-
Reagents
- Flow Cytometry Reagents
-
Western Blotting and Molecular Reagents
- Immunoassay Reagents
-
Single-Cell Multiomics Reagents
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- BD® OMICS-One Protein Panels
-
Functional Assays
-
Microscopy and Imaging Reagents
-
Cell Preparation and Separation Reagents
-
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- BD® OMICS-One Protein Panels
- Ireland (English)
-
Change country/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from United States.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?
BD Via-Probe™ Red Nucleic Acid Stain
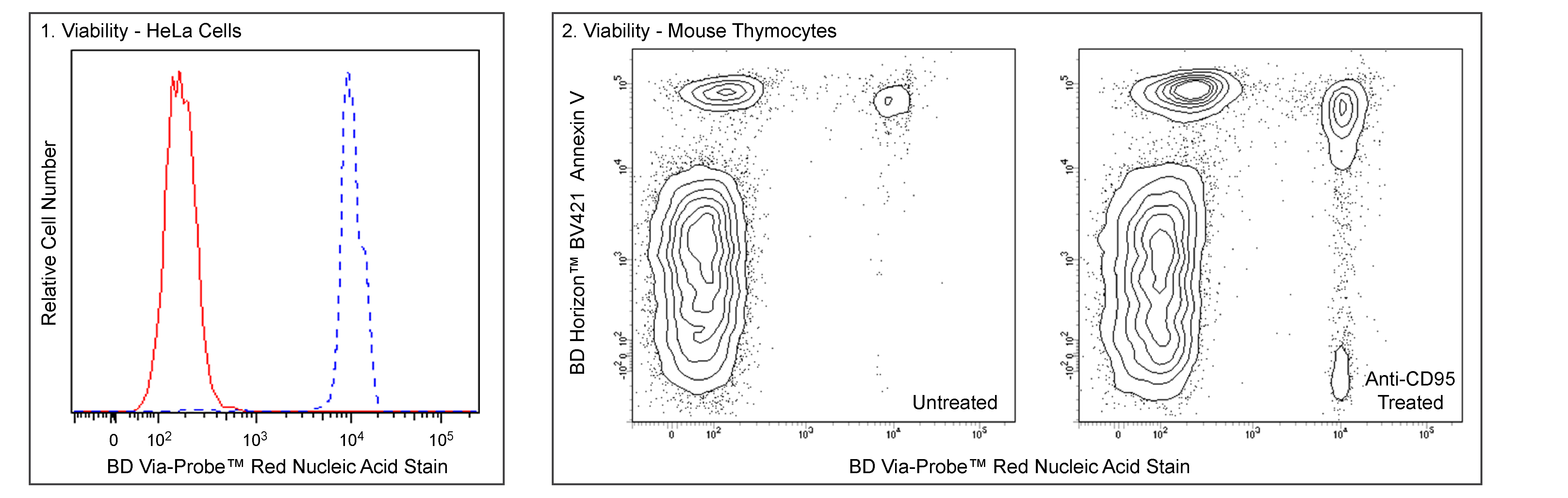
Panel 1 - Flow cytometric analysis of HeLa cell viability. Cells from the human HeLa (Cervical adenocarcinoma, ATCC CCL 2) cell line were heat-killed by incubation at 60°C (45 min), cooled to room temperature, and mixed with an equal number of untreated viable HeLa cells. Cells were then stained with BD Via-Probe™ Red Nucleic Acid Stain (Cat. No. 565803/565804; 10 nM) and then acquired by flow cytometry. Morphologically live (red solid line histogram) and dead (blue dashed line histogram) HeLa cells were gated based on their distinct forward and side light-scattering characteristics and can be clearly distinguished based on staining intensity of BD Via-Probe™ Red. Flow cytometric analysis was performed using a BD LSRFortessa™ Cell Analyzer System.
