Old Browser
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?


.png)

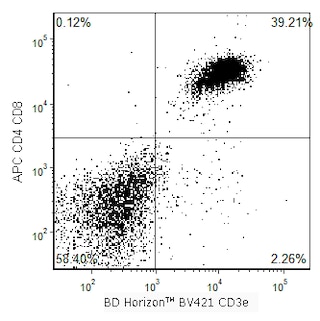
Multicolor flow cytometric analysis of NK-1.1 expression on mouse splenocytes. Splenic leucocytes from a C57BL/6 mouse were preincubated with Purified Rat Anti-Mouse CD16/CD32 antibody (Mouse BD Fc Block™) (Cat. No. 553141/553142), then stained with BD Horizon™ BV421 Hamster Anti-Mouse CD3e antibody (Cat. No. 562600) and either BD Horizon™ R718 Mouse IgG2a, κ Isotype Control (Cat. No. 566949, Left Plot) or BD Horizon™ R718 Mouse Anti-Mouse NK-1.1 antibody (Cat. No. 567360; Right Plot). BD Via-Probe™ Cell Viability 7-AAD Solution (Cat. No. 555815/555816) was added to cells right before analysis. Bivariate pseudocolor density plots showing the correlated expression patterns of NK1.1 (or Ig Isotype control staining) versus CD3e were derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of viable (7-AAD-negative) splenic leucocytes. Flow cytometric analysis was performed using a BD™ LSR II Flow Cytometer System and FlowJo™ software.
.png)

BD Horizon™ R718 Mouse Anti-Mouse NK-1.1
.png)
监管状态图例
未经BD明确书面授权,严禁使用未经许可的任何商品。
准备和存储
推荐的实验流程
BD® CompBeads can be used as surrogates to assess fluorescence spillover (Compensation). When fluorochrome conjugated antibodies are bound to BD® CompBeads, they have spectral properties very similar to cells. However, for some fluorochromes there can be small differences in spectral emissions compared to cells, resulting in spillover values that differ when compared to biological controls. It is strongly recommended that when using a reagent for the first time, users compare the spillover on cells and BD CompBeads to ensure that BD® CompBeads are appropriate for your specific cellular application.
商品通知
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- This product is provided under an Agreement between BIOTIUM and BD Biosciences. This product, and only in the amount purchased by buyer, may be used solely for buyer’s own internal research, in a manner consistent with the accompanying product literature. No other right to use, sell or otherwise transfer (a) this product, or (b) its components is hereby granted expressly, by implication or by estoppel. This product is for research use only. Diagnostic uses require a separate license from Biotium, Inc. For information on purchasing a license to this product including for purposes other than research, contact Biotium, Inc., 3159 Corporate Place, Hayward, CA 94545, Tel: (510) 265-1027. Fax: (510) 265-1352. Email: btinfo@biotium.com.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- Please refer to http://regdocs.bd.com to access safety data sheets (SDS).
- Alexa Fluor™ is a trademark of Life Technologies Corporation.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
配套商品




