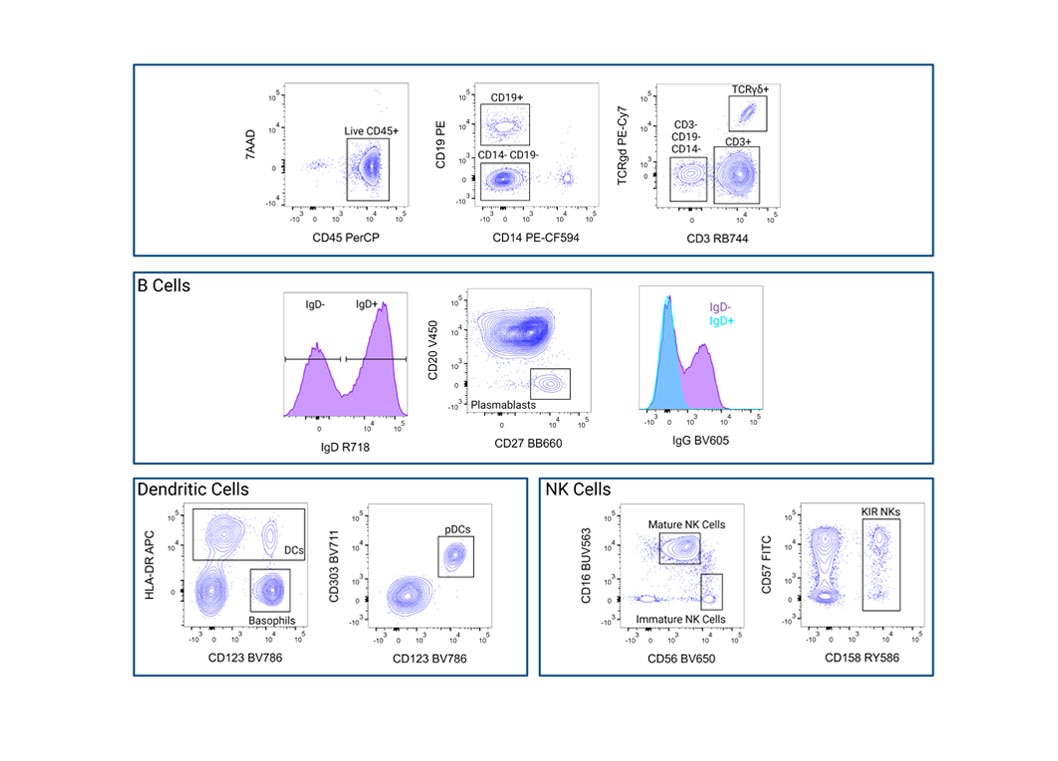
Representative analysis of freshly isolated human PBMCs obtained from healthy volunteer donors stained with a 32-color broad immunophenotyping panel
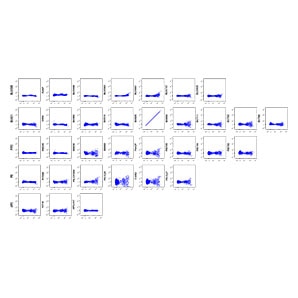
IgG BV605 matrix for single-color cells sample unmixed using BD™ SpectraComp™ Unmixing and Compensation Particles.
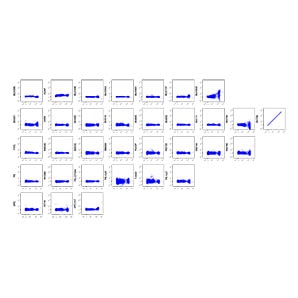
CD123 BV786 matrix for single-color samples unmixed using BD™ SpectraComp™ Unmixing and Compensation Particles.
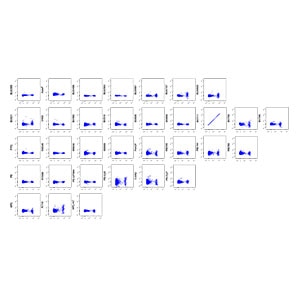
CD303 BV711 matrix for single-color samples unmixed using BD™ SpectraComp™ Unmixing and Compensation Particles.
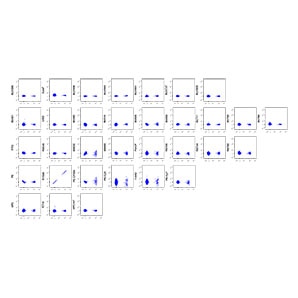
CD158 RY586 matrix for single-color samples unmixed using BD™ SpectraComp™ Unmixing and Compensation Particles.
List of Reagents in a 32-color Panel
| Marker | Clone | Dye | Cat. No. |
|---|---|---|---|
| CD45RA | 5H9 | BUV395 | 740315 |
| Auto F | — | Cells | |
| CD45RO | UCHL1 | BUV496 | 749888 |
| CD16 | 3G8 | BUV563 | 748851 |
| CD185/CXCR5 | RF8B2 | BUV661 | 741559 |
| CD28 | CD28.2 | BUV737 | 612815 |
| CD127 | HIL-7R-M21 | BUV805 | 748486 |
| CD25 | BC96 | BV421 | 567485 |
| CD20 | L27 | V450 | 561164 |
| CD62L | DREG-56 | BV480 | 566174 |
| CD39 | A1 | BV510 | 567526 |
| IgG* | G18-145 | BV605 | 563246 |
| CD56 | NCAM16.2 | BV650 | 564057 |
| CD303* | V24-785 | BV711 | 748002 |
| KLRG1 | Z7-205.rMAb | BV750 | 753692 |
| CD123* | 7G3 | BV786 | 564196 |
| CD57 | NK-1 | FITC | 555619 |
| CD4 | SK3 | RB545 | 569184 |
| CD11c | B-LY6 | BB630 | Custom |
| CD27 | M-T271 | BB660 | Custom |
| CD45 | 2D1 | PerCP | 340665 |
| CD279/PD-1 | EH12.1 | RB705 | 570245 |
| CD3 | UCHT1 | RB744 | 570470 |
| CCR7/CD197 | 2-L1-A | RB780 | 568749 |
| CD19 | HIB19 | PE | 555413 |
| CD158* | HP-MA4 | RY586 | 753232 |
| CD14 | MφP9 | PE-CF594 | 562335 |
| CD95 | DX2 | PE-Cy5 | 559773 |
| 7-AAD | — | — | — |
| TCRγδ | 11F2 | PE-Cy7 | 655434 |
| HLA-DR | TU36 | APC | 559868 |
| IgD | IA6-2 | R718 | 567993 |
| CD8 | SK1 | APC-H7 | 641409 |
This table contains all markers used to stain human PBMCs in all the data shown above.
* BD™ SpectraComp™ Unmixing and Compensation Particles used as single-color controls
Cy is a trademark of Global Life Sciences Solutions Germany GmbH or an affiliate doing business as Cytiva.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.