Panel 2 - Two-color flow cytometric analysis of mouse thymocyte viability. BALB/c thymocytes were left untreated (Left Plot) or stimulated with Purified NA/LE Hamster Anti-Mouse CD95 antibody (Cat. No. 554254; Right Plot) for 4 hours. Cells were harvested, stained with BD Horizon™ BV421 Annexin V (Cat. No. 563973) and BD Via-Probe™ Red Nucleic Acid Stain (5 nM), and analyzed by flow cytometry. Anti-CD95-stimulated cells show an increase in Annexin V-positive and BD Via-Probe™ Red-positive cells, indicating an increase in apoptosis and cell death. Flow cytometric analysis was performed using a BD LSRFortessa™ X-20 Cell Analyzer System.
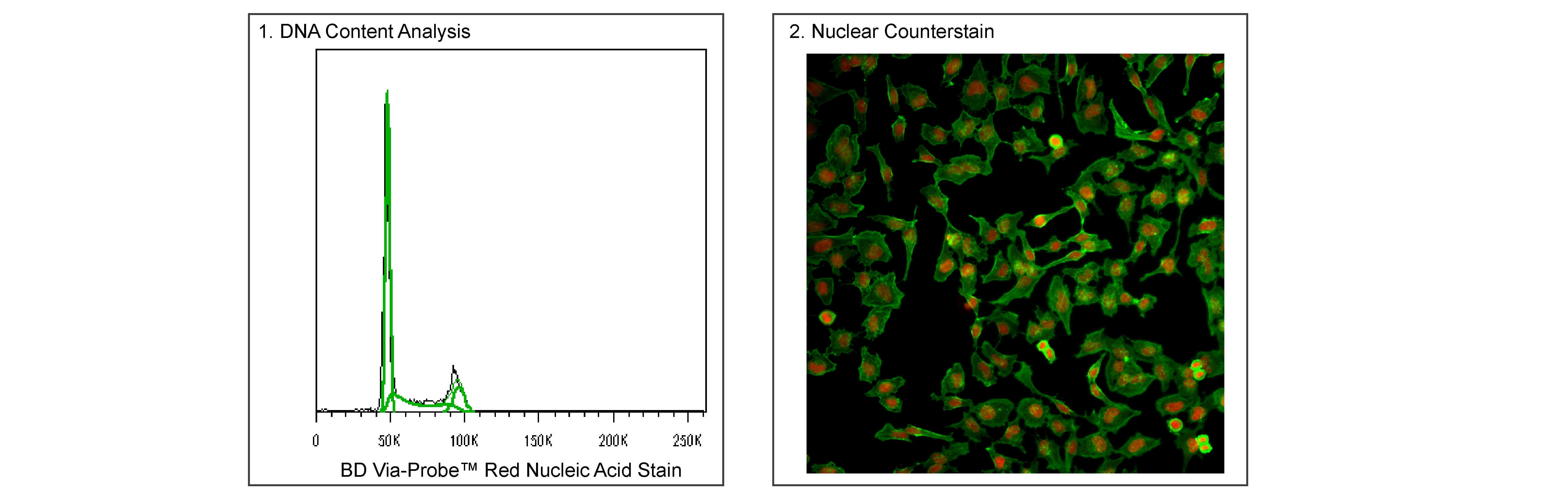
Panel 1 - Flow cytometric analysis of HeLa cell DNA content. HeLa cells in log phase growth were harvested, fixed, and permeabilized using 70% ice-cold ethanol while vortexing. Cells were resuspended in DPBS with 0.1 μM BD Via-Probe™ Red Nucleic Acid Stain and 0.25 μg/mL RNAse A (Sigma, Cat. No. R6513) and acquired by flow cytometry at a low flow rate using a BD LSRFortessa™ Cell Analyzer System. DNA histograms were deconvoluted by FlowJo™ software into G0/G1, S, and G2/M populations. Please note that for DNA content analysis, this dye is also compatible with BD Pharmingen™ Transcription Factor Buffer Set (Cat. No. 562574/562725).
