Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?




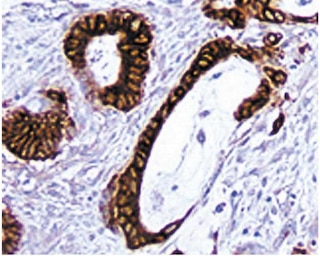
Immunohistochemical staining of CD29 positive cells. Frozen sections of normal mouse spleen were reacted with the anti- CD29 antibody. Endothelial cells of the central arteriole and splenic sinuses can be identified by the brown labeling of their cell membranes. Amplification 20X.


BD Pharmingen™ Purified Rat Anti-Mouse CD29

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
Immunohistochemistry: The 9EG7 antibody specific for mouse CD29 is recommended to test for immunohistochemical staining of acetone-fixed frozen sections and Zinc-fixed paraffin sections. Tissues tested were mouse spleen and thymus. The antibody stains lymphocytes and endothelial cells. The isotype control recommended for use with this antibody is purified rat IgG2a (559073). For optimal indirect immunohistochemical staining, the 9EG7 antibody should be titrated (1:10 to 1:50 dilution) and visualized via a three-step staining procedure in combination with polyclonal, biotin conjugated anti-rat Igs (multiple adsorbed) (Cat. No. 559286) as the secondary antibody and Streptavidin-HRP (Cat. No. 550946) together with the DAB detection system (Cat. No. 550880). The clone 9EG7 is not recommended for formalin-fixed paraffin embedded sections.
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- This antibody has been developed for the immunohistochemistry application. However, a routine immunohistochemistry test is not performed on every lot. Researchers are encouraged to titrate the reagent for optimal performance.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products




The 9EG7 antibody reacts with the 130-kDa integrin β1 chain (CD29). CD29 is expressed on the cell surface as a heterodimer with one of the distinct integrin α chains. With α1 through α6 (CD49a through CD49f), it forms the VLA-1 through VLA-6 complexes, respectively, and with αv (CD51), it forms αvβ1 integrin. It also associates with the integrin α7 α8 and α9 chains in non-lymphoid tissues. As a result, CD29 has a broad tissue distribution, including lymphocytes, endothelia, smooth muscle, and epithelia. 9EG7 mAb has been shown to inhibit both the α6β1-mediated binding of lymphocytes to endothelial cells and the adhesion mediated by activated, but not unactivated, α4β1-integrin. The source of the immunogen was mouse lymph node-derived endothelial cell line TME.
Development References (3)
-
Lenter M, Uhlig H, Hamann A, Jenö P, Imhof B, Vestweber D. A monoclonal antibody against an activation epitope on mouse integrin chain beta 1 blocks adhesion of lymphocytes to the endothelial integrin alpha 6 beta 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993; 90(19):9051-9055. (Immunogen). View Reference
-
Mouse Genome Database (MGD), Mouse Genome Informatics, The Jackson Laboratory. B2m, beta-2 microglobulin. Available: http://www.informatics.jax.org 4/15/1998.
-
Springer TA. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature. 1990; 346(6283):425-434. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.