-
Training
- Flow Cytometry Basic Training
-
Product-Based Training
- BD FACSDiscover™ S8 Cell Sorter Product Training
- Accuri C6 Plus Product-Based Training
- FACSAria Product Based Training
- FACSCanto Product-Based Training
- FACSLyric Product-Based Training
- FACSMelody Product-Based Training
- FACSymphony Product-Based Training
- HTS Product-Based Training
- LSRFortessa Product-Based Training
- Advanced Training
-
- BD FACSDiscover™ S8 Cell Sorter Product Training
- Accuri C6 Plus Product-Based Training
- FACSAria Product Based Training
- FACSCanto Product-Based Training
- FACSLyric Product-Based Training
- FACSMelody Product-Based Training
- FACSymphony Product-Based Training
- HTS Product-Based Training
- LSRFortessa Product-Based Training
- United States (English)
-
Change country/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?





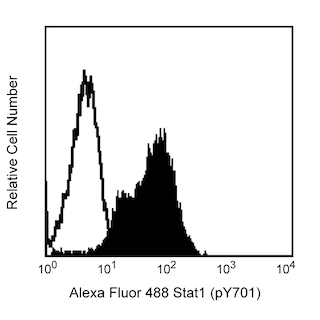
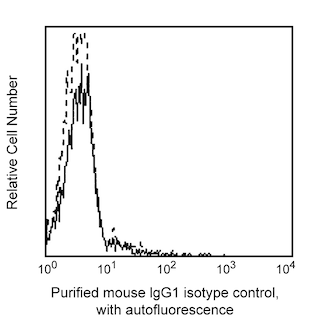
Flow cytometric analysis of C-Peptide expression in human INS-transfected cells and a mouse insulinoma cell line. LEFT PANEL: Untransfected (dashed-line histogram) and human INS-transfected (solid-line histogram) 293F cells were fixed with BD Cytofix™ Fixation Buffer (Cat. No. 554655) and permeabilized with BD Phosflow™ Perm Buffer III (Cat. No. 558050). The cells were then washed and stained with Purified Mouse Anti-C-Peptide (Cat. No. 565830) followed by APC Goat Anti-Mouse Ig (Cat. No. 550826). RIGHT PANEL: Beta-TC-6 cells (ATCC CRL-11505) were fixed with BD Cytofix™ Fixation Buffer (Cat. No. 554655) and permeabilized with BD Phosflow™ Perm Buffer III (Cat. No. 558050). The cells were washed and stained with either Purified Mouse IgG1, κ isotype control (Cat. No. 554121, dashed-line histogram) or Purified Mouse Anti-C-Peptide (Cat. No. 565830, solid-line histogram) followed by APC Goat Anti-Mouse Ig (Cat. No. 550826). All fluorescence histograms were derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of intact cells. Flow cytometry was performed on a BD FACSCanto™ II flow cytometry system.