Panel 2 - Immunofluorescent staining of HeLa cells. HeLa cells were seeded into a 96-well imaging plate at ~10,000 cells/well. After overnight incubation, the cells were fixed in BD Cytofix™ Fixation Buffer (Cat. No. 554655), permeabilized with BD Phosflow™ Perm Buffer III (Cat. No. 558050), and then stained with Alexa Fluor® 488 Mouse Anti-Actin antibody (Cat. No. 558623; pseudocolored green). Cell nuclei were counterstained with BD Via-Probe™ Red Nucleic Acid Stain (pseudocolored red) with 0.25 mg/mL RNAse A (Sigma Aldrich, Cat. No. R6513). The images were captured on a Molecular Devices ImageXpress® Micro XLS using a 20× objective and merged using Molecular Devices MetaXpress® software. Red Nucleic Acid Stain is also compatible with Saponin and Triton™ X-100 fix/perm protocols.


Panel 1 - Flow cytometric analysis of HeLa cell viability. Cells from the human HeLa (Cervical adenocarcinoma, ATCC CCL 2) cell line were heat-killed by incubation at 60°C (45 min), cooled to room temperature, and mixed with an equal number of untreated viable HeLa cells. Cells were then stained with BD Via-Probe™ Red Nucleic Acid Stain (Cat. No. 565803/565804; 10 nM) and then acquired by flow cytometry. Morphologically live (red solid line histogram) and dead (blue dashed line histogram) HeLa cells were gated based on their distinct forward and side light-scattering characteristics and can be clearly distinguished based on staining intensity of BD Via-Probe™ Red. Flow cytometric analysis was performed using a BD LSRFortessa™ Cell Analyzer System.
Panel 2 - Two-color flow cytometric analysis of mouse thymocyte viability. BALB/c thymocytes were left untreated (Left Plot) or stimulated with Purified NA/LE Hamster Anti-Mouse CD95 antibody (Cat. No. 554254; Right Plot) for 4 hours. Cells were harvested, stained with BD Horizon™ BV421 Annexin V (Cat. No. 563973) and BD Via-Probe™ Red Nucleic Acid Stain (5 nM), and analyzed by flow cytometry. Anti-CD95-stimulated cells show an increase in Annexin V-positive and BD Via-Probe™ Red-positive cells, indicating an increase in apoptosis and cell death. Flow cytometric analysis was performed using a BD LSRFortessa™ X-20 Cell Analyzer System.
Panel 1 - Flow cytometric analysis of HeLa cell DNA content. HeLa cells in log phase growth were harvested, fixed, and permeabilized using 70% ice-cold ethanol while vortexing. Cells were resuspended in DPBS with 0.1 μM BD Via-Probe™ Red Nucleic Acid Stain and 0.25 μg/mL RNAse A (Sigma, Cat. No. R6513) and acquired by flow cytometry at a low flow rate using a BD LSRFortessa™ Cell Analyzer System. DNA histograms were deconvoluted by FlowJo™ software into G0/G1, S, and G2/M populations. Please note that for DNA content analysis, this dye is also compatible with BD Pharmingen™ Transcription Factor Buffer Set (Cat. No. 562574/562725).
Panel 2 - Immunofluorescent staining of HeLa cells. HeLa cells were seeded into a 96-well imaging plate at ~10,000 cells/well. After overnight incubation, the cells were fixed in BD Cytofix™ Fixation Buffer (Cat. No. 554655), permeabilized with BD Phosflow™ Perm Buffer III (Cat. No. 558050), and then stained with Alexa Fluor® 488 Mouse Anti-Actin antibody (Cat. No. 558623; pseudocolored green). Cell nuclei were counterstained with BD Via-Probe™ Red Nucleic Acid Stain (pseudocolored red) with 0.25 mg/mL RNAse A (Sigma Aldrich, Cat. No. R6513). The images were captured on a Molecular Devices ImageXpress® Micro XLS using a 20× objective and merged using Molecular Devices MetaXpress® software. Red Nucleic Acid Stain is also compatible with Saponin and Triton™ X-100 fix/perm protocols.

