Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?




Multiparameter flow cytometric analysis of CD34 expressed by Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC). Human PBMC were stained with APC Mouse Anti-Human CD14 antibody (Cat. No. 555399/561708/561383) and either BD Horizon™ RY586 Mouse IgG1, κ Isotype Control (Cat No. 568097, Left Plot) or BD Horizon™ RY586 Mouse Anti-Human CD34 antibody (Cat No. 568437/568438, Right Plot). The bivariate pseudocolor density plot showing the correlated expression of CD34 (or Ig Isotype control staining) versus side light-scatter (SSC) signals was derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of CD14-negative cells. Flow cytometry and data analysis were performed using a BD LSRFortessa™ X-20 Cell Analyzer System and FlowJo™ software.


BD Horizon™ RY586 Mouse Anti-Human CD34

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
BD® CompBeads can be used as surrogates to assess fluorescence spillover (compensation). When fluorochrome conjugated antibodies are bound to BD® CompBeads, they have spectral properties very similar to cells. However, for some fluorochromes there can be small differences in spectral emissions compared to cells, resulting in spillover values that differ when compared to biological controls. It is strongly recommended that when using a reagent for the first time, users compare the spillover on cells and BD® CompBeads to ensure that BD® CompBeads are appropriate for your specific cellular application.
Product Notices
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- This reagent has been pre-diluted for use at the recommended Volume per Test. We typically use 1 × 10^6 cells in a 100-µl experimental sample (a test).
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Human donor specific background has been observed in relation to the presence of anti-polyethylene glycol (PEG) antibodies, developed as a result of certain vaccines containing PEG, including some COVID-19 vaccines. We recommend use of BD Horizon Brilliant™ Stain Buffer in your experiments to help mitigate potential background. For more information visit https://www.bdbiosciences.com/en-us/support/product-notices.
- CF™ is a trademark of Biotium, Inc.
- Please refer to http://regdocs.bd.com to access safety data sheets (SDS).
Companion Products



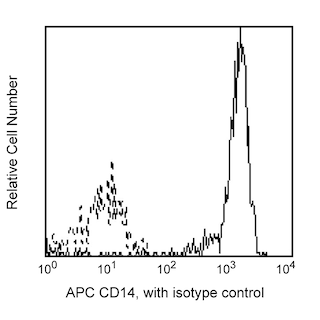
The 581 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to CD34, a sialomucin-like type I transmembrane glycoprotein. This single-chain, 105-120 kDa, heavily O-glycosylated protein is expressed on hematopoietic progenitor cells, vascular endothelium, bone marrow stromal cells and embryonic fibroblasts. The cytoplasmic region of the CD34 antigen is a target for phosphorylation by activated protein kinase C suggesting CD34 may play a role in signal transduction. CD34 may also play a role as an adhesion molecule since it binds to CD62E and CD62L. Clone 581 binds to the class III CD34 epitope. It is resistant to neuraminidase, chymopapain and glycoprotease. The 581 antibody blocks reactivity of another anti-CD34 monoclonal antibody, 8G12.
Development References (5)
-
Egeland T, Tjonnfjord G, Steen R, Gaudernack G, Thorsby E. Positive selection of bone marrow-derived CD34 positive cells for possible stem cell transplantation. Transplant Proc. 1993; 25(1):1261-1263. (Biology). View Reference
-
Kishimoto T. Tadamitsu Kishimoto .. et al., ed. Leucocyte typing VI : white cell differentiation antigens : proceedings of the sixth international workshop and conference held in Kobe, Japan, 10-14 November 1996. New York: Garland Pub.; 1997.
-
Knapp W. W. Knapp .. et al., ed. Leucocyte typing IV : white cell differentiation antigens. Oxford New York: Oxford University Press; 1989:1-1182.
-
Schlossman SF. Stuart F. Schlossman .. et al., ed. Leucocyte typing V : white cell differentiation antigens : proceedings of the fifth international workshop and conference held in Boston, USA, 3-7 November, 1993. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1995.
-
Zola H. Leukocyte and stromal cell molecules : the CD markers. Hoboken, N.J.: Wiley-Liss; 2007.
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.