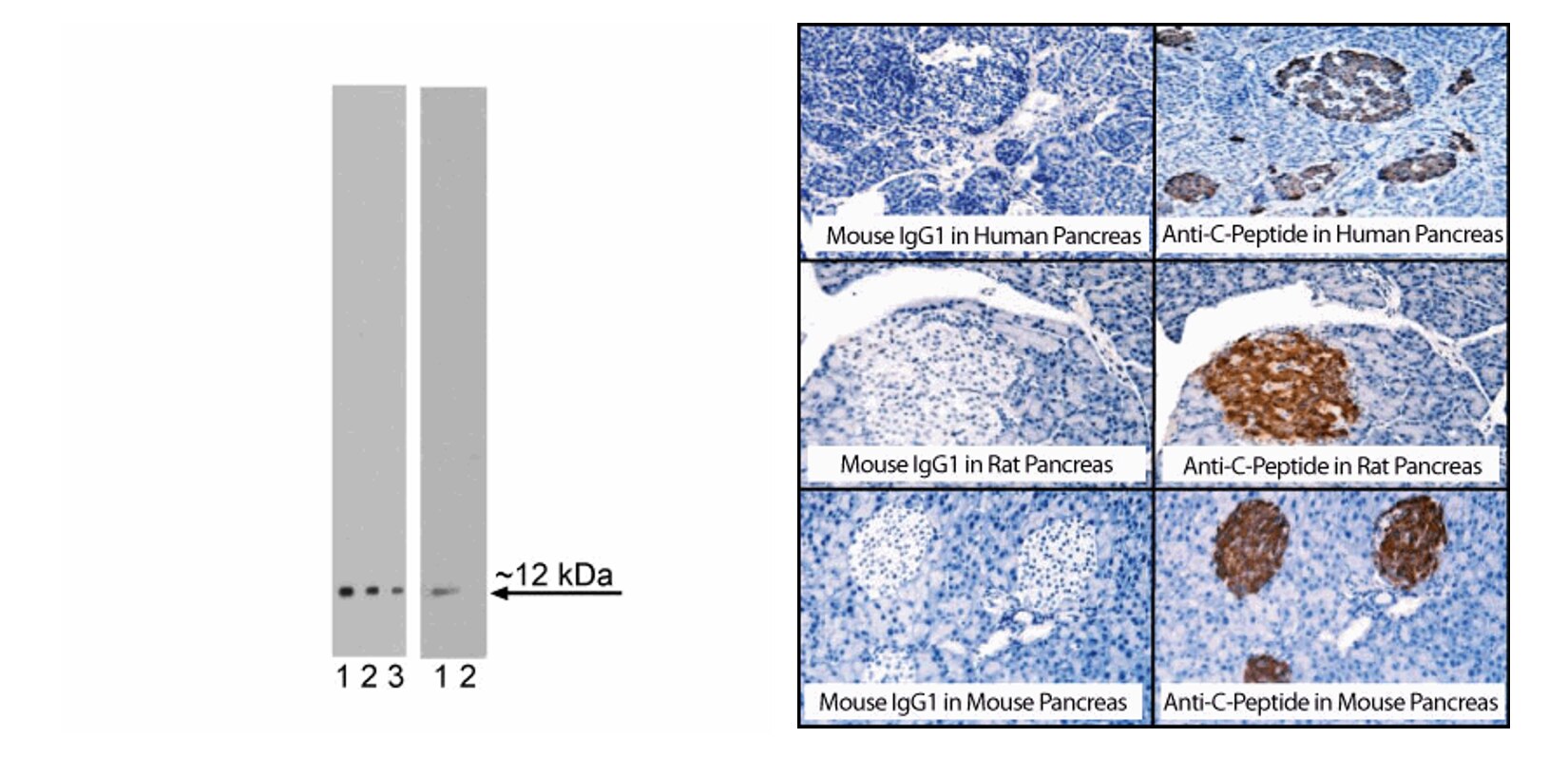
LEFT PANEL: Western blot and peptide blocking analysis of C-Peptide expression. Lysate from INS-transfected 293F cells was prepared for electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) in a 2D Tris-Glycine polyacrylamide gel. The proteins were transferred to PVDF membranes. The left membrane was probed with 8 (lane 1), 4 (lane 2), and 2 (lane 3) µg/mL of Purified Mouse Anti-C-Peptide (Cat. No. 565830). The right membrane was probed with 4 µg/mL Purified Mouse Anti-C-Peptide (lane 1) and with 4 µg/mL Purified Mouse Anti-C-Peptide that was mixed with 40 µg/mL C-Peptide for one hour (lane 2). Specific staining was detected with HRP Goat Anti-Mouse Ig (Cat No 554002). RIGHT PANEL: Immunohistochemical staining of C-Peptide in human, rat, and mouse islets of Langerhans. Following antigen retrieval with BD Retrievagen A Buffer (Cat. No. 550524), sections from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human (top row), rat (middle row), and mouse (bottom row) pancreata were blocked using an Avidin/ Biotin Blocking Kit (Vector Laboratories, Cat. No. SP-2001) as recommended by the manufacturer. The sections were then stained overnight with either Purified Mouse IgG1 κ Isotype Control (Cat. No. 550878, left column) or Purified Mouse Anti-C-Peptide (Cat. No. 565830, right column). A three-step staining procedure that employs either Biotin Goat Anti-Mouse Ig (Cat. No. 550337, top and middle rows) or Biotin Rat Anti-Mouse IgG1 (Cat. No.553441, bottom row), Streptavidin HRP (Cat. No. 550946) and DAB (Cat. No. 550880) was used to reveal the primary staining reagents. Counterstaining was with Hematoxylin. Original magnifications: 40X.