Panel 1 - Flow cytometric analysis of HeLa cell viability. Cells from the human HeLa (Cervical adenocarcinoma, ATCC CCL 2) cell line were heat-killed by incubation at 60°C (45 min), cooled to room temperature, and mixed with an equal number of untreated viable HeLa cells. Cells were then stained with BD Via-Probe™ Red Nucleic Acid Stain (Cat. No. 565803/565804; 10 nM) and then acquired by flow cytometry. Morphologically live (red solid line histogram) and dead (blue dashed line histogram) HeLa cells were gated based on their distinct forward and side light-scattering characteristics and can be clearly distinguished based on staining intensity of BD Via-Probe™ Red. Flow cytometric analysis was performed using a BD LSRFortessa™ Cell Analyzer System.
Panel 2 - Two-color flow cytometric analysis of mouse thymocyte viability. BALB/c thymocytes were left untreated (Left Plot) or stimulated with Purified NA/LE Hamster Anti-Mouse CD95 antibody (Cat. No. 554254; Right Plot) for 4 hours. Cells were harvested, stained with BD Horizon™ BV421 Annexin V (Cat. No. 563973) and BD Via-Probe™ Red Nucleic Acid Stain (5 nM), and analyzed by flow cytometry. Anti-CD95-stimulated cells show an increase in Annexin V-positive and BD Via-Probe™ Red-positive cells, indicating an increase in apoptosis and cell death. Flow cytometric analysis was performed using a BD LSRFortessa™ X-20 Cell Analyzer System.

Panel 1 - Flow cytometric analysis of HeLa cell DNA content. HeLa cells in log phase growth were harvested, fixed, and permeabilized using 70% ice-cold ethanol while vortexing. Cells were resuspended in DPBS with 0.1 μM BD Via-Probe™ Red Nucleic Acid Stain and 0.25 μg/mL RNAse A (Sigma, Cat. No. R6513) and acquired by flow cytometry at a low flow rate using a BD LSRFortessa™ Cell Analyzer System. DNA histograms were deconvoluted by FlowJo™ software into G0/G1, S, and G2/M populations. Please note that for DNA content analysis, this dye is also compatible with BD Pharmingen™ Transcription Factor Buffer Set (Cat. No. 562574/562725).
Panel 2 - Immunofluorescent staining of HeLa cells. HeLa cells were seeded into a 96-well imaging plate at ~10,000 cells/well. After overnight incubation, the cells were fixed in BD Cytofix™ Fixation Buffer (Cat. No. 554655), permeabilized with BD Phosflow™ Perm Buffer III (Cat. No. 558050), and then stained with Alexa Fluor® 488 Mouse Anti-Actin antibody (Cat. No. 558623; pseudocolored green). Cell nuclei were counterstained with BD Via-Probe™ Red Nucleic Acid Stain (pseudocolored red) with 0.25 mg/mL RNAse A (Sigma Aldrich, Cat. No. R6513). The images were captured on a Molecular Devices ImageXpress® Micro XLS using a 20× objective and merged using Molecular Devices MetaXpress® software. Red Nucleic Acid Stain is also compatible with Saponin and Triton™ X-100 fix/perm protocols.

BD Via-Probe™ Red Nucleic Acid Stain

BD Via-Probe™ Red Nucleic Acid Stain
Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
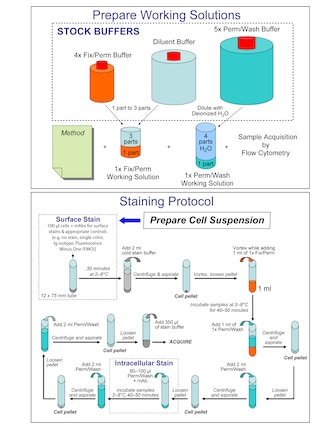
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
Please Note: This nucleic acid dye has been developed for the flow cytometry (intracellular) and immunofluorescence microscopy applications. Chemically characterized for consistency, researchers should determine the optimal concentration of this reagent for individual applications.
Staining of Live Cells for Viability Analysis by Flow Cytometry
1. Obtain a single cell suspension.
2. Resuspend cells at 1-2 × 10^6 cells/mL in BD Pharmingen™ Stain Buffer (FBS) (Cat. No. 554656) or 1× DPBS containing 5-20 nM BD Via-Probe™ Red.
a. The optimal concentration of BD Via-Probe™ Red for viability analysis may vary by cell type. Using high concentrations may result in the dye entering viable cells. Therefore, we recommend titrating the reagent for your cell type of interest in preliminary experiments.
b. Additionally, apoptotic cells may stain with variable amounts of probe. We recommend co-staining with a probe for apoptotic cells, eg, BD Horizon Annexin V (Cat. No. 563973), if further analysis of apoptotic cells is desired.
