-
Reagents
- Flow Cytometry Reagents
-
Western Blotting and Molecular Reagents
- Immunoassay Reagents
-
Single-Cell Multiomics Reagents
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- BD® OMICS-One Protein Panels
-
Functional Assays
-
Microscopy and Imaging Reagents
-
Cell Preparation and Separation Reagents
-
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- BD® OMICS-One Protein Panels
- Denmark (English)
-
Change country/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from United States.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?
BD IMag™ Anti-CD11b Magnetic Particles - DM
Clone M1/70 (RUO)

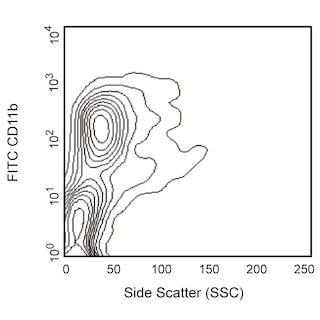
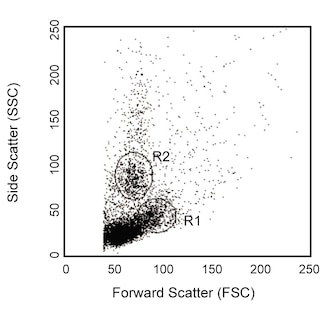
Positive selection and depletion of mouse CD11b-positive lymphocytes. Bone marrow cells were labeled with BD IMag™ anti-CD11b Particles - DM (Cat. No. 558013) as described in the protocol. After labeling, the cells were separated using the BD IMag™ Cell Separation Magnet (Cat. No. 552311), and the negative (CD11b-) and positive (CD11b+) fractions were collected. Please refer to the Separation Flow Chart to identify the separated cell populations represented in this figure. For flow cytometric analysis, fresh bone marrow (left panel), the negative fraction (middle panel), and the positive fraction (right panel) were stained with FITC Rat Anti-CD11b (Cat. No. 553310) and PE Rat Anti-mouse Ly-6G and Ly-6C RB6-8C5 (Cat. No. 553128). The percent CD11b+ cells in each smple is given. The expected cell recovery ranges from 60-80%.


Positive selection and depletion of mouse CD11b-positive lymphocytes. Bone marrow cells were labeled with BD IMag™ anti-CD11b Particles - DM (Cat. No. 558013) as described in the protocol. After labeling, the cells were separated using the BD IMag™ Cell Separation Magnet (Cat. No. 552311), and the negative (CD11b-) and positive (CD11b+) fractions were collected. Please refer to the Separation Flow Chart to identify the separated cell populations represented in this figure. For flow cytometric analysis, fresh bone marrow (left panel), the negative fraction (middle panel), and the positive fraction (right panel) were stained with FITC Rat Anti-CD11b (Cat. No. 553310) and PE Rat Anti-mouse Ly-6G and Ly-6C RB6-8C5 (Cat. No. 553128). The percent CD11b+ cells in each smple is given. The expected cell recovery ranges from 60-80%.

Positive selection and depletion of mouse CD11b-positive lymphocytes. Bone marrow cells were labeled with BD IMag™ anti-CD11b Particles - DM (Cat. No. 558013) as described in the protocol. After labeling, the cells were separated using the BD IMag™ Cell Separation Magnet (Cat. No. 552311), and the negative (CD11b-) and positive (CD11b+) fractions were collected. Please refer to the Separation Flow Chart to identify the separated cell populations represented in this figure. For flow cytometric analysis, fresh bone marrow (left panel), the negative fraction (middle panel), and the positive fraction (right panel) were stained with FITC Rat Anti-CD11b (Cat. No. 553310) and PE Rat Anti-mouse Ly-6G and Ly-6C RB6-8C5 (Cat. No. 553128). The percent CD11b+ cells in each smple is given. The expected cell recovery ranges from 60-80%.



