Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?


Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
For optimal and reproducible results, BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer should be used anytime two or more BD Horizon Brilliant dyes (including BD Optibuild Brilliant reagents) are used in the same experiment. Fluorescent dye interactions may cause staining artifacts which may affect data interpretation. The BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer was designed to minimize these interactions. More information can be found in the Technical Data Sheet of the BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer (Cat. No. 563794/566349) or the BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer Plus (Cat. No. 566385).
Product Notices
- This antibody was developed for use in flow cytometry.
- The production process underwent stringent testing and validation to assure that it generates a high-quality conjugate with consistent performance and specific binding activity. However, verification testing has not been performed on all conjugate lots.
- Researchers should determine the optimal concentration of this reagent for their individual applications.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,110,673; 8,158,444; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Ultraviolet 737 is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,110,673; 8,158,444; 8,227,187; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
- Alexa Fluor® is a registered trademark of Life Technologies Corporation.
- Cy is a trademark of GE Healthcare.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products






The TM-β1 monoclonal antibody specifically recognizes the 90-100-kDa β chain shared by the IL-2 and IL-15 receptors (IL-2Rβ, CD122). In the periphery, CD122 is expressed on CD8+ T lymphocytes, NK cells, NK-T cells, dendritic epidermal T cells, subsets of intraepithelial lymphocytes, and macrophages. Small subsets of fetal and adult thymocytes constitutively express CD122. CD122+ cells in the bone marrow include committed NK-cell progenitors. IL-2Rβ expression is upregulated by IL-2. CD122 is a transmembrane glycoprotein of the hematopoietin receptor superfamily which can combine with CD132 (γc) alone or CD132 plus CD25 (IL-2Rα) to form intermediate or high-affinity IL-2 receptor complexes, respectively. The β chain of these complexes, CD122, is involved in signal transduction and immunoregulation. The TM-β1 antibody blocks high affinity binding of IL-2 or IL-15 to IL-2Rβ.
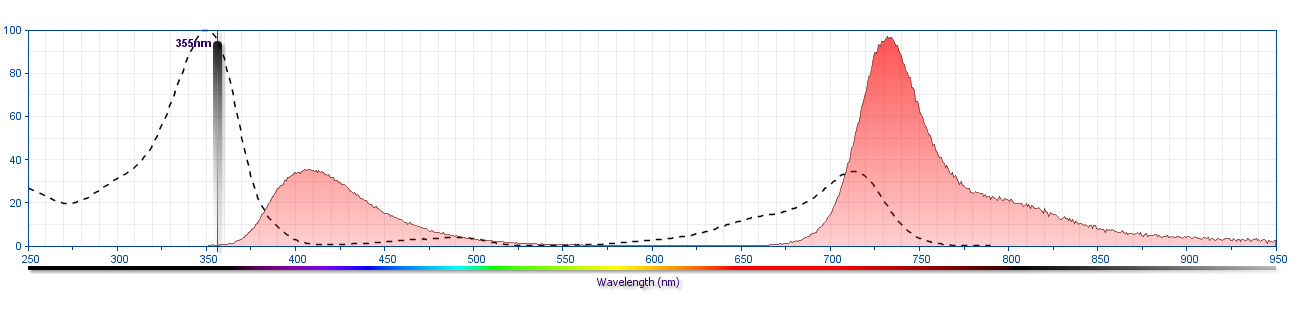
The antibody was conjugated to BD Horizon™ BUV737 which is part of the BD Horizon Brilliant™ Ultraviolet family of dyes. This dye is a tandem fluorochrome of BD Horizon BUV395 with an Ex Max of 348-nm and an acceptor dye with an Em Max at 737-nm. BD Horizon Brilliant BUV737 can be excited by the ultraviolet laser (355 nm) and detected with a 740/35 filter. Due to the excitation of the acceptor dye by other laser lines, there may be significant spillover into channels detecting Alexa Fluor® 700-like dyes (eg, 712/20-nm filter).
Due to spectral differences between labeled cells and beads, using BD™ CompBeads can result in incorrect spillover values when used with BD Horizon BUV737 reagents. Therefore, the use of BD CompBeads or BD CompBeads Plus to determine spillover values for these reagents is not recommended. Different BUV737 reagents (eg, CD4 vs. CD45) can have slightly different fluorescence spillover therefore, it may also be necessary to use clone specific compensation controls when using these reagents.
