Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?


.png)

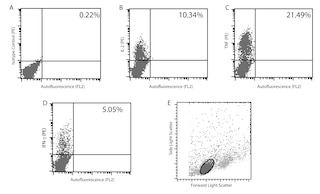
Expression of IFN-γ by stimulated CD4+ and CD4-C3H spleen cells. Splenocytes from C3H mice were stimulated in culture for 4 hours using PMA (5 ng/ml final concentration; Sigma Cat. #P-8139) and Ionomycin (500 ng/ml final concentration; Sigma Cat. #I0634) in the presence of GolgiPlug™ Protein Transport Inhibitor (1 µl/ml, Cat. No. 555029). The splenocytes were harvested and stained with 0.06 µg of FITC Rat Anti-Mouse CD4 (FITC-Rm4-5, Cat. No. 553047), fixed, permeabilized and subsequently stained with 0.12 µg of APC Rat IgG1 isotype control antibody (APC-R3-34, Cat. No. 554686, left panel) or with APC Rat Anti-Mouse IFN-γ (APC-XMG1.2, Cat. No. 554413, middle panel) by using the BD Pharmingen staining protocol. To demonstrate specificity of staining, the binding by the APC-XMG1.2 antibody was blocked by preincubation of the fixed, premeabilized cells with unlabeled XMG1.2 antibody (5.0 µg; Cat. No. 554409, right panel) prior to staining. The quadrant markers for the bivariate dot plots were set based on the autofluorescence controls and verified using the unlabeled antibody blocking specificity control.
.png)

BD Pharmingen™ APC Rat Anti-Mouse IFN-γ
.png)
Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
Recommended Assay Procedure:
Immunofluorescent Staining for Flow Cytometric Analysis: The APC-XMG1.2 antibody is useful for immunofluorescent staining and flow cytometric analysis to identify and enumerate IFN-γ producing cells within mixed cell populations. For optimal immunofluorescent staining for flow cytometric analysis, the anti-cytokine antibody should be titrated (≤ 0.5 µg mAb/million cells). For specific methodology, please visit the protocols section or chapter on intracellular staining in the Immune Function Handbook, both of which are posted on our web site, www.bdbiosciences.com.
A suitable rat IgG1 isotype control for assessing the level of background staining on paraformaldehyde-fixed/saponin-permeabilized mouse cells is APC-R3-34 (Cat. No. 554686); use at comparable concentrations to antibody of interest. A useful control for demonstrating specificity of staining is either of the following: (1) pre-block the APC-conjugated XMG1.2 antibody with ligand (e.g., recombinant mIFN-γ, Cat. No. 554587) prior to staining, or (2) pre-block the fixed/permeabilized cells with unlabeled XMG1.2 antibody (Cat. No. 554409) prior to staining.
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
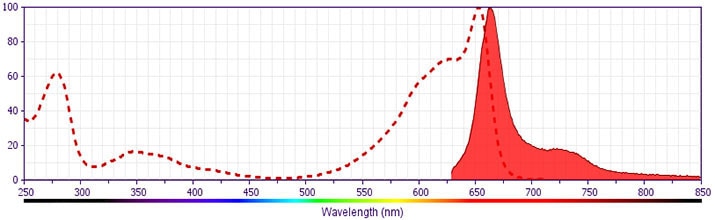
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
Companion Products

.png?imwidth=320)
The XMG1.2 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to mouse interferon-γ (IFN-γ) protein. IFN-γ is a pleiotropic cytokine, of approximately 15-17 kDa, involved in the regulation of inflammatory and immune responses. It plays an important role in activation, growth, and differentiation of T and B lymphocytes, macrophages, NK cells and other non-hematopoietic cell types. IFN-γ production is associated with the Th1 cell differentiation. The purified form of this antibody has been reported to be a neutralizing antibody.
Development References (7)
-
Abrams JS, Roncarolo MG, Yssel H, Andersson U, Gleich GJ, Silver JE. Strategies of anti-cytokine monoclonal antibody development: immunoassay of IL-10 and IL-5 in clinical samples. Immunol Rev. 1992; 127:5-24. (Clone-specific). View Reference
-
Cherwinski HM, Schumacher JH, Brown KD, Mosmann TR. Two types of mouse helper T cell clone. III. Further differences in lymphokine synthesis between Th1 and Th2 clones revealed by RNA hybridization, functionally monospecific bioassays, and monoclonal antibodies. J Exp Med. 1987; 166(5):1229-1244. (Clone-specific). View Reference
-
Ferrick DA, Schrenzel MD, Mulvania T, Hsieh B, Ferlin WG, Lepper H. Differential production of interferon-gamma and interleukin-4 in response to Th1- and Th2-stimulating pathogens by gamma delta T cells in vivo. Nature. 1995; 373(6511):255-257. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Hsieh B, Schrenzel MD, Mulvania T, Lepper HD, DiMolfetto-Landon L, Ferrick DA. In vivo cytokine production in murine listeriosis. Evidence for immunoregulation by gamma delta+ T cells. J Immunol. 1996; 156(1):232-237. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Prussin C, Metcalfe DD. Detection of intracytoplasmic cytokine using flow cytometry and directly conjugated anti-cytokine antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1995; 188(1):117-128. (Methodology: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Sander B, Hoiden I, Andersson U, Moller E, Abrams JS. Similar frequencies and kinetics of cytokine producing cells in murine peripheral blood and spleen. Cytokine detection by immunoassay and intracellular immunostaining. J Immunol Methods. 1993; 166(2):201-214. (Clone-specific). View Reference
-
Vikingsson A, Pederson K, Muller D. Enumeration of IFN-gamma producing lymphocytes by flow cytometry and correlation with quantitative measurement of IFN-gamma. J Immunol Methods. 1994; 173(2):219-228. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.