BD IMag™ Anti-CD11b Magnetic Particles - DM

BD IMag™ Anti-CD11b Magnetic Particles - DM

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
Leukocytes are labeled with BD IMag™ anti-CD11b Particles - DM according to the Magnetic Labeling Protocol. This labeled cell suspension is then placed within the magnetic field of the BD IMag™ Cell Separation Magnet (Cat. No. 552311). Labeled cells migrate toward the magnet (positive fraction), leaving the unlabeled cells in suspension so they can be drawn off (negative fraction). The tube is then removed from the magnetic field for resuspension of the positive fraction. The separation is repeated twice to increase the purity of the positive fraction. The magnetic separation steps are diagrammed in the Separation Flow Chart. After the positive fraction is washed, the small size of the magnetic particles allows the positive fraction to be further evaluated in downstream applications such as flow cytometry.
MAGNETIC LABELING PROTOCOL
1. Prepare a single-cell suspension from the lymphoid tissue of interest according to standard laboratory procedures. Remove clumps of cells and/or debris by passing the suspension through a 70-µm nylon cell strainer.
2. Dilute BD IMag™ Buffer (10X) (Cat. no. 552362) 1:10 with sterile distilled water or prepare 1X BD IMag™ buffer by supplementing Phosphate Buffered Saline with 0.5% BSA, 2 mM EDTA, and 0.09% sodium azide. Place on ice. In our experience, Mouse BD Fc Block™ purified anti-mouse CD16/CD32 mAb 2.4G2 (Cat. no. 553141/553142) is not required for optimal cell separation, but some laboratories may use it.If adding Mouse BD Fc Block™, proceed to Step 3.If not adding Mouse BD Fc Block™, proceed to Step 4.
3. Add Mouse BD Fc Block at 0.25 µg/10e6 cells, and incubate on ice for 15 minutes.
4. Wash cells with at least an equal volume of 1X BD IMag™ buffer, and carefully aspirate all the supernatant.
5. Vortex the BD IMag™ anti-CD11b Particles - DM thoroughly, and add 50 µl of particles for every 10e7 total cells.
6. MIX THOROUGHLY. Refrigerate at 6°C - 12°C for 30 minutes.
7. Bring the BD IMag-particle labeling volume up to 1 - 8 x 10e7 cells/ml with 1X BD IMag™ buffer, and immediately place the tube on the Cell Separation Magnet. Incubate at room temperature for 6 - 8 minutes.
8. With the tube on the Cell Separation Magnet, carefully aspirate off the supernatant. This supernatant contains the negative fraction.
9. Remove the tube from the Cell Separation Magnet, and add 1X BD IMag™ buffer to the same volume as in Step 7. Gently resuspend cells by pipetting briefly, and return the tube to the Cell Separation Magnet for another 2 - 4 minutes.
10. With the tube on the Cell Separation Magnet, carefully aspirate off the supernatant and discard.
11. Repeat Steps 9 and 10.
12. After the final wash step, resuspend the positive fraction in an appropriate buffer and at an appropriate concentration for further analysis.
NOTE: Avoid nonspecific labeling by working quickly and adhering to recommended incubation times.
Product Notices
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
- BD IMag™ particles are prepared from carboxy-functionalized magnetic particles which are manufactured by Skold Technology and are licensed under US patent number 7,169,618.
- Species cross-reactivity detected in product development may not have been confirmed on every format and/or application.
Data Sheets
Companion Products



BD IMag™ anti-CD11b Particles - DM are magnetic nanoparticles that have monoclonal antibody conjugated to their surfaces. These particles are optimized for the positive selection or depletion of CD11b-bearing leukocytes using the BD IMag™ Cell Separation Magnet. CD11b is expressed at varying levels on granulocytes, macrophages, myeloid-derived dendritic cells, natural killer cells, and B-1 cells and is rapidly upregulated on neutrophils after activation.
Development References (4)
-
Ault KA, Springer TA. Cross-reaction of a rat-anti-mouse phagocyte-specific monoclonal antibody (anti-Mac-1) with human monocytes and natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1981; 126(1):359-364. (Clone-specific). View Reference
-
Kishimoto TK, Jutila MA, Berg EL, Butcher EC. Neutrophil Mac-1 and MEL-14 adhesion proteins inversely regulated by chemotactic factors. Science. 1989; 245(4923):1238-1241. (Biology). View Reference
-
Lagasse E, Weissman IL. Flow cytometric identification of murine neutrophils and monocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1996; 197(1-2):139-150. (Methodology: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Springer T, Galfre G, Secher DS, Milstein C. Mac-1: a macrophage differentiation antigen identified by monoclonal antibody. Eur J Immunol. 1979; 9(4):301-306. (Immunogen: Immunoprecipitation). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.