-
Reagents
- Flow Cytometry Reagents
-
Western Blotting and Molecular Reagents
- Immunoassay Reagents
-
Single-Cell Multiomics Reagents
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- BD® OMICS-One Protein Panels
-
Functional Assays
-
Microscopy and Imaging Reagents
-
Cell Preparation and Separation Reagents
-
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- BD® OMICS-One Protein Panels
- Ireland (English)
-
Change country/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from United States.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?
BD OptiBuild™ RB613 Rat Anti-Mouse CD324 (E-Cadherin)
Clone DECMA-1 (RUO)


Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
BD® CompBeads can be used as surrogates to assess fluorescence spillover (compensation). When fluorochrome conjugated antibodies are bound to BD® CompBeads, they have spectral properties very similar to cells. However, for some fluorochromes there can be small differences in spectral emissions compared to cells, resulting in spillover values that differ when compared to biological controls. It is strongly recommended that when using a reagent for the first time, users compare the spillover on cells and BD® CompBeads to ensure that BD® CompBeads are appropriate for your specific cellular application.
Product Notices
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- Please refer to http://regdocs.bd.com to access safety data sheets (SDS).
- For U.S. patents that may apply, see bd.com/patents.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- The production process underwent stringent testing and validation to assure that it generates a high-quality conjugate with consistent performance and specific binding activity. However, verification testing has not been performed on all conjugate lots.
- Please observe the following precautions: We recommend that special precautions be taken (such as wrapping vials, tubes, or racks in aluminum foil) to protect exposure of conjugated reagents, including cells stained with those reagents, to any room illumination. Absorption of visible light can significantly affect the emission spectra and quantum yield of tandem fluorochrome conjugates.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- When using high concentrations of antibody, background binding of this dye to erythroid fragments produced by ammonium chloride-based lysis, such as with BD Pharm Lyse™ Lysing Buffer (Cat. No. 555899), has been observed when the antibody conjugate was present during the lysis procedure. This may cause nonspecific staining of target cells, such as leukocytes, which have bound the resulting erythroid fragments. This background can be mitigated by any of the following: titrating the antibody conjugate to a lower concentration, fixing samples with formaldehyde, or removing erythrocytes before staining (eg, gradient centrifugation or pre-lysis with wash). This background has not been observed when cells were lysed with BD FACS™ Lysing Solution (Cat. No. 349202) after staining.
- Species cross-reactivity detected in product development may not have been confirmed on every format and/or application.
- Tandem fluorochromes contain both an energy donor and an energy acceptor. Although every effort is made to minimize the lot-to-lot variation in the efficiency of the fluorochrome energy transfer, differences in the residual emission from the donor may be observed. Additionally, multi-laser cytometers may directly excite both the donor and acceptor fluorochromes. Therefore, we recommend for every tandem conjugate, a matched individual single-stain control be acquired for generating a compensation or spectral unmixing matrix.
- CF™ is a trademark of Biotium, Inc.
Data Sheets
Companion Products




The DECMA-1 monoclonal antibody specifically recognizes the extracellular domain of mouse E-Cadherin (CD324). E-Cadherin is a 120-kDa transmembrane glycoprotein that is localized in the adherens junctions of epithelial cells. There it interacts with the cytoskeleton through the associated cytoplasmic catenin proteins. In addition to being a calcium-dependent adhesion molecule, E-Cadherin is also a critical regulator of epithelial junction formation. Its association with catenins is necessary for cell-to-cell adhesion. These E-Cadherin/catenin complexes associate with cortical actin bundles at both the zonula adherens and the lateral adhesion plaques. Tyrosine phosphorylation can disrupt these complexes, leading to changes in cell adhesion properties. E-Cadherin expression is often down-regulated in highly invasive, poorly differentiated carcinomas. Increased expression of E-Cadherin in these cells reduces their invasiveness. Thus, loss of expression or function of E-Cadherin appears to be an important step in tumorigenic progression. Pluripotent stem cells express E-Cadherin. Upon differentiation, an epithelial to mesenchymal transition results in the loss of E-cadherin expression and a gain in the expression of N-cadherin. The DECMA-1 mAb recognizes the membrane proximal part of the extracellular region of E-Cadherin and blocks E-Cadherin-mediated aggregation of cells. It has been reported to cross-react with E-Cadherin in humans, as well as several other species. However, the human cross-reactivity was weak when tested by flow cytometry on the MCF-7 breast cancer cell line in comparison to BD Biosciences' Anti-Human DECMA-1 mAb 67A4.
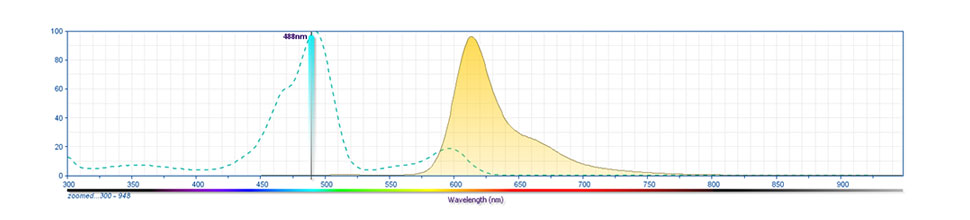
Development References (9)
-
Batchuluun K, Azuma M, Yashiro T, Kikuchi M. Notch signaling-mediated cell-to-cell interaction is dependent on E-cadherin adhesion in adult rat anterior pituitary.. Cell Tissue Res. 2017; 368(1):125-133. (Clone-specific: Immunohistochemistry). View Reference
-
Brouxhon SM, Kyrkanides S, Teng X, et al. Monoclonal antibody against the ectodomain of E-cadherin (DECMA-1) suppresses breast carcinogenesis: involvement of the HER/PI3K/Akt/mTOR and IAP pathways. Clin Cancer Res. 2013; 19(12):3234-46. (Clone-specific: Functional assay). View Reference
-
Mohri Y. Prognostic significance of E-cadherin expression in human colorectal cancer tissue.. Surg Today. 1997; 27(7):606-12. (Clone-specific: Immunohistochemistry). View Reference
-
Ozawa M, Hoschützky H, Herrenknecht K, Kemler R. A possible new adhesive site in the cell-adhesion molecule uvomorulin.. Mech Dev. 1990; 33(1):49-56. (Clone-specific: Immunofluorescence). View Reference
-
Schuh R, Vestweber D, Riede I, et al. Molecular cloning of the mouse cell adhesion molecule uvomorulin: cDNA contains a B1-related sequence.. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1986; 83(5):1364-8. (Clone-specific: Immunoaffinity chromatography). View Reference
-
Sugiyama D, Joshi A, Kulkeaw K, et al. A Transcriptional Switch Point During Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cell Ontogeny.. Stem Cells Dev. 2017; 26(5):314-327. (Biology). View Reference
-
Takeichi M. The cadherins: cell-cell adhesion molecules controlling animal morphogenesis.. Development. 1988; 102(4):639-55. (Biology). View Reference
-
Vestweber D, Kemler R. Identification of a putative cell adhesion domain of uvomorulin.. EMBO J. 1985; 4(13A):3393-8. (Immunogen: Blocking, Immunofluorescence, Immunoprecipitation). View Reference
-
Vleminckx K, Vakaet L, Mareel M, Fiers W, van Roy F. Genetic manipulation of E-cadherin expression by epithelial tumor cells reveals an invasion suppressor role.. Cell. 1991; 66(1):107-19. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.