Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?


Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
For optimal and reproducible results, BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer should be used anytime two or more BD Horizon Brilliant dyes (including BD OptiBuild Brilliant reagents) are used in the same experiment. Fluorescent dye interactions may cause staining artifacts which may affect data interpretation. The BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer was designed to minimize these interactions. More information can be found in the Technical Data Sheet of the BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer (Cat. No. 563794).
Product Notices
- This antibody was developed for use in flow cytometry.
- The production process underwent stringent testing and validation to assure that it generates a high-quality conjugate with consistent performance and specific binding activity. However, verification testing has not been performed on all conjugate lots.
- Researchers should determine the optimal concentration of this reagent for their individual applications.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,110,673; 8,158,444; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Violet 480 is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
Companion Products





The GL3 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to a common epitope of the δ chain of the T-cell Receptor (TCR) complex on γδ TCR-expressing T lymphocytes and NK-T cells of all mouse strains tested. It does not react with αβ TCR-bearing T cells. In the mouse, cells expressing the γδ TCR are found in the thymus, intestinal epithelium, epidermis, dermis, pulmonsry epithelium, peritoneum, liver, and peripheral lymphoid organs.
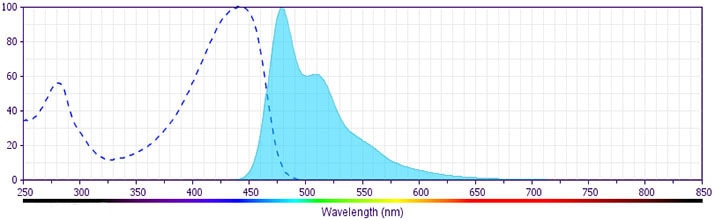
The antibody was conjugated to BD Horizon™ BV480 which is part of the BD Horizon Brilliant™ Violet family of dyes. With an Ex Max of 436-nm and Em Max at 478-nm, BD Horizon BV480 can be excited by the violet laser and detected in the BD Horizon BV510 (525/40-nm) filter set. BV480 has less spillover into the BV605 detector and, in general, is brighter than BV510.
Development References (15)
-
Goodman T, LeCorre R, Lefrancois L. A T-cell receptor gamma delta-specific monoclonal antibody detects a V gamma 5 region polymorphism. Immunogenetics. 1992; 35(1):65-68. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Goodman T, Lefrancois L. Intraepithelial lymphocytes. Anatomical site, not T cell receptor form, dictates phenotype and function. J Exp Med. 1989; 170(5):1569-1581. (Immunogen: Flow cytometry, Immunoprecipitation). View Reference
-
Kaufmann SH, Blum C, Yamamoto S. Crosstalk between alpha/beta T cells and gamma/delta T cells in vivo: activation of alpha/beta T-cell responses after gamma/delta T-cell modulation with the monoclonal antibody GL3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993; 90(20):9620-9624. (Clone-specific: Depletion). View Reference
-
King DP, Hyde DM, Jackson KA, et al. Cutting edge: protective response to pulmonary injury requires gamma delta T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1999; 162(9):5033-5036. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Lefrancois L, Barrett TA, Havran WL, Puddington L. Developmental expression of the alpha IEL beta 7 integrin on T cell receptor gamma delta and T cell receptor alpha beta T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1994; 24(3):635-640. (Clone-specific: Immunohistochemistry). View Reference
-
Lefrancois L. Phenotypic complexity of intraepithelial lymphocytes of the small intestine. J Immunol. 1991; 147(6):1746-1751. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
MacDonald HR, Schreyer M, Howe RC, Bron C. Selective expression of CD8 alpha (Ly-2) subunit on activated thymic gamma/delta cells. Eur J Immunol. 1990; 20(4):927-930. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Nakazawa S, Brown AE, Maeno Y, Smith CD, Aikawa M. Malaria-induced increase of splenic gamma delta T cells in humans, monkeys, and mice. 1994; 79(3):391-398. (Clone-specific: Immunohistochemistry). View Reference
-
Shinohara K, Ikarashi Y, Maruoka H, et al. Functional and phenotypical characteristics of hepatic NK-like T cells in NK1.1-positive and -negative mouse strains. Eur J Immunol. 1999; 29(6):1871-1878. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Skeen MJ, Ziegler HK. Induction of murine peritoneal gamma/delta T cells and their role in resistance to bacterial infection. J Exp Med. 1993; 178(3):971-984. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry, In vivo exacerbation). View Reference
-
Tamaki K, Yasaka N, Chang CH, et al. Identification and characterization of novel dermal Thy-1 antigen-bearing dendritic cells in murine skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1996; 106(3):571-575. (Clone-specific: Fluorescence microscopy, Immunofluorescence, Immunohistochemistry). View Reference
-
Tigelaar RE, Lewis JM, Bergstresser PR. TCR gamma/delta+ dendritic epidermal T cells as constituents of skin-associated lymphoid tissue. J Invest Dermatol. 1990; 94(6):58S-63S. (Biology). View Reference
-
Vicari AP, Mocci S, Openshaw P, O'Garra A, Zlotnik A. Mouse gamma delta TCR+NK1.1+ thymocytes specifically produce interleukin-4, are major histocompatibility complex class I independent, and are developmentally related to alpha beta TCR+NK1.1+ thymocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1996; 26(7):1424-1429. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry, Fluorescence activated cell sorting). View Reference
-
Yanez DM, Batchelder J, van der Heyde HC, Manning DD, Weidanz WP. Gamma delta T-cell function in pathogenesis of cerebral malaria in mice infected with Plasmodium berghei ANKA. Infect Immun. 1999; 67(1):446-448. (Clone-specific: Depletion). View Reference
-
van der Heyde HC, Elloso MM, Chang WL, Kaplan M, Manning DD, Weidanz WP. Gamma delta T cells function in cell-mediated immunity to acute blood-stage Plasmodium chabaudi adami malaria. J Immunol. 1995; 154(8):3985-3990. (Clone-specific: Depletion). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.