-
Reagents
- Flow Cytometry Reagents
-
Western Blotting and Molecular Reagents
- Immunoassay Reagents
-
Single-Cell Multiomics Reagents
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- BD® OMICS-One Protein Panels
-
Functional Assays
-
Microscopy and Imaging Reagents
-
Cell Preparation and Separation Reagents
-
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- BD® OMICS-One Protein Panels
- Ireland (English)
-
Change location/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current location site or be switched to your location?
BD Transduction Laboratories™ Purified Mouse Anti-Fatty Acid Synthase
Clone 23/Fatty Acid Synthase (RUO)
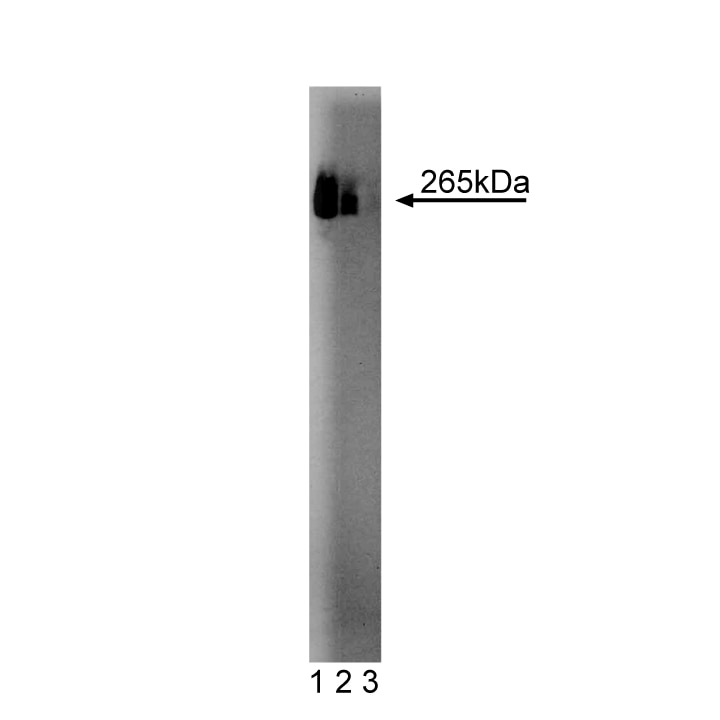





Western blot analysis of Fatty Acid Synthase on HepG2 cell lysate. Lane 1: 1:250, lane 2: 1:500, lane 3: 1:1000 dilution of anti-FAS antibody.

Western blot analysis of Fatty Acid Synthase on HepG2 cell lysate. Lane 1: 1:250, lane 2: 1:500, lane 3: 1:1000 dilution of anti-FAS antibody.

Western blot analysis of Fatty Acid Synthase on HepG2 cell lysate. Lane 1: 1:250, lane 2: 1:500, lane 3: 1:1000 dilution of anti-FAS antibody.

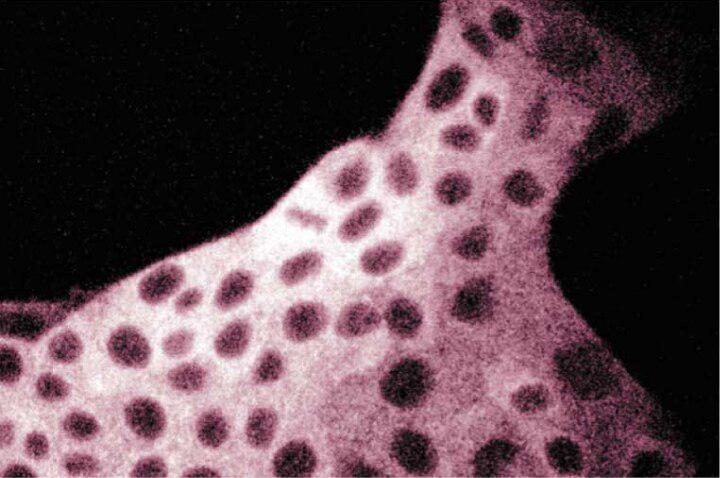
Immunofluorescent staining of MDCK cells with anti-FAS antibody.

Immunofluorescent staining of MDCK cells with anti-FAS antibody.






Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
Western blot: Please refer to http://www.bdbiosciences.com/pharmingen/protocols/Western_Blotting.shtml .
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
Fatty acid biosynthesis occurs in all living organisms and provides essential components of biological membranes as well as a form of energy storage. Animal fatty acid synthase (FAS) is a multifunctional enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of long-chain fatty acids via sequential condensation of two-carbon units from malonyl-CoA, an intermediate derived from the carboxylation of Acetyl-CoA. FAS is a homodimer of a multifunctional subunit protein that contains seven distinct activities and a site for the prosthetic group 4'-phosphopantetheine (acyl carrier protein). These domains are oriented from N-terminus to C-terminus as follows: β-keto-acyl synthase, acetyl and malonyl transacylases, enoyl reductase, ketoacyl reductase, acyl carrier protein, and thioesterase. Although all domains are found on each subunit, they are only active following the homodimerization of subunits in an antiparallel (head-to-tail) orientation. This juxtaposition and cooperation between domains forms two centers for acyl chain assembly. Alternative substrates and chain-terminating mechanisms allow for the production of a variety of fatty acids with different lengths and structures.
Development References (3)
-
Chirala SS, Huang WY, Jayakumar A, Sakai K, Wakil SJ. Animal fatty acid synthase: functional mapping and cloning and expression of the domain I constituent activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997; 94(11):5588-5593. (Biology). View Reference
-
Jayakumar A, Tai MH, Huang WY, et al. Human fatty acid synthase: properties and molecular cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995; 92(19):8695-8699. (Biology). View Reference
-
Smith S. The animal fatty acid synthase: one gene, one polypeptide, seven enzymes. FASEB J. 1994; 8(15):1248-1259. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.