-
Training
- Flow Cytometry Basic Training
-
Product-Based Training
- BD FACSDiscover™ S8 Cell Sorter Product Training
- Accuri C6 Plus Product-Based Training
- FACSAria Product Based Training
- FACSCanto Product-Based Training
- FACSLyric Product-Based Training
- FACSMelody Product-Based Training
- FACSymphony Product-Based Training
- HTS Product-Based Training
- LSRFortessa Product-Based Training
- Advanced Training
-
- BD FACSDiscover™ S8 Cell Sorter Product Training
- Accuri C6 Plus Product-Based Training
- FACSAria Product Based Training
- FACSCanto Product-Based Training
- FACSLyric Product-Based Training
- FACSMelody Product-Based Training
- FACSymphony Product-Based Training
- HTS Product-Based Training
- LSRFortessa Product-Based Training
- United States (English)
-
Change country/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?




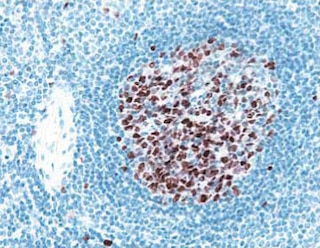
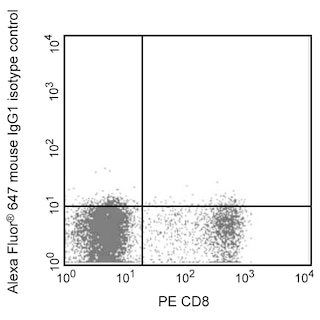
Analyses of MNDA Expression Panel 1. Human Peripheral Blood Leucocytes. Blood was treated with BD Pharm Lyse™ Lysing Buffer (Cat. No. 555899) to remove erythrocytes and then treated with BD Pharmingen™ Transcription Factor Phospho Buffer Set (Cat. No. 563239) to fix and permeabilize cells. Cells were stained with Alexa Fluor® 647 Mouse IgG1, κ Isotype Control (Cat. No. 557732; Left Plot) or Alexa Fluor® 647 Mouse Anti-Human MNDA (Cat. No. 566582; Right Plot) at 0.06 μg/test. Panel 2. Human U937 Cells. Human U937 (Histiocytic lymphoma, ATCC CRL-1593) cells were fixed and permeabilized with BD Pharmingen™ Transcription Factor Buffer Set (Cat. No. 562725) and stained with Alexa Fluor® 647 Mouse IgG1, κ Isotype Control (dashed line histogram) or Alexa Fluor® 647 Mouse Anti-Human MNDA (solid line histogram) at 0.5 μg/test. Flow cytometric figures showing the expression of MNDA (or Ig Isotype control staining) were derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of intact cells. Flow cytometric analyses were performed using a BD LSRFortessa™ X-20 Flow Cytometer System. Panel 3. Human Spleen. Following antigen retrieval with BD Retrievagen A Buffer (Cat. No. 550524), a section from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human spleen was stained with Alexa Fluor® 647 Mouse Anti-MNDA (Cat. No.566582) and BD Horizon™ BV421 Mouse Anti-Human CD45 (Cat. No. 563879) antibodies at 1.0 ug/test. Immunohistofluorescent staining of MNDA revealed nuclear staining (pseudocolored red) of some cells that also showed expression of plasma membrane CD45 (pseudocolored green). The image was generated using a standard epifluorescence microscope. Original magnification, 20x. Data shown on this Technical Data Sheet are not lot specific.


BD Pharmingen™ Alexa Fluor® 647 Mouse Anti-Human MNDA

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- The Alexa Fluor®, Pacific Blue™, and Cascade Blue® dye antibody conjugates in this product are sold under license from Molecular Probes, Inc. for research use only, excluding use in combination with microarrays, or as analyte specific reagents. The Alexa Fluor® dyes (except for Alexa Fluor® 430), Pacific Blue™ dye, and Cascade Blue® dye are covered by pending and issued patents.
- Alexa Fluor® is a registered trademark of Molecular Probes, Inc., Eugene, OR.
- Alexa Fluor® 647 fluorochrome emission is collected at the same instrument settings as for allophycocyanin (APC).
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products



The monoclonal antibody 253 specifically recognizes Myeloid cell nuclear differentiation antigen (MNDA) that is encoded by MNDA which belongs to the Pyrin and Hin domain gene family. MNDA functions as a transcriptional activator or repressor in cells of the myeloid lineage including cells from the promyelocyte stage onwards to granulocytes, monocytes and macrophages. Expression of this transcription factor is upregulated by monocytes in response to Interferon alpha (IFN-α) stimulation. MNDA may also be lowly expressed in a subset of B cells and by cells in some nodal marginal zone lymphomas (NMZL) and chronic lymphocytic leukemias (CLL).
Development References (5)
-
Briggs JA, Burrus GR, Stickney BD, Briggs RC. Cloning and expression of the human myeloid cell nuclear differentiation antigen: regulation by interferon alpha.. J Cell Biochem. 1992; 49(1):82-92. (Biology). View Reference
-
Briggs RC, Briggs JA, Ozer J, et al. The human myeloid cell nuclear differentiation antigen gene is one of at least two related interferon-inducible genes located on chromosome 1q that are expressed specifically in hematopoietic cells.. Blood. 1994; 83(8):2153-62. (Biology). View Reference
-
Johnson RC, Kim J, Natkunam Y, et al. Myeloid Cell Nuclear Differentiation Antigen (MNDA) Expression Distinguishes Extramedullary Presentations of Myeloid Leukemia From Blastic Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell Neoplasm.. Am J Surg Pathol. 2016; 40(4):502-9. (Biology). View Reference
-
Kanellis G, Roncador G, Arribas A, et al. Identification of MNDA as a new marker for nodal marginal zone lymphoma.. Leukemia. 2009; 23(10):1847-57. (Immunogen: ELISA, Immunofluorescence, Immunohistochemistry). View Reference
-
Metcalf RA, Monabati A, Vyas M, et al. Myeloid cell nuclear differentiation antigen is expressed in a subset of marginal zone lymphomas and is useful in the differential diagnosis with follicular lymphoma.. Hum Pathol. 2014; 45(8):1730-6. (Clone-specific: Immunocytochemistry). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.