-
Reagents
- Flow Cytometry Reagents
-
Western Blotting and Molecular Reagents
- Immunoassay Reagents
-
Single-Cell Multiomics Reagents
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- BD® OMICS-One Protein Panels
-
Functional Assays
-
Microscopy and Imaging Reagents
-
Cell Preparation and Separation Reagents
-
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- BD® OMICS-One Protein Panels
- Austria (English)
-
Change country/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from United States.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?
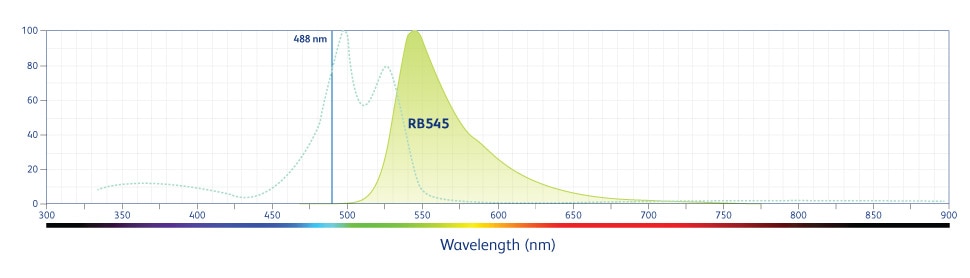
BD OptiBuild™ RB545 Mouse Anti-Mouse CD272 (BTLA)
Clone 6F7/BTLA (also known as 6F7) (RUO)


Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Product Notices
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- Please observe the following precautions: Absorption of visible light can significantly alter the energy transfer occurring in any tandem fluorochrome conjugate; therefore, we recommend that special precautions be taken (such as wrapping vials, tubes, or racks in aluminum foil) to prevent exposure of conjugated reagents, including cells stained with those reagents, to room illumination.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Please refer to http://regdocs.bd.com to access safety data sheets (SDS).
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- The production process underwent stringent testing and validation to assure that it generates a high-quality conjugate with consistent performance and specific binding activity. However, verification testing has not been performed on all conjugate lots.
- Researchers should determine the optimal concentration of this reagent for their individual applications.
Data Sheets
Companion Products



The 6F7 monoclonal antibody specifically recognizes CD272 which is also known as B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA) and is exclusively expressed on lymphoid cells. CD272 (BTLA) is a type 1 transmembrane glycoprotein that is encoded by Btla (B and T lymphocyte associated). CD272 (BTLA) contains a V-type Ig-like domain in its extracellular region followed by a transmembrane sequence, and a cytoplasmic domain with three tyrosine-based motifs, two immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs (ITIM) and a Grb-2 recognition consensus sequence. The existence of three distinct BTLA alleles has been reported which encode molecules with different Ig domain structure and expression patterns on lymphoid cell subsets amongst different mouse strains. For example, whereas C57BL/6 and BALB/c mice both variably express CD272 (BTLA) on developing and mature T and B lymphocytes and dendritic cells (DC), C57BL/6 mice, but not BALB/c mice, also express CD272 (BTLA) on NK cells and macrophages. CD272 (BTLA) expression is upregulated by activated T cells including Th1, Th2, and anergic T cells. Herpesvirus entry mediator (HVEM), also known as CD270 and LIGHT-R, has been identified as a ligand for CD272 (BTLA). The crosslinking of CD272 (BTLA) by HVEM inhibits T-cell proliferation and cytokine production. CD272 (BTLA) is structurally like other coinhibitory receptors including CD152/CTLA-4 and CD279/PD-1. Although these coinhibitory receptors and their ligands maintain immunological homeostasis and self-tolerance, they may also serve as immune checkpoint molecules that inhibit adaptive immune responses against tumors and chronic infections.
No Citations Are Available for this Product
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.