Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?
BD Pharmingen™ DAPI Solution
(RUO)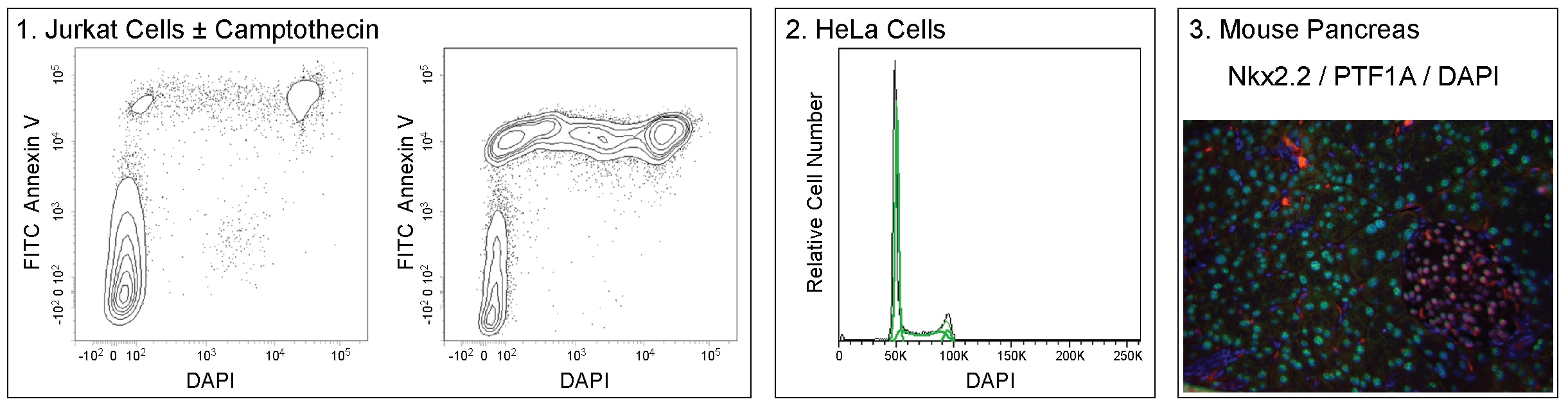


Panel 1. Two-color flow cytometric analysis of Jurkat cell viability. Jurkat cells were treated with DMSO vehicle (Left Plot) or 5 μM Camptothecin (Right Plot) overnight. Cells were resuspended in Annexin V Binding Buffer (Cat. No. 556454) and stained with FITC Annexin V (Cat. No. 556419) and 0.06 μg/mL DAPI. Camptothecin-treated cells show an increased frequency of apoptotic (Annexin V+DAPI-) and dead (Annexin V+DAPI+) cells. Analysis was performed using a BD LSRFortessa™ Cell Analyzer System. Panel 2. Flow cytometric analysis of HeLa cell DNA content. Cultured HeLa cells in log phase growth were harvested using Gibco® Cell Dissociation Buffer (Life Technologies), fixed, and permeabilized using BD Pharmingen™ Transcription Factor Buffer Set (Cat. No. 562574/562725). Cells were resuspended in DPBS with 1 μg/mL DAPI and analyzed using a low BD LSRFortessa™ cytometer flow rate. A 405 nm laser with a 450/50 nm bandpass filter was used to collect data; comparable results were obtained using a 355 nm laser with a 450/50 nm bandpass filter (not shown). Histograms were deconvoluted by FlowJo™ software into G0/G1, S, and G2/M populations. Panel 3. Multicolor immunofluorescence analysis of NKX2.2 and PTF1A expression in mouse pancreas. Following antigen retrieval with BD Retrievagen A Buffer (Cat. No. 550524), a formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded pancreas tissue section was stained with Purified Mouse Anti-Nkx2.2 antibody (Cat. No. 564731, pseudo-colored red), washed, and stained with Alexa Fluor® 488 Goat Anti-Mouse Ig (Life Technologies). After washing, the section was stained with Alexa Fluor® 647 Mouse Anti-PTF1A (pseudo-colored green) and counterstained with DAPI (pseudo-colored blue). The nuclei of islet cells (DAPI+) stain positively for both NKX2.2 and PTF1A. The nuclei of acinar cells and some islet precursor cells stain positive for PTF1A. All images were analyzed using a BD Pathway™ 435 High-Content Bioimager System and merged with BD Attovision™ Software.

