Old Browser
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?


CD56 PE
监管状态图例
未经BD明确书面授权,严禁使用未经许可的任何商品。
准备和存储
Store vials at 2°C–8°C. Conjugated forms should not be frozen. Protect from exposure to light. Each reagent is stable until the expiration date shown on the bottle label when stored as directed.
The CD56 antibody, clone NCAM16.2, is derived from the hybridization of P3-X63-Ag8.653 mouse myeloma cells with spleen cells isolated from BALB/c mice immunized with immunoaffinity-enriched NCAM from detergent extracts of adult human brain. The CD56 antibody recognizes a heavily glycosylated 140-kilodalton (kDa) isoform of NCAM, a member of the immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily. The CD56 antibody also recognizes 180-kDa and 120-kDa isoforms of NCAM found in neurons and muscle, respectively.
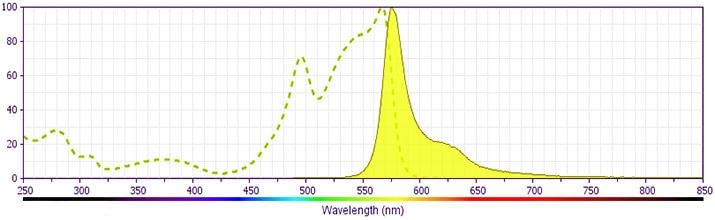
研发参考 (9)
-
Centers for Disease Control. Update: universal precautions for prevention of transmission of human immunodeficiency virus, hepatitis B virus, and other bloodborne pathogens in healthcare settings. MMWR. 1988; 37:377-388. (Biology).
-
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2005. (Biology).
-
Gerosa F, Baldani-Guerra B, Nisii C, Marchesini V, Carra G, Trinchieri G. Reciprocal activating interaction between natural killer cells and dendritic cells. J Exp Med. 2002; 195(3):327-333. (Biology). 查看参考
-
Lanier LL, Chang C, Azuma M, Ruitenberg JJ, Hemperly JJ, Phillips JH. Molecular and functional analysis of human natural killer cell-associated neural cell adhesion molecule (N-CAM/CD56). J Immunol. 1991; 146(12):4421-4426. (Biology). 查看参考
-
Lanier LL, Le AM, Civin CI, Loken MR, Phillips JH. The relationship of CD16 (Leu-11) and Leu-19 (NKH-1) antigen expression on human peripheral blood NK cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986; 136(12):4480-4486. (Biology). 查看参考
-
Lanier LL, Testi R, Bindl J, Phillips JH. Identity of Leu-19 (CD56) leukocyte differentiation antigen and neural cell adhesion molecule. J Exp Med. 1989; 169(6):2233-2238. (Biology). 查看参考
-
Phillips JH, Lanier LL. Dissection of the lymphokine-activated killer phenomenon: relative contribution of peripheral blood natural killer cells and T lymphocytes to cytolysis. J Exp Med. 1986; 164(3):814-825. (Biology). 查看参考
-
Ritz J, Trinchieri G, Lanier LL. NK-cell Antigens: Section Report. In: Schlossman SF. Stuart F. Schlossman .. et al., ed. Leucocyte typing V : white cell differentiation antigens : proceedings of the fifth international workshop and conference held in Boston, USA, 3-7 November, 1993. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1995:1367-1372.
-
Zola H, Swart B, Nicholson I, Voss E. Leukocyte and Stromal Cell Molecules: The CD Markers. 2007. (Biology).
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.