-
Reagents
- Flow Cytometry Reagents
-
Western Blotting and Molecular Reagents
- Immunoassay Reagents
-
Single-Cell Multiomics Reagents
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- BD® OMICS-One Protein Panels
-
Functional Assays
-
Microscopy and Imaging Reagents
-
Cell Preparation and Separation Reagents
-
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- BD® OMICS-One Protein Panels
- Belgium (English)
-
Change country/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from United States.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?
BD IMag™ Mouse Hematopoietic Progenitor (Stem) Cell Enrichment Set - DM

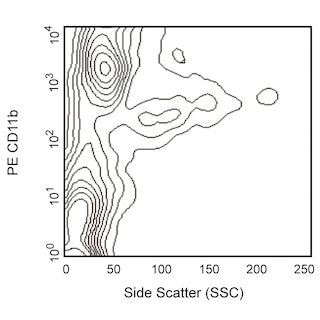
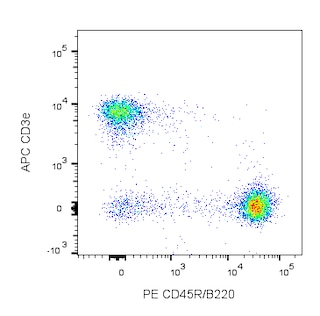
Depletion of lineage-committed cells from mouse bone marrow. BALB/c bone-marrow cells were labeled with the BD IMag™ Mouse Hematopoietic Progenitor Enrichment Set (Cat. No. 557451) and separated on the BD IMag™ Cell Separation Magnet (Cat. No. 552311) according to the accompanying Protocol. To demonstrate the efficiency of the depletion, unmanipulated bone marrow cells and the final depleted fraction were stained with APC Rat Anti-Mouse CD117 (Cat. No. 553356) to detect hematopoietic progenitors, and with PE Rat Anti-Mouse TER-119/Erythroid Cells (Cat. No. 553673), CD45R/B220 (Cat. No. 553089/553090), and CD11b (Cat. No. 557397/553311) to detect lineage-commited cells. The percentage of positive cells is indicated in each panel; placement of each marker is based upon staining with the appropriate isotype control (data not shown). The final depleted fraction contains a greatly increased proportion of CD117+ cells and less than 5% of lineage-positive contaminants.



Depletion of lineage-committed cells from mouse bone marrow. BALB/c bone-marrow cells were labeled with the BD IMag™ Mouse Hematopoietic Progenitor Enrichment Set (Cat. No. 557451) and separated on the BD IMag™ Cell Separation Magnet (Cat. No. 552311) according to the accompanying Protocol. To demonstrate the efficiency of the depletion, unmanipulated bone marrow cells and the final depleted fraction were stained with APC Rat Anti-Mouse CD117 (Cat. No. 553356) to detect hematopoietic progenitors, and with PE Rat Anti-Mouse TER-119/Erythroid Cells (Cat. No. 553673), CD45R/B220 (Cat. No. 553089/553090), and CD11b (Cat. No. 557397/553311) to detect lineage-commited cells. The percentage of positive cells is indicated in each panel; placement of each marker is based upon staining with the appropriate isotype control (data not shown). The final depleted fraction contains a greatly increased proportion of CD117+ cells and less than 5% of lineage-positive contaminants.

Depletion of lineage-committed cells from mouse bone marrow. BALB/c bone-marrow cells were labeled with the BD IMag™ Mouse Hematopoietic Progenitor Enrichment Set (Cat. No. 557451) and separated on the BD IMag™ Cell Separation Magnet (Cat. No. 552311) according to the accompanying Protocol. To demonstrate the efficiency of the depletion, unmanipulated bone marrow cells and the final depleted fraction were stained with APC Rat Anti-Mouse CD117 (Cat. No. 553356) to detect hematopoietic progenitors, and with PE Rat Anti-Mouse TER-119/Erythroid Cells (Cat. No. 553673), CD45R/B220 (Cat. No. 553089/553090), and CD11b (Cat. No. 557397/553311) to detect lineage-commited cells. The percentage of positive cells is indicated in each panel; placement of each marker is based upon staining with the appropriate isotype control (data not shown). The final depleted fraction contains a greatly increased proportion of CD117+ cells and less than 5% of lineage-positive contaminants.