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
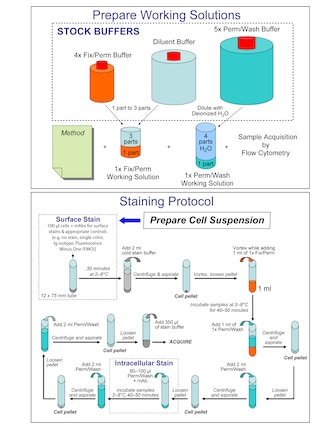
Staining of Live Cells for Viability Analysis by Flow Cytometry
1. Obtain a single cell suspension.
2. Resuspend cells in BD Pharmingen™ Stain Buffer (FBS) (Cat. No. 554656) or 1× Dulbecco's Phosphate Buffered Saline (DPBS) containing 0.05-0.2 μg/mL DAPI.
a. The optimal concentration of DAPI for viability analysis may vary by cell type. We recommend titrating the reagent for your cell type of interest in early experiments.
b. Additionally, apoptotic cells may stain with variable amounts of DAPI. We recommend co-staining with BD Pharmingen™ FITC Annexin V (Cat. No. 556419) if further analysis of apoptotic cells is desired.
3. Incubate 5 minutes at room temperature. No wash is necessary prior to analysis.
4. Proceed to analysis by flow cytometry.
Staining of Fixed Cells for DNA Content Analysis by Flow Cytometry
1. Obtain a single cell suspension.
2. Treat cells on ice for 30 minutes with 70-80% ice-cold ethanol.
a. Ethanol fixation typically provides the most resolved histograms. However, this reagent has also been successfully used for DNA content analysis with the Transcription Factor Buffer Set (Cat. No. 562574/ 562725) or BD Cytofix™ Fixation Buffer (Cat. No. 554655) and BD Phosflow™ Perm Buffer III (Cat. No. 558050) protocol.
3. Wash cells once with BD Pharmingen™ Stain Buffer (FBS).
4. Dilute DAPI solution to 0.5-1 μg/mL in Stain Buffer (FBS) or 1× DPBS immediately prior to use.
5. Stain cells for 5-15 minutes at a cell density of 1 - 2 x 10^6 cells/mL. No further wash is necessary prior to analysis.
a. The optimal cell density and concentration of DAPI for DNA content analysis may vary by cell type. Assay conditions should be optimized in early experiments for best results.
6. Proceed to analysis by flow cytometry.
Immunofluorescent Staining of Fixed Cells for Nuclear Visualization
1. Fix and permeabilize cells as desired.
2. Dilute DAPI solution to 1 µg/ml in 1× DPBS immediately prior to use.
3. Add DAPI solution to each sample at least 15 minutes before analysis.
4. Proceed to imaging.
Note: This reagent has been developed and certified for the Bioimaging application. However, routine Bioimaging testing is not performed on every lot.
Product Notices
- FlowJo is a trademark of Tree Star Inc.
- Alexa Fluor® is a registered trademark of Molecular Probes, Inc., Eugene, OR.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products



DAPI (4',6-Diamidino-2-Phenylindole, Dihydrochloride) is a nucleic acid stain that binds to A-T rich regions of DNA along the minor groove. DAPI is predominantly impermeant to live cells, allowing it to be used as a viability dye in unfixed cells to discriminate intact from membrane-compromised cells. Note, however, that high concentrations of the dye may still enter intact cells. Additionally, DAPI may be used to analyze DNA content in fixed cells, or as a nuclear counterstain in imaging or flow cytometry.
When bound to double-stranded DNA, DAPI has an excitation wavelength maximum of 358 nm and an emission maximum of 461 nm. DAPI is also well excited by the violet laser line (eg, 405 nm). Note that DAPI also binds RNA. Under these conditions, DAPI emits maximally at 500 nm, but with less intensity than when bound to double-stranded DNA.
Development References (5)
-
Darzynkiewicz Z, Bruno S, Del Bino G, et al. Features of apoptotic cells measured by flow cytometry. Cytometry. 1992; 13(8):795-808. (Methodology: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Hotz MA, Gong J, Traganos F, and Darzynkiewicz Z. Flow cytometric detection of apoptosis: Comparison of the assays of in situ DNA degradation and chromatin changes. Cytometry. 1994; 15(3):237-244. (Methodology: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Otto F. DAPI staining of fixed cells for high-resolution flow cytometry of nuclear DNA. Methods Cell Biol. 1990; 33:105-110. (Methodology: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Shapiro HM. Practical flow cytometry, 3rd ed.. New York: Wiley-Liss; 1995:280-282.
-
Tanious FA, Veal JM, Buczak H, Ratmeyer LS, Wilson WD. DAPI (4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) binds differently to DNA and RNA: minor-groove binding at AT sites and intercalation at AU sites. Biochemistry. 1992; 31(12):3103-3112. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.