3. Incubate the cells and dye for 5 minutes at room temperature protected from light. No further cell washes are necessary prior to analysis.
4. Proceed to analysis by flow cytometry.
Staining of Fixed Cells for DNA Content Analysis by Flow Cytometry
1. Obtain a single cell suspension.
2. Treat cells on ice for 30 minutes with 70 - 80% ice-cold ethanol.
a. Ethanol fixation typically provides the most resolved DNA histograms. However, this reagent has also been successfully used for DNA content analysis with the BD Pharmingen™ Transcription Factor Buffer Set (Cat. No. 562574/562725) protocol.
3. Wash cells once with BD Pharmingen™ Stain Buffer (FBS).
4. Resuspend cells at 1-2 × 10^6 cells/mL in 0.1-1 μM BD Via-Probe™ Red in the presence of 0.1-0.5 mg/mL DNAse-free RNAse (eg, Sigma Aldrich, Cat. No. D6513) diluted in BD Pharmingen™ Stain Buffer (FBS) or 1× DPBS immediately before use.
a. The optimal cell density and concentration of BD Via-Probe™ Red for DNA content analysis may vary by cell type. Assay conditions should be optimized in preliminary experiments for best results.
5. Incubate cells for 5-15 minutes. No further cell washes are necessary prior to analysis.
6. Proceed to analysis by flow cytometry. Samples should be run at a low flow rate to achieve the best results. High flow rates may result in higher % CV for each cell cycle compartment in the DNA histogram.
Immunofluorescent Staining of Fixed Cells for Nuclear Visualization
1. Fix and permeabilize cells as desired.
2. Dilute BD Via-Probe™ Red solution to 0.1-1 μM in 1× DPBS with 0.1-0.5 mg/mL DNase-free RNase (eg, Sigma Aldrich, Cat. No. D6513) immediately prior to use.
3. Add BD Via-Probe™ Red solution to each sample at least 15 minutes before analysis.
4. Proceed to fluorescence microscopy and image analysis.
Product Notices
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- Triton is a trademark of the Dow Chemical Company.
- FlowJo is a trademark of Tree Star Inc.
- Alexa Fluor® is a registered trademark of Molecular Probes, Inc., Eugene, OR.
Data Sheets
Companion Products

BD Via-Probe™ Red Nucleic Acid Stain is a nucleic acid dye that is useful for the discrimination of viable from nonviable cells, DNA content analysis in fixed cells, or nuclear counterstaining for fixed cells in immunofluorescence or flow cytometry applications. Although this dye is impermeant to viable cells with intact plasma membranes, it brightly stains nonviable or fixed cells with permeable membranes. BD Via-Probe™ Red Nucleic Acid Stain has an excitation maximum of 631 nm, and is best excited by the red laser. BD Via-Probe™ Red Nucleic Acid Stain has an emission maximum of 651 nm.
Development References (4)
-
Darzynkiewicz Z, Bruno S, Del Bino G, et al. Features of apoptotic cells measured by flow cytometry. Cytometry. 1992; 13(8):795-808. (Methodology: Immunocytochemistry). View Reference
-
Darzynkiewicz Z, Halicka HD, Zhao H. Analysis of cellular DNA content by flow and laser scanning cytometry.. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010; 676:137-47. (Methodology). View Reference
-
Hotz MA, Gong J, Traganos F, and Darzynkiewicz Z. Flow cytometric detection of apoptosis: Comparison of the assays of in situ DNA degradation and chromatin changes. Cytometry. 1994; 15(3):237-244. (Methodology). View Reference
-
Schimenti KJ, Jacobberger JW. Fixation of mammalian cells for flow cytometric evaluation of DNA content and nuclear immunofluorescence.. Cytometry. 1992; 13(1):48-59. (Methodology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.