Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?




Flow cytometric analysis of CCR7 (CD197) on human peripheral blood leukocytes and lymphocytes. Whole blood was stained with BD Horizon™ BUV395 Mouse Anti-Human CD4 (clone RPA-T4, Cat. No. 564724), BD Horizon BV421 Mouse Anti-Human CD8 (clone RPA-T8, Cat. No. 562429 or 562428), APC Mouse Anti-Human CD45RA (clone HI100, Cat. No.550855 or 561884), and either BD Horizon BB515 Mouse IgG1, κ Isotype Control (Cat. No. 564416) or BD Horizon BB515 Mouse Anti-Human CCR7 (CD197) (Cat. No. 566764 or 566765). The erythrocytes were lysed with BD PharmLyse™ Lysing Buffer (Cat. No. 555899). Flow cytometry and data analysis were performed using a BD LSRFortessa™ Flow Cytometer and FlowJo™ software. Plots 1 and 2: The contour plots showing Ig isotype control or CCR7 (CD197) staining versus side light-scatter were derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of viable leucocytes. Plot 3: The contour plot showing CCR7 (CD197) staining versus CD45RA was derived from CD4-positive T cell gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of viable lymphocytes. Please note that we have observed considerable donor-to-donor variation in the proportion of CCR7 (CD197)-negative CD4-positive lymphocytes. Plot 4: The contour plot showing CCR7 (CD197) staining versus CD45RA was derived from CD8-positive T cell gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of viable lymphocytes.


BD Horizon™ BB515 Mouse Anti-Human CCR7 (CD197)

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
BD™ CompBeads can be used as surrogates to assess fluorescence spillover (Compensation). When fluorochrome conjugated antibodies are bound to CompBeads, they have spectral properties very similar to cells. However, for some fluorochromes there can be small differences in spectral emissions compared to cells, resulting in spillover values that differ when compared to biological controls. It is strongly recommended that when using a reagent for the first time, users compare the spillover on cells and CompBead to ensure that BD Comp beads are appropriate for your specific cellular application.
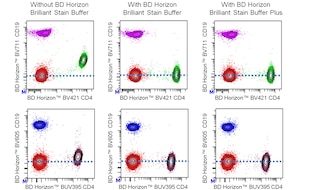
For optimal and reproducible results, BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer should be used anytime two or more BD Horizon Brilliant dyes are used in the same experiment. Fluorescent dye interactions may cause staining artifacts which may affect data interpretation. The BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer was designed to minimize these interactions. More information can be found in the Technical Data Sheet of the BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer (Cat. No. 563794/566349) or the BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer Plus (Cat. No. 566385).
For optimal results, it is recommended to perform 2 washes after staining with antibodies. Cells may be prepared, stained with antibodies and washed twice with wash buffer per established protocols for immunofluorescence staining, prior to acquisition on a flow cytometer. Performing fewer than the recommended wash steps may lead to increased spread of the negative population.
Product Notices
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- This reagent has been pre-diluted for use at the recommended Volume per Test. We typically use 1 × 10^6 cells in a 100-µl experimental sample (a test).
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- The manufacture, use, sale, offer for sale, or import of this product is subject to one or more patents or pending applications. This product, and only in the amount purchased by buyer, may be used solely for buyer’s own internal research, in a manner consistent with the accompanying product literature. No other right to use, sell or otherwise transfer (a) this product, or (b) its components is hereby granted expressly, by implication or by estoppel. Diagnostic uses require a separate license.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,110,673; 8,158,444; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
- Please refer to http://regdocs.bd.com to access safety data sheets (SDS).
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products





