Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?
.png)
.png)
Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
BD® CompBeads can be used as surrogates to assess fluorescence spillover (compensation). When fluorochrome conjugated antibodies are bound to BD® CompBeads, they have spectral properties very similar to cells. However, for some fluorochromes there can be small differences in spectral emissions compared to cells, resulting in spillover values that differ when compared to biological controls. It is strongly recommended that when using a reagent for the first time, users compare the spillover on cells and BD® CompBeads to ensure that BD® CompBeads are appropriate for your specific cellular application.
Product Notices
- When using high concentrations of antibody, background binding of this dye to erythroid fragments produced by ammonium chloride-based lysis, such as with BD Pharm Lyse™ Lysing Buffer (Cat. No. 555899), has been observed when the antibody conjugate was present during the lysis procedure. This may cause nonspecific staining of target cells, such as leukocytes, which have bound the resulting erythroid fragments. This background can be mitigated by any of the following: titrating the antibody conjugate to a lower concentration, fixing samples with formaldehyde, or removing erythrocytes before staining (eg, gradient centrifugation or pre-lysis with wash). This background has not been observed when cells were lysed with BD FACS™ Lysing Solution (Cat. No. 349202) after staining.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Researchers should determine the optimal concentration of this reagent for their individual applications.
- The production process underwent stringent testing and validation to assure that it generates a high-quality conjugate with consistent performance and specific binding activity. However, verification testing has not been performed on all conjugate lots.
- Please observe the following precautions: Absorption of visible light can significantly alter the energy transfer occurring in any tandem fluorochrome conjugate; therefore, we recommend that special precautions be taken (such as wrapping vials, tubes, or racks in aluminum foil) to prevent exposure of conjugated reagents, including cells stained with those reagents, to room illumination.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
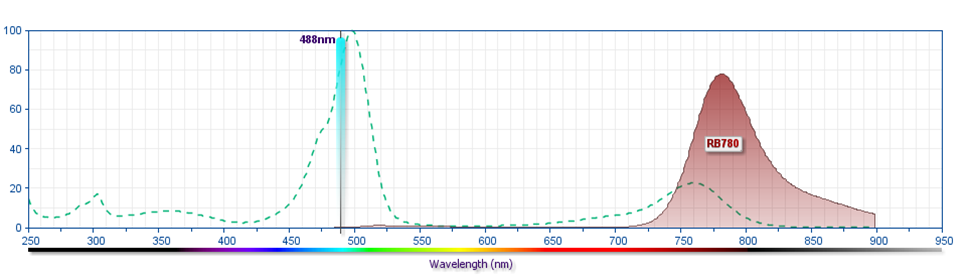
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to http://regdocs.bd.com to access safety data sheets (SDS).
- Cy is a trademark of Global Life Sciences Solutions Germany GmbH or an affiliate doing business as Cytiva.
Companion Products




The 536 monoclonal antibody specifically recognizes Vγ 3† T-cell Receptor (TCR)-bearing T lymphocytes, which are the predominant γδ TCR-bearing cells in the early fetal thymus and the adult epidermis of euthymic mice. The first T cells to mature in the embryonic thymus express the Vγ 3 and Vδ 1 TCR chains, and their development is dependent upon IL-7. There is evidence that the Vγ 3 TCR-bearing fetal thymocytes are the precursors of the majority of dendritic epidermal T cells (DEC), which may be replenished in the adult by proliferation in situ rather than by seeding from primary lymphoid organs. Although the Vγ 3 TCR is almost exclusively found in the DEC population, it has been shown that the homing of DEC to the epidermis does not require expression of the Vγ 3 gene segment. Vγ 3 TCR-bearing dermal dendritic cells have also been described. Vγ 3 TCR has also been found on a subset of T lymphocytes in the lactating mammary gland and at the site of antigenic challenge in contact-sensitized mice. Plate-bound 536 antibody activates Vγ 3 TCR-bearing T cells, and Fab fragments of mAb 536 block in vitro stimulation of DEC by keratinocytes.
† Please note that the Vγ 3 designation correlates with the nomenclature of Garman, Doherty, and Raulet; the Vγ 5 designation of Heilig and Tonegawa is equivalent.
