Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?


Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
For optimal and reproducible results, BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer should be used anytime two or more BD Horizon Brilliant dyes are used in the same experiment. Fluorescent dye interactions may cause staining artifacts which may affect data interpretation. The BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer was designed to minimize these interactions. More information can be found in the Technical Data Sheet of the BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer (Cat. No. 563794 or 566349).
When setting up compensation, it is recommended to compare spillover values obtained from cells and BD™ CompBeads to ensure that beads will provide sufficiently accurate spillover values.
For optimal results, it is recommended to perform two washes after staining with antibodies. Cells may be prepared, stained with antibodies and washed twice with wash buffer per established protocols for immunofluorescent staining prior to acquisition on a flow cytometer. Performing fewer than the recommended wash steps may lead to increased spread of the negative population.
Product Notices
- This antibody was developed for use in flow cytometry.
- The production process underwent stringent testing and validation to assure that it generates a high-quality conjugate with consistent performance and specific binding activity. However, verification testing has not been performed on all conjugate lots.
- Researchers should determine the optimal concentration of this reagent for their individual applications.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,110,673; 8,158,444; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Blue 700 is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,455,613 and 8,575,303.
- Cy is a trademark of GE Healthcare.
Companion Products





The F23.1 antibody specifically reacts with the Vβ 8.1, Vβ 8.2, and Vβ 8.3 T-cell receptors (TCR) of mice having the b haplotype (e.g., A, AKR, BALB/c, CBA/Ca, CBA/J, C3H/He, C57BL, C58, DBA/1, DBA/2) of the Tcrb gene complex. The Tcrb-V8 subfamily gene loci are deleted in mice having the a (e.g., C57BR, C57L, SJL, SWR) or c (e.g., RIII) haplotype. Vβ 8.1 TCR-bearing T lymphocytes are clonally eliminated in mice expressing superantigen coded by Mtv-7 (Mls-1a, Mlsa) provirus (e.g., AKR, CBA/J, C58, DBA/2), and activation or elimination of Vβ 8.1 TCR-expressing T cells by this determinant is partially dependent upon presentation by I-E. Mtv-43 and/or exogenous MMTV-SW superantigens also cause incomplete elimination of Vβ 8.1 TCR-bearing T cells. In addition to expression on conventional T lymphocytes, Vβ 8.2 is the predominant β chain of the TCR on NK-T cells. Staphylococcal enterotoxin B, in association with antigen-presenting cells expressing I-A and/or I-E, stimulates lymphocytes bearing Vβ 8 TCR and selectively eliminates those T cells in vivo. Soluble and plate-bound F23.1 antibody activates Vβ 8 TCR-bearing T cells, soluble antibody blocks cytolysis mediated by Vβ 8 TCR-bearing cytotoxic T lymphocytes, and in vivo treatment of neonatal mice can arrest intrathymic maturation of Vβ 8 TCR-bearing T cells.
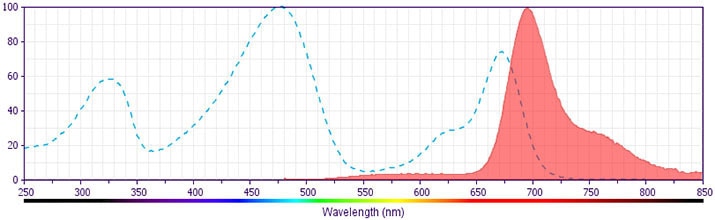
The antibody was conjugated to BD Horizon™ BB700, which is part of the BD Horizon Brilliant™ Blue family of dyes. It is a polymer-based tandem dye developed exclusively by BD Biosciences. With an excitation max of 485 nm and an emission max of 693 nm, BD Horizon BB700 can be excited by the 488 nm laser and detected in a standard PerCP-Cy™5.5 set (eg, 695/40-nm filter). This dye provides a much brighter alternative to PerCP-Cy5.5 with less cross laser excitation off the 405 nm and 355 nm lasers.
