Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?


Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
For optimal and reproducible results, BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer should be used anytime two or more BD Horizon Brilliant dyes (including BD OptiBuild Brilliant reagents) are used in the same experiment. Fluorescent dye interactions may cause staining artifacts which may affect data interpretation. The BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer was designed to minimize these interactions. More information can be found in the Technical Data Sheet of the BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer (Cat. No. 563794).
Product Notices
- This antibody was developed for use in flow cytometry.
- The production process underwent stringent testing and validation to assure that it generates a high-quality conjugate with consistent performance and specific binding activity. However, verification testing has not been performed on all conjugate lots.
- Researchers should determine the optimal concentration of this reagent for their individual applications.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,110,673; 8,158,444; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Violet 711 is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,110,673; 8,158,444; 8,227,187; 8,455,613; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
- Cy is a trademark of GE Healthcare.
- Alexa Fluor® is a registered trademark of Life Technologies Corporation.
Companion Products
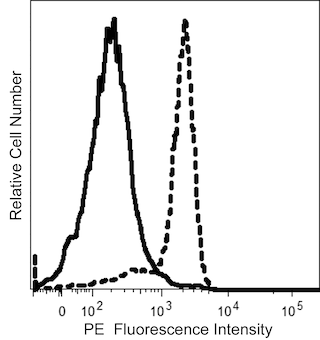





The M.Ab.F11 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to CD321 which is also known as JAM-1 (Junctional adhesion molecule 1), Junctional adhesion molecule A (JAM-A), and F11 Receptor (F11R). CD321 is a 32-35 kDa type I transmembrane glycoprotein that includes two extracellular immunoglobulin-like domains. CD321 is expressed on platelets, leucocytes, red blood cells, endothelial cells, epithelial cells, and various cell lines. CD321 functions as an adhesion receptor molecule on platelets. It also supports the tight junction formation between endothelial cells, where it may regulate the transendothelial migration of leucocytes, and epithelial cells. M.Ab.F11 is a stimulatory antibody that can induce morphological changes, granule secretion, and aggregation in human platelets.
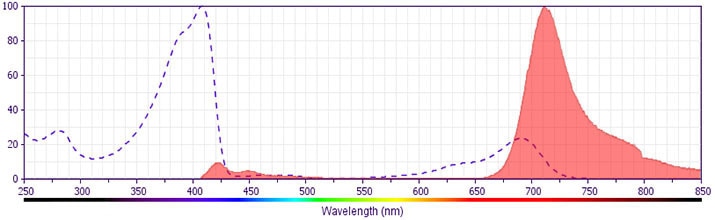
The antibody was conjugated to BD Horizon™ BV711 which is part of the BD Horizon Brilliant™ Violet family of dyes. This dye is a tandem fluorochrome of BD Horizon BV421 with an Ex Max of 405-nm and an acceptor dye with an Em Max at 711-nm. BD Horizon BV711 can be excited by the violet laser and detected in a filter used to detect Cy™5.5 / Alexa Fluor® 700-like dyes (eg, 712/20-nm filter). Due to the excitation and emission characteristics of the acceptor dye, there may be moderate spillover into the Alexa Fluor® 700 and PerCP-Cy5.5 detectors. However, the spillover can be corrected through compensation as with any other dye combination.
Development References (8)
-
Babinska A, Kedees MH, Athar H, et al. Two regions of the human platelet F11-receptor (F11R) are critical for platelet aggregation, potentiation and adhesion. Thromb Haemost. 2002; 87(4):712-721. (Biology). View Reference
-
Florian S, Sonneck K, Czerny M, et al. Detection of novel leukocyte differentiation antigens on basophils and mast cells by HLDA8 antibodies. Allergy. 2006; 61(9):1054-1062. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Halasz P, Fleming FE, Coulson BS. Evaluation of specificity and effects of monoclonal antibodies submitted to the Eighth Human Leucocyte Differentiation Antigen Workshop on rotavirus-cell attachment and entry. Cell Immunol. 2005; 236(1-2):179-187. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Horváth O, Drbel K, Angelisová P, Hilgert I, Horejsí V. Non-lineage antigens: section report. Cell Immunol. 2005; 236(1-2):42-47. (Clone-specific). View Reference
-
Kornecki E, Walkowiak B, Naik UP, Ehrlich YH. Activation of human platelets by a stimulatory monoclonal antibody. J Biol Chem. 1990; 265(17):10042-10048. (Immunogen). View Reference
-
Naik UP, Ehrlich YH, Kornecki E. Mechanisms of platelet activation by a stimulatory antibody: cross-linking of a novel platelet receptor for monoclonal antibody F11 with the Fc gamma RII receptor. Biochem J. 1995; 310(1):155-162. (Biology). View Reference
-
Sobocka MB, Sobocki T, Banerjee P, et al. Cloning of the human platelet F11 receptor: a cell adhesion molecule member of the immunoglobulin superfamily involved in platelet aggregation. Blood. 2000; 95(8):2600-2609. (Biology). View Reference
-
Wang F, Naik UP, Ehrlich YH, Osada S, Ohno S, Kornecki E. Stimulatory antibody-induced activation and selective translocation of protein kinase C isoenzymes in human platelets. Biochem J. 1995; 311(2):401-406. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.