Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?




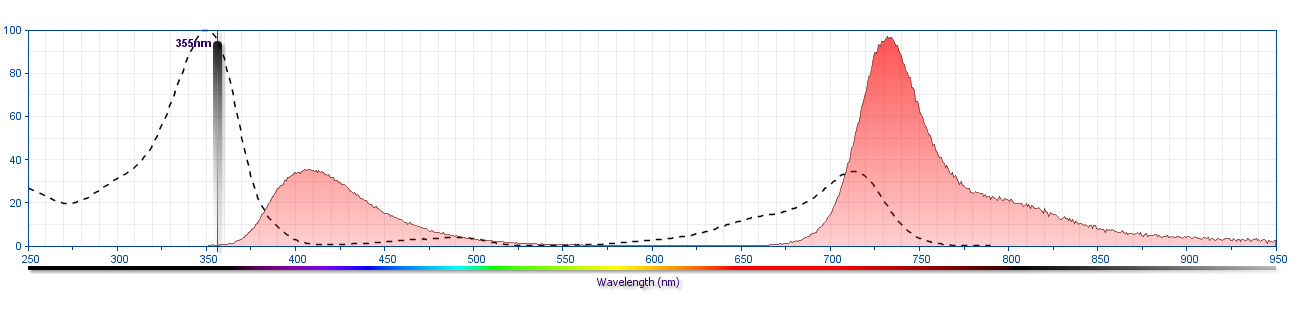
Flow cytometric analysis of CD279 (PD-1) expression on resting and activated mouse splenocytes. Splenocytes from a C57BL/6 mouse were activated in culture with plate-bound Purified NA/LE Hamster Anti-Mouse CD3e antibody (Cat. No. 553057) for 3 days. The resting (Left Plot) or activated (Right Plot) splenocytes were preincubated with Purified Rat Anti-Mouse CD16/CD32 antibody (Mouse BD Fc Block™) [Cat. No. 553141/553142]. The cells were then stained with either BD Horizon™ BUV737 Hamster IgG2, κ Isotype Control (Cat. No. 612774; dashed line histograms) or BD Horizon™ BUV737 Hamster Anti-Mouse CD279 (PD-1) antibody (Cat. No. 568362; solid line histograms) at 1.0 µg/test. BD Via-Probe™ Cell Viability 7-AAD Solution (Cat. No. 555815/555816) was added to cells right before analysis. The fluorescence histograms showing CD279 expression (or Ig Isotype control staining) were derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of viable (7-AAD-negative) splenic leucocytes. Flow cytometry and data analysis were performed using a BD LSRFortessa™ X-20 Cell Analyzer System and FlowJo™ software. Data shown on this Technical Data Sheet are not lot specific.


BD Horizon™ BUV737 Hamster Anti-Mouse CD279 (PD-1)

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
BD® CompBeads can be used as surrogates to assess fluorescence spillover (compensation). When fluorochrome conjugated antibodies are bound to BD® CompBeads, they have spectral properties very similar to cells. However, for some fluorochromes there can be small differences in spectral emissions compared to cells, resulting in spillover values that differ when compared to biological controls. It is strongly recommended that when using a reagent for the first time, users compare the spillover on cells and BD® CompBeads to ensure that BD® CompBeads are appropriate for your specific cellular application.
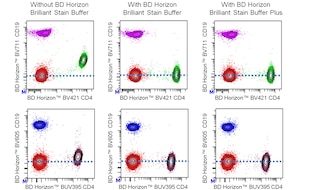
For optimal and reproducible results, BD Horizon Brilliant™ Stain Buffer should be used anytime BD Horizon Brilliant dyes are used in a multicolor flow cytometry panel. Fluorescent dye interactions may cause staining artifacts which may affect data interpretation. The BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer was designed to minimize these interactions. When BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer is used in in the multicolor panel, it should also be used in the corresponding compensation controls for all dyes to achieve the most accurate compensation. For the most accurate compensation, compensation controls created with either cells or beads should be exposed to BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer for the same length of time as the corresponding multicolor panel. More information can be found in the Technical Data Sheet of the BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer (Cat. No. 563794/566349) or the BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer Plus (Cat. No. 566385).
Note: When using high concentrations of antibody, background binding of this dye to erythroid cell subsets (mature erythrocytes and precursors) has been observed. For researchers studying these cell populations, or in cases where light scatter gating does not adequately exclude these cells from the analysis, this background may be an important factor to consider when selecting reagents for panel(s).
Product Notices
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Ultraviolet 737 is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,110,673; 8,158,444; 8,227,187; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,110,673; 8,158,444; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
- Please refer to http://regdocs.bd.com to access safety data sheets (SDS).
Companion Products





