Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?




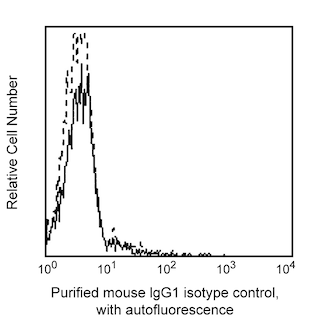
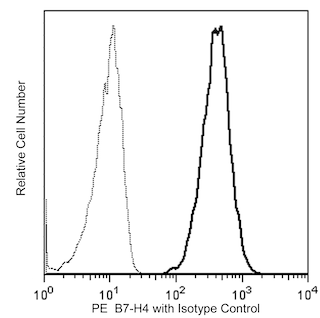
Flow cytometric analysis of human B7-H4 protein expression on B7-H4-transfected cells. Non-transfected (Left Panel) and B7-H4-transfected (Right Panel) mouse P815 mastocytoma cells were stained with either Purified Mouse IgG1 κ Isotype Control (Cat. No. 554121; dotted line histogram) or Purified Mouse anti-Human B7-H4 (Cat. No. 562506; solid line histogram) followed by PE Goat Anti-Mouse Ig (Multiple Adsorption) (Cat. No. 550589). Flow cytometric fluorescence histograms showing the expression of B7-H4 (or Ig Isotype staining) on non-transfected or transfected cells were derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of viable cells. Flow cytometry was performed using a BD™ LSR II Flow Cytometer System.


BD Pharmingen™ Purified Mouse anti-Human B7-H4

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Sodium azide is a reversible inhibitor of oxidative metabolism; therefore, antibody preparations containing this preservative agent must not be used in cell cultures nor injected into animals. Sodium azide may be removed by washing stained cells or plate-bound antibody or dialyzing soluble antibody in sodium azide-free buffer. Since endotoxin may also affect the results of functional studies, we recommend the NA/LE (No Azide/Low Endotoxin) antibody format, if available, for in vitro and in vivo use.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products


.png?imwidth=320)
The MIH43 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to human B7-H4 (B7 family member, H4) that is encoded by the VTCN1 (V-set domain containing T cell activation inhibitor 1) gene. B7-H4 is a type I membrane glycoprotein with a calculated molecular weight of 30.89 kDa. It is also known as VCTN1, B7h.5, B7S1 (B7 superfamily member 1) or B7X. B7-H4 is a newly discovered member of the B7 family of costimulatory proteins. B7-H4 is not constitutively expressed on peripheral tissues. Its expression can be induced on macrophages, dendritic cells, B cells and T cells. By binding to its putative receptor, the function of B7-H4 was initially reported to be a negative regulator of T cell activation, proliferation and differentiation related to cytokine production and cytotoxic effector cell functions. B7-H4 is reportedly overexpressed in a variety tumors. B7-H4 expression by tumor macrophages appears to play a role in suppression antigen-specific T cell mediated immunity. Recent studies indicate that B7-H4 can also be a positive regulator of T cell responses. B7-H4 can be involved innate immunity as well, eg, by inhibiting neutrophil expansion.
Development References (4)
-
Choi IH, Zhu G, Sica GL, et al. Genomic organization and expression analysis of B7-H4, an immune inhibitory molecule of the B7 family. J Immunol. 2003; 171(9):4650-4654. (Biology). View Reference
-
Kryczek I, Zou L, Rodriguez P, et al. B7-H4 expression identifies a novel suppressive macrophage population in human ovarian carcinoma. J Exp Med. 2006; 203(4):871-881. (Biology). View Reference
-
Quandt D, Fiedler E, Boettcher D, Marsch WCh, Seliger B. B7-h4 expression in human melanoma: its association with patients' survival and antitumor immune response.. Clin Cancer Res. 2011; 17(10):3100-11. (Biology). View Reference
-
Sica GL, Choi IH, Zhu G, et al. B7-H4, a molecule of the B7 family, negatively regulates T cell immunity. Immunity. 2003; 18(6):849-861. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.