Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?






Western Blot analysis of TRA-1-60 in mouse and human ES cell lines. Lysates from ES-E14TG2a mouse ES cells (ATCC CRL-1821, left blot) and H9 human ES cells* (WiCell, Madison, WI, right blot) were probed with purified mouse anti-human TRA-1-60 Antigen monoclonal antibody at titrations of 2.0 (lanes 1), 1.0 (lanes 2), and 0.5 µg/ml (lanes 3). High-molecular-weight molecules bearing the TRA-1-60 epitope are identified above 200 kDa in the human ES cells. Expression of the TRA-1-60 epitope has not been reported in mouse ES cells. *The H9 cells were cultured on a mitomycin C-treated mouse embryonic fibroblast feeder layer [MEF (CF-1), ATCC SCRC-1040] that maintains the undifferentiated state of the ES cells. The lysate was made from a mixture of the 2 cell types, the majority of which were H9 cells.

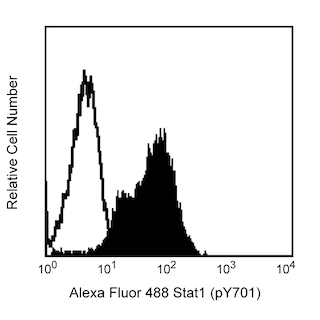
Immunofluorescent staining of human ES cell line. The H9 cell line (WiCell, Madison, WI) was cultured, fixed, and stained with purified mouse anti-human TRA-1-60 Antigen monoclonal antibody (clone TRA-1-60) (pseudo-colored green) according to the Recommended Assay Procedure. The second step reagent was Alexa Fluor® 647 goat anti-mouse Ig (Invitrogen). The left image shows the plasma membrane staining by the TRA-1-60 mAb, and the right image shows TRA-1-60 with counter-staining of the nuclei by Hoechst 33342 (pseudo-colored blue). The images were captured on a BD Pathway™ 435 Cell Analyzer using a 10X objective and merged using BD Attovision™ software. If permeabilization is required for staining additional markers, we recommend the use of cold 90% methanol or BD™ Phosflow Perm Buffer III (Cat. No. 558050).


BD Pharmingen™ Purified Mouse anti-Human TRA-1-60 Antigen

BD Pharmingen™ Purified Mouse anti-Human TRA-1-60 Antigen

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
Bioimaging:
1. Seed the cells in appropriate culture medium at an appropriate cell density in a BD Falcon™ 96-well Imaging Plate (Cat. No. 353219), and
culture overnight to 48 hours.
2. Remove the culture medium from the wells, wash the wells twice with 100 μl of 1× PBS, and fix the cells by adding 100 µl of fresh 3.7% Formaldehyde in PBS or BD Cytofix™ fixation buffer (Cat. No. 554655) to each well and incubating for 10 minutes at room temperature (RT).
3. Remove the fixative from the wells, and wash the wells twice with 100 μl of 1× PBS.
4. Dilute the antibody in 1× PBS, and stain the cells by adding 50 µl of the diluted antibody to each well and incubating for 1 hour at RT.
5. Remove the diluted antibody, and wash the wells three times with 100 μl of 1× PBS.
6. Remove the PBS, dilute the second-step reagent in 1× PBS, and stain the cells by adding 50 µl of the diluted second-step reagent to each well and incubating for 1 hour at RT.
7. Remove the diluted second-step reagent, and wash the wells twice with 100 μl of 1× PBS.
8. Remove the PBS, and counter-stain the nuclei by adding 100 μl of a 2 μg/ml solution of Hoechst 33342 (eg, Sigma-Aldrich Cat. No. B2261) in 1× PBS to each well at least 15 minutes before imaging.
9. View and analyze the cells on an appropriate imaging instrument.
Bioimaging: For more detailed information please refer to http://www.bdbiosciences.com/support/resources/protocols/ceritifed_reagents.jsp
Western blot: For more detailed information please refer to http://www.bdbiosciences.com/pharmingen/protocols/Western_Blotting.shtml
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- This antibody has been developed and certified for the bioimaging application. However, a routine bioimaging test is not performed on every lot. Researchers are encouraged to titrate the reagent for optimal performance.
Companion Products


The TRA-1-60 monoclonal antibody reacts with the neuraminidase-resistant form of a pluripotent-stem-cell-specific epitope on a high-molecular-weight transmembrane glycoprotein. The TRA-1-60 antigen is a sialylated epitope on the same keratan sulfate core molecule, podocalyxin, as 4 other distinct antigens on tumor-derived cell lines, TRA-1-81, GCTM2, K4, and K21. The expression of TRA-1-60 antigen is stage-specific and can be used to characterize embryonic cells and monitor their differentiation. The antigen is found on teratocarcinoma (embryonal carcinoma or EC), embryonic inner cell mass (but not morula or trophoblast), and embryonic stem (ES) cells. TRA-1-60 antigen is released into the serum of patients bearing testicular tumors containing EC cells. As human EC and ES cells undergo differentiation, expression of TRA-1-60 antigen is lost. Expression of TRA-1-60 antigen has also been observed on a rhesus monkey ES cell line (Thomson et al, 1995).
Development References (7)
-
Andrews PW, Banting G, Damanov I, Arnaud D, Avner P. Three monoclonal antibodies defining distinct differentiation antigens associated with different high molecular weight polypeptides on the surface of human embryonal carcinoma cells. Hybridoma. 1984; 3(4):347-361. (Immunogen: Immunofluorescence, Immunoprecipitation, Radioimmunoassay). View Reference
-
Badcock G, Pigott C, Goepel J, Andrews PW. The human embryonal carcinoma marker antigen TRA-1-60 is a sialylated keratan sulfate proteoglycan. Cancer Res. 1999; 59:4715-4719. (Clone-specific: Immunoprecipitation, Western blot). View Reference
-
Draper JS, Pigott C, Thomson JA, Andrews PW. Surface antigens of human embryonic stem cells: changes upon differentiation in culture. J Anat. 2002; 200:249-258. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Henderson JK, Draper JS, Baillie HS, et al. Preimplantation human embryos and embryonic stem cells show comparable expression of stage-specific embryonic antigens. Stem Cells. 2002; 20:329-337. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry, Immunofluorescence). View Reference
-
Schopperle WM, DeWolf WC. The TRA-1-60 and TRA-1-81 human pluripotent stem cell markers are expressed on podocalyxin in embryonal carcinoma. Stem Cells. 2007; 25:723-730. (Clone-specific: Immunofluorescence, Western blot). View Reference
-
Thomson JA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Shapiro SS, et al. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science. 1998; 282:1145-1147. (Clone-specific: Immunocytochemistry (cytospins)). View Reference
-
Thomson JA, Kalishman J, Golos TG, et al. Isolation of a primate embryonic stem cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995; 92:7844-7848. (Clone-specific: Immunocytochemistry (cytospins)). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.