The J43 monoclonal antibody specifically recognizes CD279 which is also known as PD-1 (programmed death-1). CD279 is a 50-55-kDa glycoprotein encoded by the Pdcd1 gene of the CD28 family of the Ig superfamily. The expression of Pdcd1 mRNA and PD-1 protein is tightly regulated. PD-1 is transiently expressed on CD4-CD8 thymocytes, it is upregulated on some cell lines upon induction of apoptosis, it is induced on thymocytes and splenic T and B lymphocytes after stimulation through their antigen receptors, and it is induced on activated myeloid cells. In addition, Pdcd1 mRNA is transiently expressed in developing B lymphocytes at the pro-B-cell stage. The presence of an ITIM (Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-based Inhibitory Motif) on PD-1's intracytoplasmic region and the development of splenomegaly and breakdown of peripheral tolerance in PD-1[-/-] mice suggest that PD-1 is involved in the negative regulation of immune responses. The PD-1 ligands, B7-H1 (also known as PD-L1, CD274) and B7-DC (PD-L2, CD273), are members of the B7 family of the Ig superfamily. The J43 antibody blocks the binding of PD-1 to its two ligands.
Development References (8)
-
Agata Y, Kawasaki A, Nishimura H, et al. Expression of the PD-1 antigen on the surface of stimulated mouse T and B lymphocytes. Int Immunol. 1996 May; 8(5):765-772. (Immunogen: Flow cytometry, Immunoprecipitation). View Reference
-
Ansari MJ, Salama AD, Chitnis T, et al. The programmed death-1 (PD-1) pathway regulates autoimmune diabetes in nonobese diabetic (NOD) mice. J Exp Med. 2003 July; 198(1):63-69. (Clone-specific: Blocking, Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Carreno BM, Collins M. The B7 family of ligands and its receptors: New pathways for costimulation and inhibition of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002; 20:29-53. (Biology). View Reference
-
Finger LR, Pu J, Wasserman R, et al. The human PD-1 gene: complete cDNA, genomic organization, and developmentally regulated expression in B cell progenitors. Gene. 1997 September; 197(1-2):177-187. (Biology). View Reference
-
Nishimura H, Agata Y, Kawasaki A, et al. Developmentally regulated expression of the PD-1 protein on the surface of double-negative (CD4-CD8-) thymocytes. Int Immunol. 1996 May; 8(5):773-780. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Nishimura H, Minato N, Nakano T, Honjo T. Immunological studies on PD-1 deficient mice: implication of PD-1 as a negative regulator for B cell responses. Int Immunol. 1998; 10(10):1563-1572. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Salama AD, Chitnis T, Imitola J, et al. Critical role of the programmed death-1 (PD-1) pathway in regulation of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Exp Med. 2003 July; 198(1):71-78. (Clone-specific: Blocking). View Reference
-
Tsushima F, Iwai H, Otsuki N, et al. Preferential contribution of B7-H1 to programmed death-1-mediated regulation of hapten-specific allergic inflammatory responses. Eur J Immunol. 2003; 33(10):2773-2782. (Clone-specific). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.