Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
For optimal and reproducible results, BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer should be used anytime two or more BD Horizon Brilliant dyes (including BD OptiBuild Brilliant reagents) are used in the same experiment. Fluorescent dye interactions may cause staining artifacts which may affect data interpretation. The BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer was designed to minimize these interactions. More information can be found in the Technical Data Sheet of the BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer (Cat. No. 563794).
Product Notices
- This antibody was developed for use in flow cytometry.
- The production process underwent stringent testing and validation to assure that it generates a high-quality conjugate with consistent performance and specific binding activity. However, verification testing has not been performed on all conjugate lots.
- Researchers should determine the optimal concentration of this reagent for their individual applications.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,110,673; 8,158,444; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Ultraviolet 395 is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,158,444; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
Companion Products





The 7G6 antibody recognizes an epitope shared by 145-150-kDa and 190-kDa complement receptor proteins, originally designated CR2 (CD21) and CR1 (CD35), respectively. In the mouse, CD21 and CD35 are expressed on the majority of peripheral B lymphocytes, on the majority of resident peritoneal macrophages and mast cells, on peripheral blood granulocytes after treatment with N-formyl-Met-Leu-Phe, and on follicular dendritic cells, but not on thymocytes, T cells, erythrocytes, or platelets. CD21 is a ligand-binding component of the CD19/CD21/CD81 signal-transduction complex associated with the antigen receptor on B lymphocytes. CD21/CD35 also co-localizes with CD19 on the surface of peritoneal mast cells. Cr2null mice display impaired inflammatory and humoral immune responses in vivo. The 7G6 mAb has been reported to inhibit rosette formation by C3d-bearing sheep erythrocytes, to block the complement dependent trapping of immune complexes by follicular dendritic cells, and to down-regulate mouse CD21/CD35 expression upon in vivo application, thus inhibiting primary antibody responses to immunization. Co-stimulation of B-cell differentiation via Sepharose-coupled 7G6 antibody has also been observed. The 7G6 mAb recognizes an epitope on CD35 distinct from the epitope recognized by anti-mouse CD35, clone 8C12, and it does not block binding of 8C12 mAb to mouse CD35.
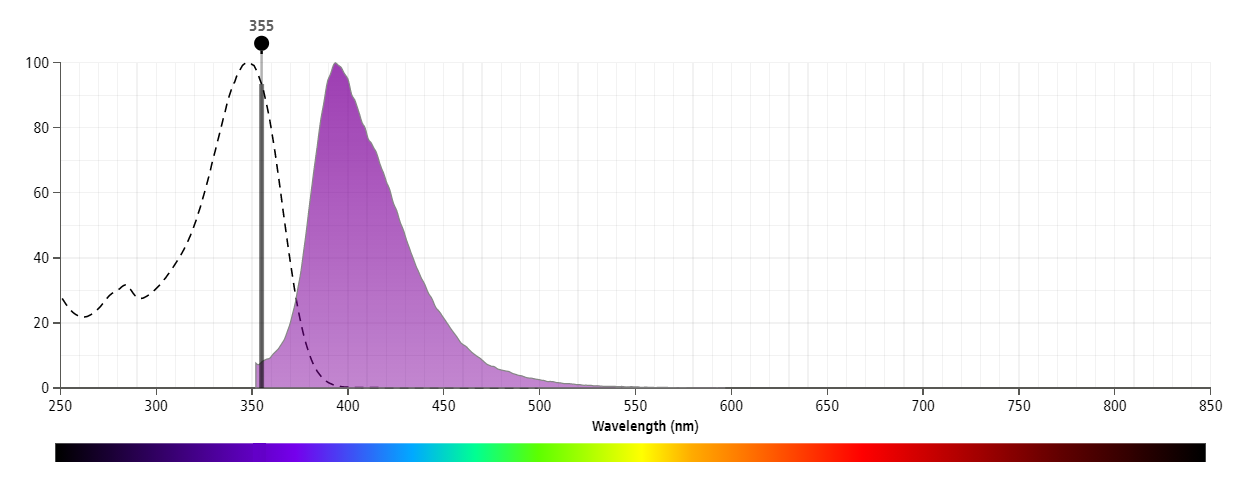
The antibody was conjugated to BD Horizon™ BUV395 which is part of the BD Horizon Brilliant™ Ultraviolet family of dyes. This dye has been exclusively developed by BD Biosciences to have minimal spillover into other detectors, making it an optimal choice for multicolor flow cytometry. With an Ex Max at 348 nm and an Em Max at 395 nm, BD Horizon BUV395 can be excited with a 355 nm laser and detected with a 379/28 filter.
