Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?




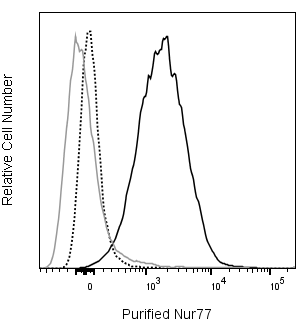
Flow cytometric analysis of upregulated Nur77 expression in stimulated mouse thymocytes. Thymocytes from C57BL/6 mice were left unstimulated (gray line histogram) or stimulated (dashed and solid black line histograms) with Phorbol 12-Myristate 13-Acetate (PMA; 20 ng/ml) and Ionomycin (500 ng/ml) for 2 hours. The cells were then stained intracellularly with Alexa Fluor® 647 Mouse IgG1, κ Isotype Control (Cat. No. 557732; black dashed line histogram) or Alexa Fluor® 647 Mouse Anti-Nur77 antibody (Cat. No. 566735; gray line or solid black line histogram) at 0.125 μg/test using the BD Pharmingen™ Transcription Factor Buffer Set (Cat. No. 562574). Histograms showing Nur77 expression (or Ig Isotype control staining) were derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of intact cells. Flow cytometry and data analysis were performed using a BD LSRFortessa™ X-20 Cell Analyzer System and FlowJo™ software. Data shown on this Technical Data Sheet are not lot specific.


BD Pharmingen™ Alexa Fluor® 647 Mouse Anti-Nur77

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- The Alexa Fluor®, Pacific Blue™, and Cascade Blue® dye antibody conjugates in this product are sold under license from Molecular Probes, Inc. for research use only, excluding use in combination with microarrays, or as analyte specific reagents. The Alexa Fluor® dyes (except for Alexa Fluor® 430), Pacific Blue™ dye, and Cascade Blue® dye are covered by pending and issued patents.
- Alexa Fluor® is a registered trademark of Molecular Probes, Inc., Eugene, OR.
- Alexa Fluor® 647 fluorochrome emission is collected at the same instrument settings as for allophycocyanin (APC).
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products


The 12.14 monoclonal antibody specifically recognizes Nur77, a zinc-finger transcription factor also known as Nerve growth factor IB (NGFI-B), Testicular receptor 3 (TR3), or Nuclear protein N10. Nur77 is encoded by Nr4a1 (Nuclear receptor subfamily 4 group A member 1), an immediate-early response gene that belongs to the nuclear receptor superfamily. This inducible orphan nuclear receptor is comprised of an N-terminal transactivation domain, followed by a central DNA-binding domain and a putative C-terminal ligand-binding domain for which no ligand has been identified. In electrophoretic analyses, Nur77 migrates as diffuse protein bands between 67 and 88 kDa depending on its level of phosphorylation or other post-translational modifications. Nr4a1 expression can be rapidly induced by diverse stimuli in cells from primary and secondary lymphoid tissues and other tissues including the brain, muscle, ovary, and testis. Nur77 expression is rapidly upregulated by antigen-stimulated mouse thymocytes and may promote activation- induced apoptosis during negative selection. Ag receptor-mediated signaling by B cells, T cells, or T cell hybridomas can also lead to rapid upregulated Nur77 expression which may regulate cellular proliferation and survival. In response to certain growth factors, cytokines, inflammatory mediators, or stress-inducing stimuli, other cell types, including myeloid or stromal cell types, can upregulate Nur77 expression which affects their growth, differentiation, proliferation or survival. Clone 12.14 recognizes mouse Nur77 and reportedly crossreacts with human Nur77.
Development References (9)
-
Amsen D, Revilla Calvo C, Osborne BA, Kruisbeek AM. Costimulatory signals are required for induction of transcription factor Nur77 during negative selection of CD4+CD8+ thymocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999; 96(2):622-627. (Clone-specific: Western blot). View Reference
-
Ashouri JF, Weiss A. Endogenous Nur77 Is a Specific Indicator of Antigen Receptor Signaling in Human T and B Cells.. J Immunol. 2017; 198(2):657-668. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry, Western blot). View Reference
-
Cho HJ, Edmondson SG, Miller AD, et al. Cutting edge: identification of the targets of clonal deletion in an unmanipulated thymus. J Immunol. 2003; 170(1):10-13. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Cunningham NR, Artim SC, Fornadel CM, et al. Immature CD4+CD8+ thymocytes and mature T cells regulate Nur77 distinctly in response to TCR stimulation. J Immunol. 2006; 177(10):6660-6666. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry, Western blot). View Reference
-
Davis IJ, Hazel TG, Chen RH, Blenis J, Lau LF. Functional domains and phosphorylation of the orphan receptor Nur77. Mol Endocrinol. 1993; 7(8):953-964. (Biology). View Reference
-
Davis IJ, Lau LF. Endocrine and neurogenic regulation of the orphan nuclear receptors Nur77 and Nurr-1 in the adrenal glands. Mol Cell Biol. 1994; 14(5):3469-3483. (Biology). View Reference
-
Hazel TG, Misra R, Davis IJ, Greenberg ME, Lau LF. Nur77 is differentially modified in PC12 cells upon membrane depolarization and growth factor treatment. Mol Cell Biol. 1991; 11(6):3239-3246. (Biology). View Reference
-
Liu ZG, Smith SW, McLaughlin KA, Schwartz LM, Osborne BA. Apoptotic signals delivered through the T-cell receptor of a T-cell hybrid require the immediate-early gene nur77. Nature. 1994; 367(6460):281-284. (Biology). View Reference
-
Woronicz JD, Calnan B, Ngo V, Winoto A. Requirement for the orphan steroid receptor Nur77 in apoptosis of T-cell hybridomas. Nature. 1994; 367(6460):277-281. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.