Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?


.png)

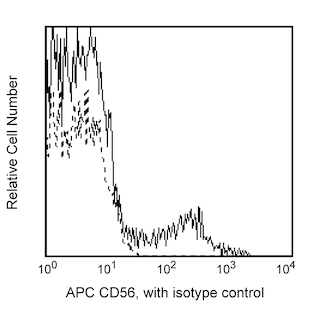
Multiparameter flow cytometric analysis of TIM-3 (CD366) expression on human peripheral blood leucocyte populations. Human whole blood was stained with APC Mouse Anti-Human CD56 antibody (Cat. No. 555518; Lower Plots) and either Alexa Fluor® 488 Mouse IgG1 κ Isotype Control (Cat. No. 565572; Left Plots) or Alexa Fluor® 488 Mouse Anti-Human TIM-3 (CD366) antibody (Cat. No. 567030/567031; Right Plots). The erythrocytes were lysed with BD FACS™ Lysing Solution (Cat. No. 349202). Flow cytometry and data analysis were performed using a BD LSRFortessa™ Cell Analyzer System and FlowJo™ software. Upper Plots: The bivariate pseudocolor density plot showing TIM-3 (CD366) expression (or Ig Isotype control staining) versus side scattered-light signals (SSC-A) was derived from gated events with the forward and side-light scattering characteristics of intact leucocyte populations. Lower Plots: The plot showing the coexpression of TIM-3 (CD366) [or Ig Isotype control staining] versus CD56 was derived from gated events with the light scatter characteristics of intact lymphocytes.
.png)

BD Pharmingen™ Alexa Fluor® 488 Mouse Anti-Human TIM-3 (CD366)
.png)
Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
BD™ CompBeads can be used as surrogates to assess fluorescence spillover (Compensation). When fluorochrome conjugated antibodies are bound to CompBeads, they have spectral properties very similar to cells. However, for some fluorochromes there can be small differences in spectral emissions compared to cells, resulting in spillover values that differ when compared to biological controls. It is strongly recommended that when using a reagent for the first time, users compare the spillover on cells and CompBead to ensure that BD Comp beads are appropriate for your specific cellular application.
Product Notices
- This reagent has been pre-diluted for use at the recommended Volume per Test. We typically use 1 × 10^6 cells in a 100-µl experimental sample (a test).
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- The Alexa Fluor®, Pacific Blue™, and Cascade Blue® dye antibody conjugates in this product are sold under license from Molecular Probes, Inc. for research use only, excluding use in combination with microarrays, or as analyte specific reagents. The Alexa Fluor® dyes (except for Alexa Fluor® 430), Pacific Blue™ dye, and Cascade Blue® dye are covered by pending and issued patents.
- Alexa Fluor® 488 fluorochrome emission is collected at the same instrument settings as for fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC).
- Alexa Fluor® is a registered trademark of Molecular Probes, Inc., Eugene, OR.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to http://regdocs.bd.com to access safety data sheets (SDS).
- This product is provided under an intellectual property license between Life Technologies Corporation and BD Businesses. The purchase of this product conveys to the buyer the non-transferable right to use the purchased amount of the product and components of the product in research conducted by the buyer (whether the buyer is an academic or for-profit entity). The buyer cannot sell or otherwise transfer (a) this product (b) its components or (c) materials made using this product or its components to a third party or otherwise use this product or its components or materials made using this product or its components for Commercial Purposes. Commercial Purposes means any activity by a party for consideration and may include, but is not limited to: (1) use of the product or its components in manufacturing; (2) use of the product or its components to provide a service, information, or data; (3) use of the product or its components for therapeutic, diagnostic or prophylactic purposes; or (4) resale of the product or its components, whether or not such product or its components are resold for use in research. For information on purchasing a license to this product for any other use, contact Life Technologies Corporation, Cell Analysis Business Unit Business Development, 29851 Willow Creek Road, Eugene, OR 97402, USA, Tel: (541) 465-8300. Fax: (541) 335-0504.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products