BD IMag™ Mouse Hematopoietic Progenitor (Stem) Cell Enrichment Set - DM

BD IMag™ Mouse Hematopoietic Progenitor (Stem) Cell Enrichment Set - DM

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Description
The BD IMag™ Mouse Hematopoietic Progenitor Cell Enrichment Set - DM reacts with cells from the major hematopoietic cell lineages, such as T lymphocytes, B lymphocytes, monocytes/macrophages, granulocytes, and erythrocytes. The BD IMag™ Streptavidin Particles Plus - DM are magnetic nanoparticles that have streptavidin covalently conjugated to their surfaces. This Set is designed for the immunomagnetic enrichment of hematopoietic progenitors from mouse bone marrow by depletion of cells committed to the T- and B-lymphocytic, myeloid (monocytic and granulocytic), and erythroid lineages. The Set contains sufficient reagents to label 10^9 bone marrow cells.
Biotin Mouse Lineage Depletion Cocktail is comprised of the following biotin-conjugated monoclonal antibodies:
Anti-mouse CD3e, clone 145-2C11 Anti-mouse CD11, clone M1/70
Anti-mouse CD45R/B220, clone RA3-6B2 Anti-mouse Ly-6G and Ly-6C (Gr-1), clone RB6-8C5
Anti-mouse TER-119/Erythroid Cells, clone TER-119
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
The detailed Magnetic Labeling and Depletion Protocol follows. In summary, the Biotinylated Mouse Lineage Depletion Cocktail simultaneously stains the lineage-committed hematopoietic cells according to their different specificities. After washing away excess antibody, BD IMag™ Streptavidin Particles Plus - DM are added to the cell suspension and bind the cells bearing the biotinylated antibodies. The tube containing this labeled cell suspension is then placed within the magnetic field of the Cell Separation Magnet (Cat. No. 552311). Negative selection is then performed to enrich for uncommitted hematopoietic progenitors. Labeled cells migrate toward the magnet (positive fraction), leaving the unlabeled cells in suspension so they can be drawn off and retained (depleted fraction). Additional negative selections are performed to optimize the yield and purity of the depleted fraction. The magnetic separation steps are diagrammed in the Depletion Flow Chart. Both the positive and depleted fractions can be evaluated in downstream applications such as flow cytometry and tissue culture. The antibodies in the Biotinylated Mouse Lineage Depletion Cocktail have been optimized and pre-diluted to provide maximum efficiency for enrichment of bone marrow hematopoietic progenitors.
MAGNETIC LABELING AND DEPLETION PROTOCOL
1. Prepare sterile buffers and place on ice.
a. Cell-staining buffer: Phosphate Buffered Saline supplemented with 3% heat-inactivated fetal calf serum and 0.1% sodium azide
b. 1X BD IMag™ buffer: Dilute BD IMag™ Buffer (10X) (Cat. No. 552362) 1:10 with sterile distilled water or prepare Phosphate Buffered Saline supplemented with 0.5% BSA, 2 mM EDTA, and 0.1% sodium azide.
2. Aseptically prepare a single-cell suspension from mouse bone marrow. Remove clumps of cells and/or debris by passing the suspended cells through a 70-µm nylon cell strainer. Note: The femurs and tibiae of one adult mouse typically yield 20-60 x 10^6 hematopoietic cells. One mouse will yield approximately 0.3-1.0 x 10^6 lineage-negative cells.
3. Count the cells and resuspend them in sterile cell-staining buffer at 10 to 20 x 10^6 cells/ml. Set aside a sample of unstained cells (~5 x 10^6 cells) to be used in the flow cytometric analysis in Step 17.
4. Add Mouse BD Fc Block™ purified anti-mouse CD16/CD32 mAb 2.4G2 (Cat. No. 553141/553142) at 0.25 µg/10^6 cells, and incubate on ice for 15 minutes.
5. Add the Biotinylated Mouse Lineage Depletion Cocktail at 5 µl per 1 x 106 cells, and incubate on ice for 15 minutes.
6. Wash the labeled cells with a 10X excess volume of 1X BD IMag™ buffer, centrifuge at 300 x g for 7 minutes, and carefully aspirate ALL the supernatant.
7. Vortex the BD IMag™ Streptavidin Particles Plus - DM thoroughly, and add 5 µl of particles for every 1 x 10^6 total cells.
8. MIX THOROUGHLY. Refrigerate for 30 minutes at 6°C - 12°C.
9. Bring the labeling volume up to 20 to 80 x 10^6 cells/ml with 1X BD IMag™ buffer.
10. Transfer the labeled cells to a 12 x 75 mm round-bottom test tube, maximum volume added not to exceed 1.0 ml. Place this positive-fraction tube on the Cell Separation Magnet (horizontal position) for 8 minutes.
-For greater volume, transfer the cells to a 17 x 100 mm round-bottom test tube, maximum volume added not to exceed 3.0 ml. Place this positive-fraction tube on the Cell Separation Magnet (vertical position) for 10 minutes.
11. With the tube on the Cell Separation Magnet and using a sterile glass Pasteur pipette, carefully aspirate the supernatant (depleted fraction) and place in a new sterile tube.
12. Remove the positive-fraction tube from the Cell Separation Magnet, and add 1X BD IMag™ buffer to the same volume as in Step 9. Resuspend the positive fraction well by pipetting up and down 10 to 15 times, and place the tube back on the Cell Separation Magnet for 8 minutes.
-17 x 100 mm tube: Place on the Cell Separation Magnet for 10 minutes.
13. Using a new sterile Pasteur pipette, carefully aspirate the supernatant and combine with the depleted fraction from Step 11 above.
14. The positive-fraction cells remaining in the original tube can be resuspended in an appropriate buffer or culture medium for downstream applications, including flow cytometry, if desired.
15. Place the tube containing the combined depleted fraction on the Cell Separation Magnet for a final 8 minutes.
-17 x 100 mm tube: Place on the Cell Separation Magnet for 10 minutes.
16. Carefully aspirate the supernatant and place in a new sterile tube. This is the final depleted fraction containing enriched hematopoietic progenitors. The cells are ready to be processed for downstream applications.
17. Samples of the total cell suspension and the positive and final depleted fractions should be analyzed by flow cytometry to evaluate the efficiency of the cell-separation procedure.
NOTES:
-After washing away excess biotinylated antibody, completely aspirate the supernatant. Supernatant left in the tube will increase the labeling volume, which will decrease the efficiency of magnetic labeling.
-When labeling cells with the BD IMag™ Streptavidin Particles Plus - DM, use biotin-free buffer only. Free biotin will compete with the biotinylated antibody for binding to the BD IMag™ Streptavidin Particles Plus - DM.
-Avoid nonspecific labeling by working quickly and adhering to recommended incubation times.
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- BD IMag™ particles are prepared from carboxy-functionalized magnetic particles which are manufactured by Skold Technology and are licensed under US patent number 7,169,618.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Data Sheets
Companion Products