Development References (17)
-
Behlke MA, Chou HS, Huppi K, Loh DY. Murine T-cell receptor mutants with deletions of beta-chain variable region genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986; 83(3):767-771. (Biology). View Reference
-
Behlke MA, Henkel TJ, Anderson SJ, et al. Expression of a murine polyclonal T cell receptor marker correlates with the use of specific members of the V beta 8 gene segment subfamily. J Exp Med. 1987; 165(1):257-262. (Clone-specific). View Reference
-
Bendelac A. Mouse NK1+ T cells. Curr Opin Immunol. 1995; 7(3):367-374. (Biology). View Reference
-
Brodnicki TC, Holman PO, Kranz DM. Reactivity and epitope mapping of single-chain T cell receptors with monoclonal antibodies. Mol Immunol. 1996; 33(3):253-263. (Clone-specific: ELISA). View Reference
-
Haqqi TM, Banerjee S, Anderson GD, David CS. RIII S/J (H-2r). An inbred mouse strain with a massive deletion of T cell receptor V beta genes. J Exp Med. 1989; 169(6):1903-1909. (Biology). View Reference
-
Hodes RJ, Abe R. Mouse endogenous superantigens: Ms and Mls-like determinants encoded by mouse retroviruses.. Curr Protoc Immunol. 2001; Appendix 1:Appendix 1F. (Biology). View Reference
-
Hugo P, Kappler JW, Godfrey DI, Marrack PC. Thymic epithelial cell lines that mediate positive selection can also induce thymocyte clonal deletion. J Immunol. 1994; 52(3):1022-1031. (Biology). View Reference
-
Jiang Y, Moller G. In vitro effects of HgCl2 on murine lymphocytes. II. Selective activation of T cells expressing certain V beta TCR. Int Immunol. 1996; 8(11):1729-1736. (Clone-specific). View Reference
-
Kappler JW, Staerz U, White J, Marrack PC. Self-tolerance eliminates T cells specific for Mls-modified products of the major histocompatibility complex. Nature. 1988; 332(6159):35-40. (Biology). View Reference
-
Kyewski BA, Schirrmacher V, Allison JP. Antibodies against the T cell receptor/CD3 complex interfere with distinct intra-thymic cell-cell interactions in vivo: correlation with arrest of T cell differentiation. Eur J Immunol. 1989; 19(5):857-863. (Clone-specific). View Reference
-
Mogil RJ, Radvanyi L, Gonzalez-Quintial R, et al. Fas (CD95) participates in peripheral T cell deletion and associated apoptosis in vivo. Int Immunol. 1995; 7(9):1451-1458. (Biology). View Reference
-
Renno T, Hahne M, Tschopp J, MacDonald HR. Peripheral T cells undergoing superantigen-induced apoptosis in vivo express B220 and upregulate Fas and Fas ligand. J Exp Med. 1996; 183(2):431-437. (Biology). View Reference
-
Saint-Ruf C, Ungewiss K, Groettrup M, Bruno L, Fehling HJ, von Boehmer H. Analysis and expression of a cloned pre-T cell receptor gene. Science. 1994; 266(5188):1208-1212. (Clone-specific: Immunoprecipitation, Western blot). View Reference
-
Staerz UD, Rammensee HG, Benedetto JD, Bevan MJ. Characterization of a murine monoclonal antibody specific for an allotypic determinant on T cell antigen receptor. J Immunol. 1985; 134(6):3994-4000. (Immunogen: Blocking, (Co)-stimulation, Immunoprecipitation). View Reference
-
White J, Herman A, Pullen AM, Kubo R, Kappler JW, Marrack P. The V beta-specific superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin B: stimulation of mature T cells and clonal deletion in neonatal mice. Cell. 1989; 56(1):27-35. (Biology). View Reference
-
Wolff CH, Hong SC, von Grafenstein H, Janeway CA Jr. TCR-CD4 and TCR-TCR interactions as distinctive mechanisms for the induction of increased intracellular calcium in T-cell signalling. J Immunol. 1993; 151(3):1337-1345. (Clone-specific: (Co)-stimulation). View Reference
-
Yagi J, Nakata M, Uchiyama T, et al. Superantigen-like properties of an antibody bispecific for MHC class II molecules and the V beta domain of the T cell antigen receptor. J Immunol. 1994; 152(8):3833-3841. (Clone-specific: (Co)-stimulation). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.