Development References (17)
-
Boismenu R, Havran WL. Modulation of epithelial cell growth by intraepithelial gamma delta T cells. Science. 1994; 266(5188):1253-1255. (Biology). View Reference
-
Bonneville M, Itohara S, Krecko EG, et al. Transgenic mice demonstrate that epithelial homing of gamma/delta T cells is determined by cell lineages independent of T cell receptor specificity. J Exp Med. 1990; 171(4):1015-1026. (Biology). View Reference
-
Dieli F, Asherson GL, Sireci G, et al. gamma delta cells involved in contact sensitivity preferentially rearrange the Vgamma3 region and require interleukin-7. Eur J Immunol. 1997; 27(1):206-214. (Biology). View Reference
-
Havran WL, Allison JP. Developmentally ordered appearance of thymocytes expressing different T-cell antigen receptors. Nature. 1988; 335(6189):443-445. (Clone-specific). View Reference
-
Havran WL, Allison JP. Origin of Thy-1+ dendritic epidermal cells of adult mice from fetal thymic precursors. Nature. 1990; 344(6261):68-70. (Biology). View Reference
-
Havran WL, Chien YH, Allison JP. Recognition of self antigens by skin-derived T cells with invariant gamma delta antigen receptors. Science. 1991; 252(5011):1430-1432. (Biology). View Reference
-
Havran WL, Grell S, Duwe G, Kimura J. Limited diversity of T-cell receptor gamma-chain expression of murine Thy-1+ dendritic epidermal cells revealed by V gamma 3-specific monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989; 86(11):4185-4189. (Immunogen). View Reference
-
Havran WL, Poenie M, Tigelaar RE, Tsien RY, Allison JP. Phenotypic and functional analysis of gamma delta T cell receptor-positive murine dendritic epidermal clones. J Immunol. 1989; 142(5):1422-1428. (Biology). View Reference
-
Hayday A, Pao W. T cell receptor, γδ. In: Delves PJ, Roitt IM, ed. Encyclopedia of Immunology. San Diego: Academic Press; 1998:2268-2278.
-
Kelly KA, Pearse M, Lefrancois L, Scollay R. Emigration of selected subsets of gamma delta + T cells from the adult murine thymus. Int Immunol. 1993; 5(4):331-335. (Biology). View Reference
-
Mallick-Wood CA, Lewis JM, Richie LI, Owen MJ, Tigelaar RE, Hayday AC. Conservation of T cell receptor conformation in epidermal gammadelta cells with disrupted primary Vgamma gene usage. Science. 1998; 279(5357):1729-1733. (Biology). View Reference
-
Moore TA, von Freeden-Jeffry U, Murray R, Zlotnik A. Inhibition of gamma delta T cell development and early thymocyte maturation in IL-7 -/- mice. J Immunol. 1996; 157(6):2366-2373. (Biology). View Reference
-
Payer E, Elbe A, Stingl G. Circulating CD3+/T cell receptor V gamma 3+ fetal murine thymocytes home to the skin and give rise to proliferating dendritic epidermal T cells. J Immunol. 1991; 146(8):2536-2543. (Biology). View Reference
-
Raulet DH, Spencer DM, Hsiang YH. Control of gamma delta T-cell development. Immunology. 1991; 120:185-204. (Biology). View Reference
-
Reardon C, Lefrancois L, Farr A, Kubo R, O'Brien R, Born W. Expression of gamma/delta T cell receptors on lymphocytes from the lactating mammary gland. J Exp Med. 1990; 172(4):1263-1266. (Biology). View Reference
-
Tamaki K, Yasaka N, Chang CH, et al. Identification and characterization of novel dermal Thy-1 antigen-bearing dendritic cells in murine skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1996; 106(3):571-575. (Biology). View Reference
-
van Oers NS, Lowin-Kropf B, Finlay D, Connolly K, Weiss A. alpha beta T cell development is abolished in mice lacking both Lck and Fyn protein tyrosine kinases. Immunity. 1996; 5(5):429-436. (Clone-specific: Immunofluorescence). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.