Development References (18)
-
Alleva DG, Kaser SB, Monroy MA, Fenton MJ, Beller DI. IL-15 functions as a potent autocrine regulator of macrophage proinflammatory cytokine production: evidence for differential receptor subunit utilization associated with stimulation or inhibition. J Immunol. 1997; 159(6):2941-2951. (Clone-specific: Blocking). View Reference
-
Bendelac A. Mouse NK1+ T cells. Curr Opin Immunol. 1995; 7(3):367-374. (Biology). View Reference
-
Cho BK, Wang C, Sugawa S, Eisen HN, Chen J. Functional differences between memory and naive CD8 T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999; 96(6):2976-2981. (Biology). View Reference
-
Giri JG, Ahdieh M, Eisenman J, et al. Utilization of the beta and gamma chains of the IL-2 receptor by the novel cytokine IL-15. EMBO J. 1994; 13(12):2822-2830. (Biology). View Reference
-
Guy-Grand D, Cuenod-Jabri B, Malassis-Seris M, Selz F, Vassalli P. Complexity of the mouse gut T cell immune system: identification of two distinct natural killer T cell intraepithelial lineages. Eur J Immunol. 1996; 26(9):2248-2256. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Hanke T, Mitnacht R, Boyd R, Hunig T. Induction of interleukin 2 receptor beta chain expression by self-recognition in the thymus. J Exp Med. 1994; 180(5):1629-1636. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Kondo M, Ohashi Y, Tada K, Nakamura M, Sugamura K. Expression of the mouse interleukin-2 receptor gamma chain in various cell populations of the thymus and spleen. Eur J Immunol. 1994; 24(9):2026-2030. (Biology). View Reference
-
Ku CC, Murakami M, Sakamoto A, Kappler J, Marrack P. Control of homeostasis of CD8+ memory T cells by opposing cytokines. Science. 2000; 288(5466):675-678. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry, Fluorescence activated cell sorting). View Reference
-
Malek TR, Furse RK, Fleming ML, Fadell AJ, He YW. Biochemical identity and characterization of the mouse interleukin-2 receptor beta and gamma c subunits. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 1995; 15(5):447-454. (Clone-specific: Immunoprecipitation). View Reference
-
Nakanishi K, Hirose S, Yoshimoto T, et al. Role and regulation of interleukin (IL)-2 receptor alpha and beta chains in IL-2-driven B-cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992; 89(8):3551-3555. (Clone-specific: Blocking). View Reference
-
Ohno H, Ono S, Hirayama N, Shimada S, Saito T. Preferential usage of the Fc receptor gamma chain in the T cell antigen receptor complex by gamma/delta T cells localized in epithelia. J Exp Med. 1994; 179(1):365-369. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Rosmaraki EE, Douagi I, Roth C, Colucci F, Cumano A, Di Santo JP. Identification of committed NK cell progenitors in adult murine bone marrow. Eur J Immunol. 2001; 31(6):1900-1909. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry, Fluorescence activated cell sorting). View Reference
-
Suzuki H, Kundig TM, Furlonger C et al. Deregulated T cell activation and autoimmunity in mice lacking interleukin-2 receptor beta. Science. 1995; 268(5216):1472-1476. (Clone-specific: Blocking). View Reference
-
Takeuchi Y, Tanaka T, Hamamura K et al. Expression and role of interleukin-2 receptor beta chain on CD4-CD8- T cell receptor alpha beta+ cells. Eur J Immunol. 1992; 22(11):2929-2935. (Clone-specific: Blocking). View Reference
-
Tanaka T, Takeuchi Y, Shiohara T et al. In utero treatment with monoclonal antibody to IL-2 receptor beta-chain completely abrogates development of Thy-1+ dendritic epidermal cells. Int Immunol. 1992; 4(4):487-491. (Biology). View Reference
-
Tanaka T, Tsudo M, Karasuyama H, et al. A novel monoclonal antibody against murine IL-2 receptor beta-chain. Characterization of receptor expression in normal lymphoid cells and EL-4 cells. J Immunol. 1991; 147(7):2222-2228. (Immunogen: Flow cytometry, Immunoprecipitation, Inhibition). View Reference
-
Taniguchi T, Minami Y. The IL-2/IL-2 receptor system: a current overview. Cell. 1993; 73(1):5-8. (Biology). View Reference
-
Zhang X, Sun S, Hwang I, Tough DF, Sprent J. Potent and selective stimulation of memory-phenotype CD8+ T cells in vivo by IL-15. Immunity. 1998; 8(5):591-599. (Clone-specific). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.