Development References (15)
-
Axcrona K, Gray D, Leanderson T. Regulation of B cell growth and differentiation via CD21 and CD40. Eur J Immunol. 1996; 26(9):2203-2207. (Clone-specific: (Co)-stimulation, Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Cariappa A, Tang M, Parng C, et al. The follicular versus marginal zone B lymphocyte cell fate decision is regulated by Aiolos, Btk, and CD21. Immunity. 2001; 14(5):603-615. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Fagarasan S, Muramatsu M, Suzuki K, Nagaoka H, Hiai H, Honjo T. Critical roles of activation-induced cytidine deaminase in the homeostasis of gut flora. Science. 2002; 298(5597):1424-1427. (Clone-specific: Fluorescence microscopy, Immunofluorescence). View Reference
-
Fischer MB, Goerg S, Shen L, et al. Dependence of germinal center B cells on expression of CD21/CD35 for survival. Science. 1998; 280(5363):582-585. (Biology). View Reference
-
Gommerman JL, Oh DY, Zhou X, et al. A role for CD21/CD35 and CD19 in responses to acute septic peritonitis: a potential mechanism for mast cell activation. J Immunol. 2000; 165(12):6915-6921. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry, Fluorescence microscopy, Immunofluorescence). View Reference
-
Heyman B, Wiersma EJ, Kinoshita T. In vivo inhibition of the antibody response by a complement receptor-specific monoclonal antibody. J Exp Med. 1990; 172(2):665-668. (Clone-specific: Inhibition, In vivo exacerbation). View Reference
-
Hu H, Martin BK, Weis JJ, Weis JH. Expression of the murine CD21 gene is regulated by promoter and intronic sequences. J Immunol. 1997; 158(10):4758-4768. (Biology). View Reference
-
Kinoshita T, Takeda J, Hong K, Kozono H, Sakai H, Inoue K. Monoclonal antibodies to mouse complement receptor type 1 (CR1). Their use in a distribution study showing that mouse erythrocytes and platelets are CR1-negative. J Immunol. 1988; 140(9):3066-3072. (Immunogen: Immunoprecipitation, Radioimmunoassay). View Reference
-
Kinoshita T, Thyphronitis G, Tsokos GC, et al. Characterization of murine complement receptor type 2 and its immunological cross-reactivity with type 1 receptor. Int Immunol. 1990; 2(7):651-659. (Clone-specific). View Reference
-
Molina H, Holers VM, Li B, et al. Markedly impaired humoral immune response in mice deficient in complement receptors 1 and 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996; 93(8):3357-3361. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Oliver AM, Martin F, Gartland GL, Carter RH, Kearney JF. Marginal zone B cells exhibit unique activation, proliferative and immunoglobulin secretory responses. Eur J Immunol. 1997; 27(9):2366-2374. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Oliver AM, Martin F, Kearney JF. IgMhighCD21high lymphocytes enriched in the splenic marginal zone generate effector cells more rapidly than the bulk of follicular B cells. J Immunol. 1999; 162(12):7198-7207. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Thyphronitis G, Kinoshita T, Inoue K, et al. Modulation of mouse complement receptors 1 and 2 suppresses antibody responses in vivo. J Immunol. 1991; 147(1):224-230. (Clone-specific: Inhibition, In vivo exacerbation). View Reference
-
Wiersma EJ, Kinoshita T, Heyman B. Inhibition of immunological memory and T-independent humoral responses by monoclonal antibodies specific for murine complement receptors. Eur J Immunol. 1991; 21(10):2501-2506. (Clone-specific: Inhibition, In vivo exacerbation). View Reference
-
Yoshida K, van den Berg TK, Dijkstra CD. Two functionally different follicular dendritic cells in secondary lymphoid follicles of mouse spleen, as revealed by CR1/2 and FcR gamma II-mediated immune-complex trapping. Immunology. 1993; 80(1):34-39. (Clone-specific: Inhibition). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.