| Description | EntrezGene ID |
|---|---|
| Biotin Mouse Lineage Depletion Cocktail | N/A |
| Streptavidin Particles Plus - DM | N/A |
Development References (6)
-
Goodell MA, Rosenzweig M, Kim H, et al. Dye efflux studies suggest that hematopoietic stem cells expressing low or undetectable levels of CD34 antigen exist in multiple species. Nat Med. 1997; 3(12):1337-1345. (Biology). View Reference
-
Morrison SJ, Wandycz AM, Hemmati HD, Wright DE, Weissman IL. Identification of a lineage of multipotent hematopoietic progenitors. Development. 1997; 124(10):1929-1939. (Biology). View Reference
-
Osawa M, Tokumoto Y, Nakauchi H. Hematopoietic stem cells. In: Herzenberg LA, Weir DM, Blackwell C, ed. Weir's Handbook of Experimental Immunology, 5th Edition. Cambridge: Blackwell Science; 1996:66.1-66.5.
-
Sato T, Laver JH, Ogawa M. Reversible expression of CD34 by murine hematopoietic stem cells. Blood. 1999; 94(8):2548-2554. (Biology). View Reference
-
Spangrude GJ, Heimfeld S, Weissman IL. Purification and characterization of mouse hematopoietic stem cells. Science. 1988; 241(4861):58-62. (Biology). View Reference
-
Spangrude GJ, Scollay R. A simplified method for enrichment of mouse hematopoietic stem cells. Exp Hematol. 1990; 18(8):920-926. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.