Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?
BD Pharmingen™ Q-VD-OPh, General Caspase Inhibitor
(RUO)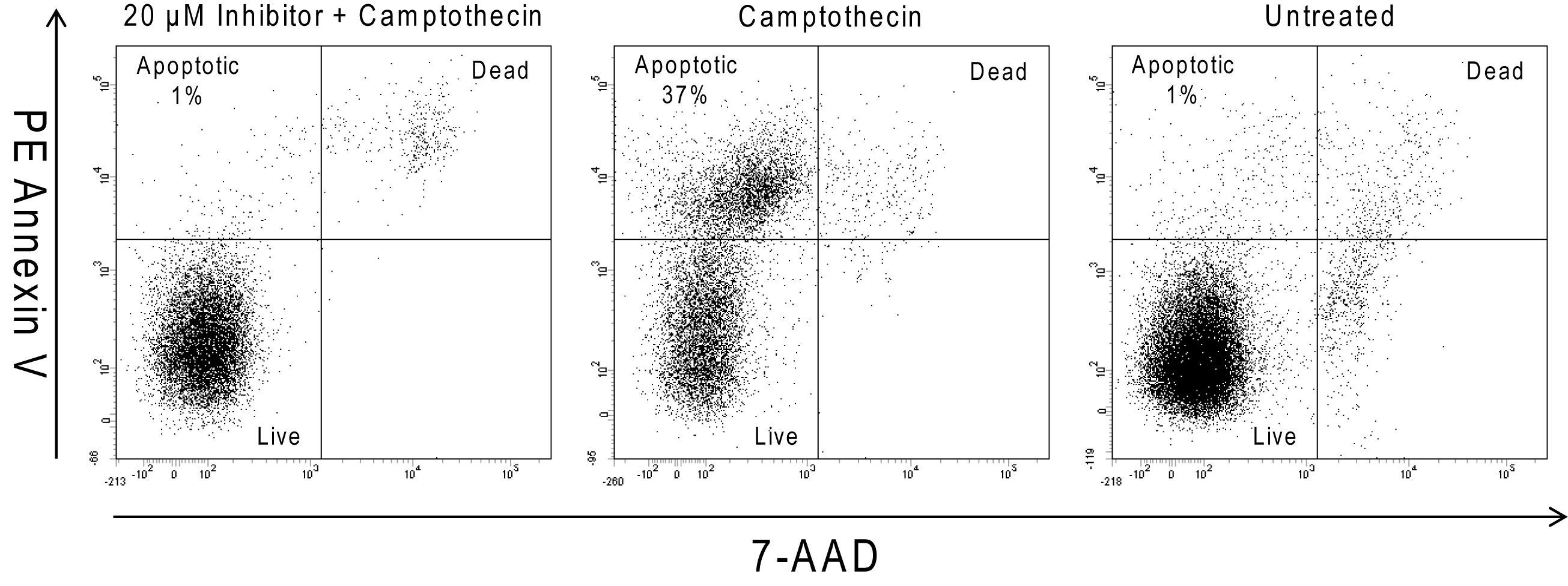


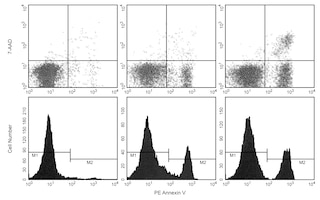
Flow cytometric analysis of apoptosis in human T-Cell leukemia. Jurkat cells (ATCC, TIB-152) were preincubated with either 20 μM Q-VD-OPh (left) or no inhibitor for 30 minutes and then either left untreated (right) or treated with 20 μM camptothecin (center) for 5 hours. Following incubation, cells were collected and stained with PE Annexin V (Cat. No. 556421) and 7-AAD (Cat. No. 559925) to identify cells undergoing apoptosis. Flow cytometry was performed on a BD LSRFortessa™ flow cytometry system. The results indicate that in camptothecin treated cells, approximately 37% of the cells were induced to undergo apoptosis. In both the inhibitor treated and untreated cells, approximately 1% of cells underwent apoptosis. Thus, the use of the general caspase inhibitor Q-VD-OPh reduced the level of apoptosis to that observed in the untreated control.


BD Pharmingen™ Q-VD-OPh, General Caspase Inhibitor

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Store the lyophilized Q-VD-OPh inhibitor at –20°C. Reconstitute the Q-VD-OPh inhibitor in DMSO before use. The reconstituted Q-VD-OPh inhibitor may be stored in small aliquots at –20°C.
Recommended Assay Procedures
The Q-VD-OPh inhibitor is designed to be used in both in vivo and in vitro cell based assays to measure the inhibition of apoptosis.
Reconstitute 1.0 mg of the Q-VD-OPh inhibitor in DMSO. A 10 mM stock solution may be made by dissolving 1.0 mg of Q-VD-OPh in 195 µl DMSO. The final concentration of inhibitor may vary between experimental systems and investigators are encouraged to titrate the inhibitor for optimal performance. As a precautionary note, do not exceed a final DMSO concentration of 0.2% as higher levels may cause cellular toxicity and mask the effects of the caspase inhibitor.
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products



The caspase family of cysteine proteases plays a key role in apoptosis and inflammation. Q-VD-OPh is a potent, cell-permeable inhibitor of caspase activity. It irreversibly inhibits the activity of a broad range of caspases, including caspases-1, -2, -3, -5, -6, -7, -8, -9, -10, and -12. Deemed a next generation caspase inhibitor, Q-VD-OPh has increased selectivity for the caspases over other cysteine proteases, increased potency, and decreased toxicity compared to the previous generation of caspase inhibitors. Additionally, other pan caspase inhibitors do not inhibit all caspases equally. Q-VD-OPh, in contrast, inhibits the spectrum of caspases more equally and at lower concentrations, thus making it a true broad spectrum caspase inhibitor.
Development References (6)
-
Brown TL. Q-VD-OPh, next generation caspase inhibitor. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2004; 559:293-300. (Biology). View Reference
-
Caserta TM, Smith AN, Gultice AD, Reedy MA, Brown T. Q-VD-OPh, a broad spectrum caspase inhibitor with potent antiapoptotic properties. Apoptosis. 2003; 8(4):345-352. (Biology). View Reference
-
Chauvier D, Ankri S, Charriaut-Marlangue C, Casimir R, Jacotot E. Broad-spectrum caspase inhibitors: from myth to reality. Cell Death Differ. 2007; 14(2):387-391. (Biology). View Reference
-
Kuželová K, Grebeňová D, Brodská B. Dose-dependent effects of the caspase inhibitor Q-VD-OPh on different apoptosis-related processes. J Cell Biochem. 2011; 112(11):3334-3342. (Biology). View Reference
-
Melnikov VY, Faubel S, Siegmund B, Lucia MS, Ljubanovic D, and Edelstein CL. Neutrophil-independent mechanisms of caspase-1– and IL-18–mediated ischemic acute tubular necrosis in mice. J Clin Invest. 2002; 110(8):1083-1091. (Biology). View Reference
-
Thornberry NA, Rano TA, Peterson EP, et al. A combinatorial approach defines specificities of members of the caspase family and granzyme B. Functional relationships established for key mediators of apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 1997; 272(29):17907-17911. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.