The 2-L1-A monoclonal antibody specifically binds to the human CC chemokine receptor CCR7, also known as CD197, on the cell surface. CCR7 (previously known as BLR2, EBI1 and CMKBR7) is a seven-transmembrane, G-protein-coupled receptor specific for two CC chemokines: CCL19 (also known as MIP-3β, Exodus-3, and ELC) and CCL21 (also known as 6Ckine, Exodus-2 SLC, TCA4, and SCYA21). CCR7 mRNA is expressed mainly in lymphoid tissues including the spleen, lymph nodes and tonsil, in bone marrow, and on peripheral T and B lymphocytes, cord blood CD34-positive cells, and mature dendritic cells. In response to its cognate chemokines, CCR7 (CD197) mediates homing of leucocytes to secondary lymphoid tissues. Differential CCR7 (CD197) expression can be used to distinguish naive, central memory, and effector memory T cell subsets. The human CCR7 gene, unlike other CC chemokine receptor genes, has been mapped to chromosome 17 (region 17q12). Because the extracellular region of CCR2 (CD192) has significant sequence homology with CCR7 (CD197), BD Biosciences has confirmed that mAb 2-L1-A does not cross-react with CCR2 on the surface of transfected cells.
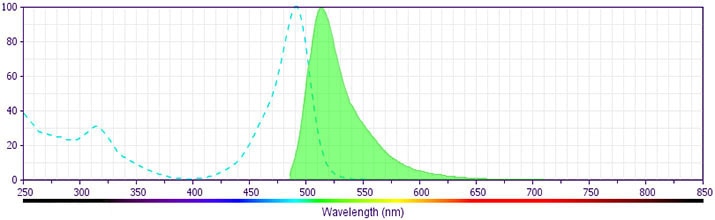
The antibody was conjugated to BD Horizon BB515 which was developed exclusively by BD Biosciences. With an excitation max of 490 nm and an emission max of 515 nm, BD Horizon BB515 can be excited by the 488 nm laser and detected in a standard FITC set (eg, 530/30-nm filter). This dye provides a much brighter alternative to FITC with less spillover into the PE detector.
Development References (8)
-
Birkenbach M, Josefsen K, Yalamanchili R, Lenoir G, Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus-induced genes: first lymphocyte-specific G protein-coupled peptide receptors. Nature. 1993; 67(4):2209-2220. (Biology). View Reference
-
Burgstahler R, Kempkes B, Steube K, Lipp M. Expression of the chemokine receptor BLR2/EBI1 is specifically transactivated by Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995; 215(2):737-743. (Biology). View Reference
-
Kim CH, Pelus LM, White JR, Broxmeyer HE. Macrophage-inflammatory protein-3 beta/EBI1-ligand chemokine/CK beta-11, a CC chemokine, is a chemoattractant with a specificity for macrophage progenitors among myeloid progenitor cells. J Immunol. 1998; 161(5):2580-2585. (Biology). View Reference
-
Schweickart VL, Raport CJ, Godiska R, et al. Cloning of human and mouse EBI1, a lymphoid-specific G-protein-coupled receptor encoded on human chromosome 17q12-q21.2. Genomics. 1994; 23(3):643-650. (Biology). View Reference
-
Yanagihara S, Komura E, Nagafune J, Watarai H, Yamaguchi Y. EBI1/CCR7 is a new member of dendritic cell chemokine receptor that is up-regulated upon maturation. J Immunol. 1998; 161(6):3096-3102. (Biology). View Reference
-
Yoshida R, Imai T, Hieshima K, et al. Molecular cloning of a novel human CC chemokine EBI1-ligand chemokine that is a specific functional ligand for EBI1, CCR7. J Biol Chem. 1997; 272(21):13803-13809. (Biology). View Reference
-
Yoshida R, Nagira M, Imai T, et al. EBI1-ligand chemokine (ELC) attracts a broad spectrum of lymphocytes: activated T cells strongly up-regulate CCR7 and efficiently migrate toward ELC. Int Immunol. 1998; 10(7):901-910. (Biology). View Reference
-
Yoshida R, Nagira M, Kitaura M, Imagawa N, Imai T, Yoshie O. Secondary lymphoid-tissue chemokine is a functional ligand for the CC chemokine receptor CCR7. J Biol Chem. 1998; 273(12):7118-7122. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.