Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?


Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
For optimal and reproducible results, BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer should be used anytime two or more BD Horizon Brilliant dyes (including BD OptiBuild Brilliant reagents) are used in the same experiment. Fluorescent dye interactions may cause staining artifacts which may affect data interpretation. The BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer was designed to minimize these interactions. More information can be found in the Technical Data Sheet of the BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer (Cat. No. 563794).
Product Notices
- This antibody was developed for use in flow cytometry.
- The production process underwent stringent testing and validation to assure that it generates a high-quality conjugate with consistent performance and specific binding activity. However, verification testing has not been performed on all conjugate lots.
- Researchers should determine the optimal concentration of this reagent for their individual applications.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,110,673; 8,158,444; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Ultraviolet 496 is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,110,673; 8,158,444; 8,227,187; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
Companion Products




The OX-49 antibody reacts with the glycoprotein CD44H (also known as CD44s) expressed on most leukocytes, except for a subset of B lymphocytes, and at greatly increased levels on T- and B-cell blasts. The epitope recognized by OX-49 antibody has been mapped to a region on both the standard, CD44s, and the splice variant, CD44v, isoforms of CD44. However, recent reports indicate that OX-49 antibody cannot detect the CD44v isoform, possibly due to conformational changes in the epitope. CD44 is a cell adhesion receptor, and its ligand, hyaluronate, is a common component of extracellular matrices.
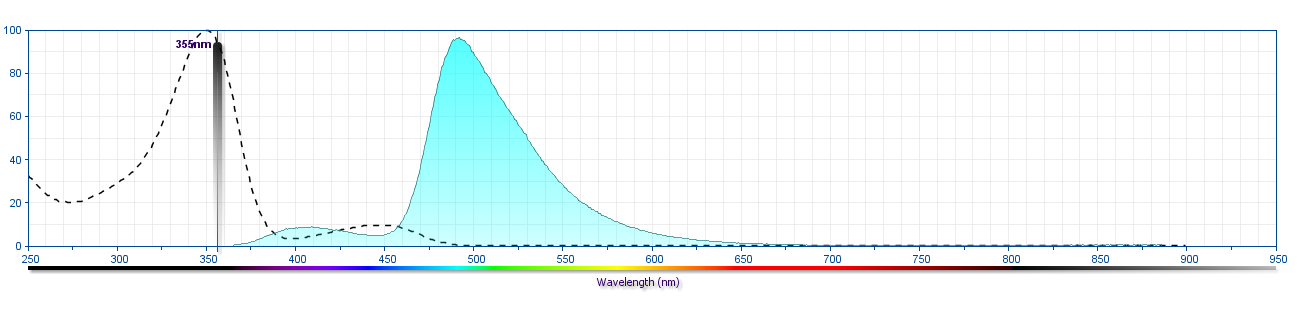
The antibody was conjugated to BD Horizon™ BUV496 which is part of the BD Horizon Brilliant™ Ultraviolet family of dyes. This dye is a tandem fluorochrome of BD Horizon BUV395 with an Ex Max of 348-nm and an acceptor dye with an Em Max at 496-nm. BD Horizon BUV496 can be excited by the ultraviolet laser (355 nm) and detected with a 515/30 nm filter with a 450LP. Due to the excitation of the acceptor dye by other laser lines, there may be significant spillover into the channel detecting BD Horizon V500 or BV510 (eg, 525/40-nm filter). However, the spillover can be corrected through compensation as with any other dye combination.
Development References (7)
-
Arch R, Wirth K, Hofmann M, et al. Participation in normal immune responses of a metastasis-inducing splice variant of CD44. Science. 1992; 257(5070):682-685. (Biology). View Reference
-
Mitnacht R, Tacke M, Hunig T. Expression of cell interaction molecules by immature rat thymocytes during passage through the CD4+8+ compartment: developmental regulation and induction by T cell receptor engagement of CD2, CD5, CD28, CD11a, CD44 and CD53. Eur J Immunol. 1995; 25(2):328-332. (Biology). View Reference
-
Noonan KJ, Stevens JW, Tammi R, Tammi M, Hernandez JA, Midura RJ. Spatial distribution of CD44 and hyaluronan in the proximal tibia of the growing rat. J Orthop Res. 1996; 14(4):573-581. (Biology). View Reference
-
Paterson DJ, Jefferies WA, Green JR. Antigens of activated rat T lymphocytes including a molecule of 50,000 Mr detected only on CD4 positive T blasts. Mol Immunol. 1987; 24(12):1281-1290. (Immunogen). View Reference
-
Stevens JW, Noonan KJ, Bosch PP, et al. CD44 in growing normal and neoplastic rat cartilage. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1996; 785:333-336. (Biology). View Reference
-
Westermann J, Nagahori Y, Walter S, Heerwagen C, Miyasaka M, Pabst R. B and T lymphocyte subsets enter peripheral lymph nodes and Peyer's patches without preference in vivo: no correlation occurs between their localization in different types of high endothelial venules and the expression of CD44, VLA-4, LFA-1, ICAM-1, CD2 or L-selectin. Eur J Immunol. 1994; 24(10):2312-2316. (Biology). View Reference
-
Zheng Z, Katoh S, He Q, et al. Monoclonal antibodies to CD44 and their influence on hyaluronan recognition. J Cell Biol. 1995; 130(2):485-495. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.