Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?




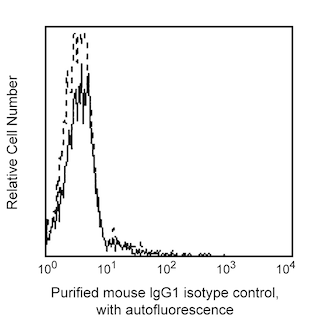
Flow cytometric analysis of CD69 expressed on stimulated peripheral blood lymphocytes. Human PBMC were stimulated for 24 hours with Phytohemagglutinin (PHA; Sigma L-1668). The cells were then stained with either Purified Mouse IgG1, κ Isotype control (Cat. No. 555746; dashed line histogram) or Purified Mouse Anti-Human CD69 antibody (Cat. No. 555529; solid line histogram), followed by FITC Goat Anti-Mouse IgG/IgM (Cat. No. 555988). The fluorescence histograms were derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of viable activated lymphocytes. Flow cytometry was performed on a BD FACScan™ system.


BD Pharmingen™ Purified Mouse Anti-Human CD69

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Species cross-reactivity detected in product development may not have been confirmed on every format and/or application.
- Sodium azide is a reversible inhibitor of oxidative metabolism; therefore, antibody preparations containing this preservative agent must not be used in cell cultures nor injected into animals. Sodium azide may be removed by washing stained cells or plate-bound antibody or dialyzing soluble antibody in sodium azide-free buffer. Since endotoxin may also affect the results of functional studies, we recommend the NA/LE (No Azide/Low Endotoxin) antibody format, if available, for in vitro and in vivo use.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products
.png?imwidth=320)
The FN50 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to human CD69. CD69 is also known as activation-induced molecule (AIM), early activation antigen (EA-1), very early activation antigen (VEA), C-type lectin domain family 2 member C (CLEC2C), MLR-3, GP32/28 and Leu-23. CD69 is a transmembrane type II homodimer receptor. CD69 is comprised of disulfide-linked, differentially glycosylated core protein subunits that are approximately 28 and 34 kDa in size. Each subunit contains a C-type lectin domain. CD69 is expressed on activated T, B, and natural killer (NK) lymphocytes, thymocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils and platelets. In normal peripheral blood, a small and variable percentage of lymphocytes typically express detectable membrane CD69 antigen. Upon activation, CD69 antigen expression increases on lymphocytes. Peak CD69 expression generally occurs within 18 hours of activation, preceding the appearance of HLA-DR, IL-2Rα (CD25) and transferrin receptor (CD71). CD69 is highly expressed on the bright CD3+ subset of thymocytes. FN50 monoclonal antibody labels NK cells and most lymphocytes of the follicular mantle and perifollicular/interfollicular zone as well as germinal center T cells of lymph nodes and tonsils. Studies indicate that CD69 serves as a signaling receptor in the activation of a variety of cell types.
Clone FN50 reacts with the human form of the 28/34 kDa dimeric glycoprotein expressed early during activation of lymphocytes, monocytes, and platelets. It also cross-reacts with a subset of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (lymphocytes and monocytes) of rhesus and cynomolgus macaque monkeys. The distribution on lymphocytes is similar to that observed with human peripheral blood lymphocytes with the majority of the cells demonstrating an increase in FN50 positivity following overnight incubation with phorbol myristrate acetate (PMA).
Development References (2)
-
Knapp W. W. Knapp .. et al., ed. Leucocyte typing IV : white cell differentiation antigens. Oxford New York: Oxford University Press; 1989:1-1182.
-
Schlossman SF. Stuart F. Schlossman .. et al., ed. Leucocyte typing V : white cell differentiation antigens : proceedings of the fifth international workshop and conference held in Boston, USA, 3-7 November, 1993. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1995.
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.