.png?imwidth=320)
In the mouse, at least three members of the Klrb (Killer cell lectin-like receptor, subfamily b; formerly NKR-P1) gene family have been identified (Klrb1a/NKR-P1A, Klrb1b/NKR-P1B, and Klrb1c/NKR-P1C); but in the human gene family, a single homologue has been designated KLRB1, NKR-P1A, or CD161. The KLRB1/NKR-P1 family of proteins are type-II-transmembrane C-type lectin receptors. KLRB1C/NKR-P1C activates NK-cell cytotoxicity, while KLRB1B/NKR-P1B functions as an inhibitory receptor. KLRB1B/NKR-P1B protein has intracellular Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-based Inhibitory Motif (ITIM), while KLRB1C/NKR-P1C lacks ITIM and activates via association with Fc Receptor γ chain. Strikingly, KLRB1B/NKR-P1B and KLRB1C/NKR-P1C share 96% amino acid sequence identity in their extracellular C-type lectin domains. The PK136 antibody reacts with the NK-1.1 surface antigen (CD161c) encoded by the Klrb1c/NKR-P1C gene expressed on natural killer (NK) cells in selected strains of mice (eg, C57BL, FVB/N, NZB, but not A, AKR, BALB/c, CBA/J, C3H, C57BR, C58, DBA/1, DBA/2, NOD, SJL, 129) and the CD161b antigen encoded by the Klrb1b/NKR-P1B gene expressed only on Swiss NIH and SJL mice, but not on C57BL/6. Expression of KLRB1C/NKR-P1C protein is correlated with the ability to lyse tumor cells in vitro and to mediate rejection of bone marrow allografts. The NK-1.1 marker is useful in defining NK cells; however, the antigen is also expressed on a rare, specialized population of T lymphocytes (NK-T cells) and some cultured monocytes. Plate-bound PK136 mAb, in combination with low concentrations of IL-2, induces proliferation of a subset of NK cells.
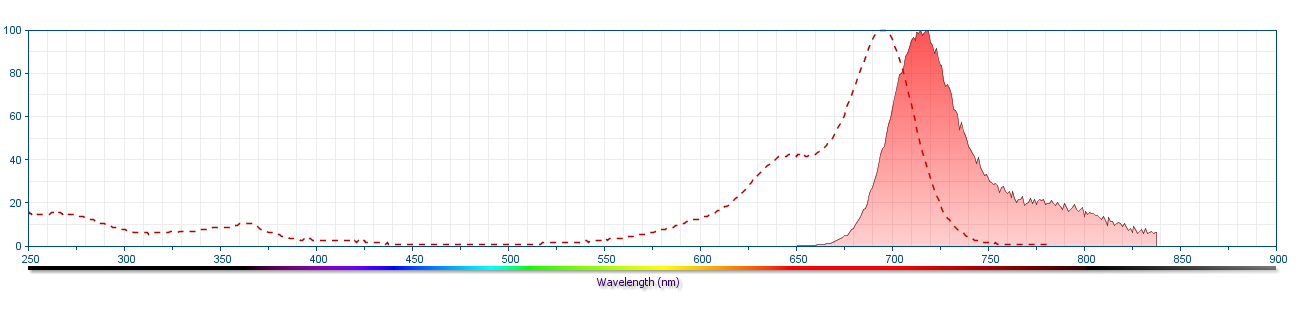
The antibody was conjugated to BD Horizon™ Red 718, which has been developed exclusively by for BD Biosciences as a better alternative to Alexa Fluor™ 700. BD Horizon™ Red 718 can be excited by the red laser (628 – 640 nm) and, with an Em Max around 718 nm, it can be detected using a 730/45 nm filter. Due to similar excitation and emission properties, we do not recommend using R718 in combination with APC-R700 or Alexa Fluor™ 700.
研发参考 (6)
-
Arase N, Arase H, Park SY, Ohno H, Ra C, Saito T. Association with FcRgamma is essential for activation signal through NKR-P1 (CD161) in natural killer (NK) cells and NK1.1+ T cells. J Exp Med. 1997; 186(12):1957-1963. (Clone-specific: Cytotoxicity, Flow cytometry, Fluorescence activated cell sorting, Functional assay, Immunofluorescence, Immunoprecipitation, Stimulation). 查看参考
-
Giorda R, Trucco M. Mouse NKR-P1. A family of genes selectively coexpressed in adherent lymphokine-activated killer cells. J Immunol. 1991; 147(5):1701-1708. (Biology). 查看参考
-
Lanier LL. Natural killer cells: from no receptors to too many. Immunity. 1997; 6(4):371-378. (Biology). 查看参考
-
Vicari AP, Zlotnik A. Mouse NK1.1+ T cells: a new family of T cells. Immunol Today. 1996; 17(2):71-76. (Biology). 查看参考
-
Yokoyama WM, Seaman WE. The Ly-49 and NKR-P1 gene families encoding lectin-like receptors on natural killer cells: the NK gene complex. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993; 11:613-635. (Biology). 查看参考
-
Yu YY, Kumar V, Bennett M. Murine natural killer cells and marrow graft rejection. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992; 10:189-213. (Biology). 查看参考
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.