.png?imwidth=320)
The 7D3 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to T cell immunoglobulin mucin 3 (TIM-3) which is also known as, CD366, or T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-containing protein 3 (TIMD-3/TIMD3). CD366 is encoded by the HAVCR2 gene (Hepatitis A virus cellular receptor 2). CD366 is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein and belongs to the human TIM family (along with TIM-1 and TIM-4) within the immunoglobulin superfamily. CD366 is expressed on Th1, Tc1, Th17, Treg, NK T, and NK cells. CD366 is also expressed on dendritic cells, mast cells, monocytes, and macrophages. It is not expressed by Th2 and B cells. CD366 helps maintain peripheral immune tolerance and homeostasis. CD366 regulates macrophage activation and is a negative regulator of Th1 cell function. Crosslinking of cell surface CD366 by binding to Galectin-9 and/or phosphatidylserine appears to play an important role in either positively or negatively regulating leucocyte functions, such as cytokine production or the phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. CD366 may also be useful as an AML stem cell surface marker because it appears to be more highly expressed by AML leukemia stem cells than by normal bone marrow hematopoietic stem cells.
Development References (13)
-
Bertrand F, Montfort A, Marcheteau E, et al. TNFα blockade overcomes resistance to anti-PD-1 in experimental melanoma.. Nat Commun. 2017; 8(1):2256. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Domenig C, Zheng XX, Sabatos CA, et al. Tim-3 inhibits T helper type 1-mediated auto- and alloimmune responses and promotes immunological tolerance. Nat Immunol. 2003; 4(11):1093-1101. (Biology). View Reference
-
Freeman GJ, Casasnovas JM, Umetsu DT, DeKruyff RH. TIM genes: a family of cell surface phosphatidylserine receptors that regulate innate and adaptive immunity.. Immunol Rev. 2010; 235(1):172-89. (Biology). View Reference
-
Hafler DA, Kuchroo V. TIMs: Central regulators of immune responses. J Exp Med. 2008; 205:2699-2701. (Biology). View Reference
-
Jan M, Chao MP, Cha AC, et al. Prospective separation of normal and leukemic stem cells based on differential expression of TIM3, a human acute myeloid leukemia stem cell marker. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011; 108(12):5009-5014. (Biology). View Reference
-
Khademi M, Illes Z, Gielen AW, et al. T Cell Ig- and mucin-domain-containing molecule-3 (TIM-3) and TIM-1 molecules are differentially expressed on human Th1 and Th2 cells and in cerebrospinal fluid-derived mononuclear cells in multiple sclerosis. J Immunol. 2004; 172(11):7169-7176. (Biology). View Reference
-
Lee J, Su EW, Zhu C, et al. Phosphotyrosine-dependent coupling of Tim-3 to T-cell receptor signaling pathways. Mol Cell Biol. 2011; 31(19):3963-3974. (Biology). View Reference
-
Lee JS, Park MJ, Park S, Lee ES. Differential expression of T cell immunoglobulin- and mucin-domain-containing molecule-3 (TIM-3) according to activity of Behcet's disease. Br J Dermatol. 2012; 65(3):220-222. (Biology). View Reference
-
Moorman JP, Wang JM, Zhang Y, et al. Tim-3 pathway controls regulatory and effector T cell balance during hepatitis C virus infection. J Immunol. 2012; 189(2):755-766. (Biology). View Reference
-
Ndhlovu LC, Lopez-Verges S, Barbour JD, et al. Tim-3 marks human natural killer cell maturation and suppresses cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Blood. 2012; 119(16):3734-3743. (Biology). View Reference
-
Rodriguez-Manzanet R, DeKruyff R, Kuchroo VK, Umetsu DT. The costimulatory role of TIM molecules. Immunol Rev. 2009; 229(1):259-270. (Biology). View Reference
-
Wang F, Wan L, Zhang C, Zheng X, Li J, Chen ZK. Tim-3-Galectin-9 pathway involves the suppression induced by CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Immunobiology. 2009; 214(5):342-349. (Biology). View Reference
-
van de Weyer PS, Muehlfeit M, Klose C, Bonventre JV, Walz G, Kuehn EW. A highly conserved tyrosine of Tim-3 is phosphorylated upon stimulation by its ligand galectin-9. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006; 351(2):571-576. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.