BD Pharmingen™ Purified Mouse Anti-C-Peptide

BD Pharmingen™ Purified Mouse Anti-C-Peptide

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Sodium azide is a reversible inhibitor of oxidative metabolism; therefore, antibody preparations containing this preservative agent must not be used in cell cultures nor injected into animals. Sodium azide may be removed by washing stained cells or plate-bound antibody or dialyzing soluble antibody in sodium azide-free buffer. Since endotoxin may also affect the results of functional studies, we recommend the NA/LE (No Azide/Low Endotoxin) antibody format, if available, for in vitro and in vivo use.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Species cross-reactivity detected in product development may not have been confirmed on every format and/or application.
Companion Products



The U8-424 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to human, mouse, and rat C-Peptide, the connecting peptide that links the A- and B-chains in the proinsulin molecule. The A- and B- chains and C-Peptide are encoded by the transcript of the INS gene and are produced by the β cells in the islets of Langerhans of the pancreas. As the biosynthesis of insulin proceeds, the C-Peptide is cleaved from proinsulin to form the mature insulin hormone, which is composed of the A- and B-chains linked by 2 disulfide bonds. Mature insulin and C-Peptide are stored in granules in the β cells and are released to the blood in response to metabolic signals such as glucose, the amino acids arginine and leucine, and acetylcholine. As a result, C-Peptide is released into the blood stream in an equimolar amount to insulin; the serum level of C-Peptide correlates with pancreatic β cell function and the amount of insulin being produced. The expression of C-Peptide can be used to monitor the pancreatic differentiation of pluripotent stem cells. Insulin is an evolutionarily conserved peptide hormone that binds to receptors on target cells (primarily adipose and muscle) to promote the absorption of glucose from the blood, thus regulating fat and carbohydrate metabolism. C-Peptide itself binds to many cell types, independently of the insulin receptor, and initiates several intracellular signaling cascades.
Development References (7)
-
D'Amour KA, Bang AG, Eliazer S, et al . Production of pancreatic hormone-expressing endocrine cells from human embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2006; 24(12):1481-1483. (Biology). View Reference
-
Kelly OG, Chan MY, Martinson LA, et al. Cell-surface markers for the isolation of pancreatic cell types derived from human embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2011; 29(8):750-756. (Biology). View Reference
-
Ko AS, Smyth DG, Marktussen J, Sundby F. The amino acid sequence of the C-peptide of human proinsulin.. Eur J Biochem. 1971; 20(2):190-9. (Biology). View Reference
-
Pagliuca FW, Millman JR, Gürtler M, et al. Generation of functional human pancreatic β cells in vitro. Cell. 2014; 159(2):428-439. (Biology). View Reference
-
Rezania A, Bruin JE, Riedel MJ et al. Maturation of human embryonic stem cell-derived pancreatic progenitors into functional islets capable of treating pre-existing diabetes in mice. Diabetes. 2012; 61(8):2016-2029. (Biology). View Reference
-
Suckale J, Solimena M. The insulin secretory granule as a signaling hub.. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2010; 21(10):599-609. (Biology). View Reference
-
Yosten GL, Kolar GR. The Physiology of Proinsulin C-Peptide: Unanswered Questions and a Proposed Model.. Physiology (Bethesda). 2015; 30(4):327-32. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.