Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?


Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
BD® CompBeads can be used as surrogates to assess fluorescence spillover (compensation). When fluorochrome conjugated antibodies are bound to BD® CompBeads, they have spectral properties very similar to cells. However, for some fluorochromes there can be small differences in spectral emissions compared to cells, resulting in spillover values that differ when compared to biological controls. It is strongly recommended that when using a reagent for the first time, users compare the spillover on cells and BD® CompBeads to ensure that BD® CompBeads are appropriate for your specific cellular application.
Product Notices
- Researchers should determine the optimal concentration of this reagent for their individual applications.
- The production process underwent stringent testing and validation to assure that it generates a high-quality conjugate with consistent performance and specific binding activity. However, verification testing has not been performed on all conjugate lots.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- CF™ is a trademark of Biotium, Inc.
- Please refer to http://regdocs.bd.com to access safety data sheets (SDS).
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- Human donor specific background has been observed in relation to the presence of anti-polyethylene glycol (PEG) antibodies, developed as a result of certain vaccines containing PEG, including some COVID-19 vaccines. We recommend use of BD Horizon Brilliant™ Stain Buffer in your experiments to help mitigate potential background. For more information visit https://www.bdbiosciences.com/en-us/support/product-notices.
Companion Products




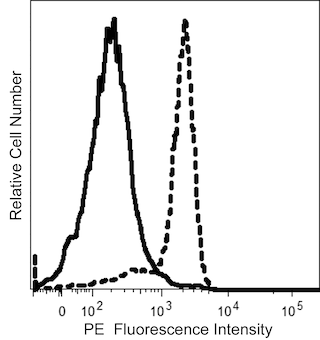

The 23C6 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to the Integrin αvβ3 heterodimeric complex (CD51/CD61) that is expressed on osteoclasts, endothelial cells, macrophages, melanoma cells, some B cells and in very low amounts on platelets. This antibody has been reported to crossreact with chicken, bovine, and rabbit, but not with rat αvβ3. The integrin αvβ3 heterodimer, often referred to as the vitronectin receptor, binds several ligands in addition to vitronectin including, von Willebrand factor, thrombospondin, osteopontin, bone sialoprotein, neural adhesion molecule L1, laminin, fibronectin, and fibrinogen. The binding of some ligands to the vitronectin receptor has been reported to be inhibited by the 23C6 monoclonal antibody.
Development References (8)
-
Athanasou NA, Quinn J, Horton MA, McGee JO. New sites of cellular vitronectin receptor immunoreactivity detected with osteoclast-reacting monoclonal antibodies 13C2 and 23C6. Bone Miner. 1990; 8(1):7-22. (Clone-specific: Immunohistochemistry). View Reference
-
Chuntharapai A, Bodary S, Horton M, Kim KJ. Blocking monoclonal antibodies to alpha V beta 3 integrin: a unique epitope of alpha V beta 3 integrin is present on human osteoclasts. Exp Cell Res. 1993; 205(2):345-352. (Biology). View Reference
-
Davies J, Warwick J, Totty N, Philp R, Helfrich M, Horton M. The osteoclast functional antigen, implicated in the regulation of bone resorption, is biochemically related to the vitronectin receptor. J Cell Biol. 1989; 109(4):1817-1826. (Clone-specific: Immunofluorescence, Immunohistochemistry, Immunoprecipitation). View Reference
-
Horton MA, Lewis D, McNulty K, Pringle JA, Chambers TJ. Monoclonal antibodies to osteoclastomas (giant cell bone tumors): definition of osteoclast-specific cellular antigens. Cancer Res. 1985; 45(11):5663-5669. (Immunogen: Immunofluorescence, Immunohistochemistry). View Reference
-
Horton MA, Taylor ML, Arnett TR, Helfrich MH. Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) peptides and the anti-vitronectin receptor antibody 23C6 inhibit dentine resorption and cell spreading by osteoclasts. Exp Cell Res. 1991; 195(2):368-375. (Clone-specific: Immunoprecipitation). View Reference
-
Nesbitt S, Nesbit A, Helfrich M, Horton M. Biochemical characterization of human osteoclast integrins. Osteoclasts express alpha v beta 3, alpha 2 beta 1, and alpha v beta 1 integrins. J Biol Chem. 1993; 268(22):16737-16745. (Biology). View Reference
-
Schlossman SF. Stuart F. Schlossman .. et al., ed. Leucocyte typing V : white cell differentiation antigens : proceedings of the fifth international workshop and conference held in Boston, USA, 3-7 November, 1993. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1995.
-
Zola H. Leukocyte and stromal cell molecules : the CD markers. Hoboken, N.J.: Wiley-Liss; 2007.
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.