Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?


Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
BD® CompBeads can be used as surrogates to assess fluorescence spillover (compensation). When fluorochrome conjugated antibodies are bound to BD® CompBeads, they have spectral properties very similar to cells. However, for some fluorochromes there can be small differences in spectral emissions compared to cells, resulting in spillover values that differ when compared to biological controls. It is strongly recommended that when using a reagent for the first time, users compare the spillover on cells and BD® CompBeads to ensure that BD® CompBeads are appropriate for your specific cellular application.
Product Notices
- Researchers should determine the optimal concentration of this reagent for their individual applications.
- The production process underwent stringent testing and validation to assure that it generates a high-quality conjugate with consistent performance and specific binding activity. However, verification testing has not been performed on all conjugate lots.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- CF™ is a trademark of Biotium, Inc.
- Please refer to http://regdocs.bd.com to access safety data sheets (SDS).
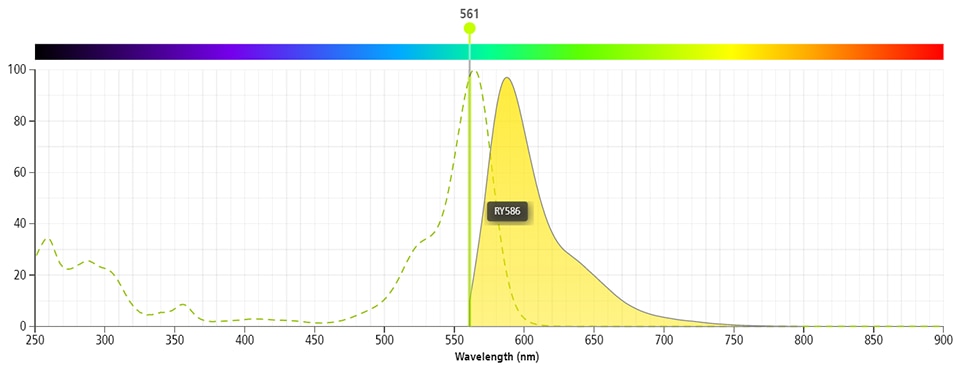
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
Companion Products





The 53-7.3 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to a monomorphic epitope of CD5, a member of the scavenger receptor cysteine-rich protein superfamily and the major ligand of CD72, found on thymocytes, T lymphocytes, thymic NKT cells, and a subset of B lymphocytes, but not on NK cells or splenic NKT cells. The level of surface CD5 expression is developmentally regulated in the thymus, starting with low levels on CD4-CD8- thymocytes and increasing as they mature to CD4+CD8+ then CD4+CD8- or CD4-CD8+ thymocytes. Relatively high levels are maintained on peripheral T lymphocytes. The level of CD5 antigen detected on T helper cells has been reported to be somewhat higher than that on T cytotoxic/suppressor and B cells. Few, if any, intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes bearing the γδ T-cell receptor express CD5. Phenotypic, anatomical, functional, developmental, and pathogenic characteristics of peripheral CD5+ B cells suggest that they may represent a distinct lineage, known as B-1 cells. The frequency of these CD5+ B cells has been reported to show strain-dependent variation. An additional population of CD5+ B lymphocytes resides in the thymus, where it matures from intrathymic B-cell progenitors. It has been proposed that CD5 is a costimulatory molecule which mediates interactions of cells in the immune system and negatively regulates signal transduction mediated by the T-cell receptor and B-cell receptor.
Development References (12)
-
Azzam HS, Grinberg A, Lui K, Shen H, Shores EW, Love PE. CD5 expression is developmentally regulated by T cell receptor (TCR) signals and TCR avidity. J Exp Med. 1998; 188(12):2301-2311. (Biology). View Reference
-
Bendelac A, Rivera MN, Park SH, Roark JH. Mouse CD1-specific NK1 T cells: development, specificity, and function. Annu Rev Immunol. 1997; 15:535-562. (Biology). View Reference
-
Cibotti R, Punt JA, Dash KS, Sharrow SO, Singer A. Surface molecules that drive T cell development in vitro in the absence of thymic epithelium and in the absence of lineage-specific signals. Immunity. 1997; 6(3):245-255. (Biology). View Reference
-
Hayakawa K, Hardy RR, Parks DR, Herzenberg LA. The "Ly-1 B" cell subpopulation in normal immunodefective, and autoimmune mice. J Exp Med. 1983; 157(1):202-218. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Hayakawa K, Hardy RR. Normal, autoimmune, and malignant CD5+ B cells: the Ly-1 B lineage. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988; 6:197-218. (Biology). View Reference
-
Kantor AB, Herzenberg LA. Origin of murine B cell lineages. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993; 11:501-538. (Biology). View Reference
-
Ledbetter JA, Herzenberg LA. Xenogeneic monoclonal antibodies to mouse lymphoid differentiation antigens. Immunol Rev. 1979; 47:63-90. (Immunogen: Immunoprecipitation). View Reference
-
Ledbetter JA, Rouse RV, Micklem HS, Herzenberg LA. T cell subsets defined by expression of Lyt-1,2,3 and Thy-1 antigens. Two-parameter immunofluorescence and cytotoxicity analysis with monoclonal antibodies modifies current views. J Exp Med. 1980; 152(2):280-295. (Clone-specific: Depletion, Flow cytometry, Fluorescence microscopy). View Reference
-
Lefrancois L. Phenotypic complexity of intraepithelial lymphocytes of the small intestine. J Immunol. 1991; 147(6):1746-1751. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Luo W, Van de Velde H, von Hoegen I, Parnes JR, Thielemans K. Ly-1 (CD5), a membrane glycoprotein of mouse T lymphocytes and a subset of B cells, is a natural ligand of the B cell surface protein Lyb-2 (CD72). J Immunol. 1992; 148(6):1630-1634. (Clone-specific: Enhancement). View Reference
-
Masuda K, Makino Y, Cui J, et al. Phenotypes and invariant alpha beta TCR expression of peripheral V alpha 14+ NK T cells. J Immunol. 1997; 158(5):2076-2082. (Biology). View Reference
-
van Ewijk W, van Soest PL, van den Engh GJ. Fluorescence analysis and anatomic distribution of mouse T lymphocyte subsets defined by monoclonal antibodies to the antigens Thy-1, Lyt-1, Lyt-2, and T-200. J Immunol. 1981; 127(6):2594-2604. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry, Immunohistochemistry). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.