-
Training
- Flow Cytometry Basic Training
-
Product-Based Training
- BD FACSDiscover™ S8 Cell Sorter Product Training
- Accuri C6 Plus Product-Based Training
- FACSAria Product Based Training
- FACSCanto Product-Based Training
- FACSLyric Product-Based Training
- FACSMelody Product-Based Training
- FACSymphony Product-Based Training
- HTS Product-Based Training
- LSRFortessa Product-Based Training
- Advanced Training
-
- BD FACSDiscover™ S8 Cell Sorter Product Training
- Accuri C6 Plus Product-Based Training
- FACSAria Product Based Training
- FACSCanto Product-Based Training
- FACSLyric Product-Based Training
- FACSMelody Product-Based Training
- FACSymphony Product-Based Training
- HTS Product-Based Training
- LSRFortessa Product-Based Training
- United States (English)
-
Change country/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?




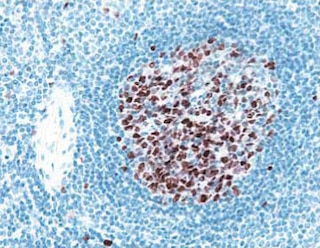
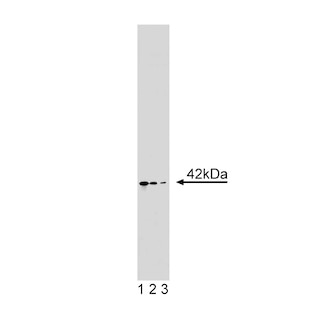
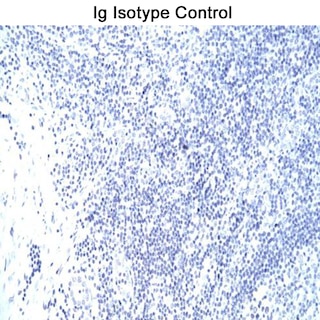
Analysis of T-bet Expression by Western Blot and Immunohistochemistry LEFT PANEL: Western blot analysis of T-bet expressed by human NK cell and T cell leukemia lines. Cell lysates from untreated NK-92 (Natural Killer cell line; lanes 1-4) and Jurkat (Cat. No. 611451; lanes 5-8) cells (15 µg total cellular protein/lane) were electrophoresed (SDS-PAGE), transferred to membranes and then probed with Purified Mouse anti-T-bet (Clone 4B10; Cat. No. 561262) antibody at concentrations of 0.5 (lanes 2, 6), 0.25 (lanes 3, 7), and 0.125 µg/ml (lanes 4, 8) with Purified Mouse Anti-Actin Ab-5 as a loading control antibody (Cat. No. 612657; 0.083 µg/ml; lanes 1, 5; ~42 kDa band). T-bet is identified as a band of ~62 kDa in the NK-92 cell lysate. MIDDLE LEFT PANEL: Western blot analysis of T-bet expressed by Mouse Th1 and Th2 cells and Human NK cell and T cell leukemia lines and Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMC). Lysates from mouse D10.G4.1 (Th2, lane 1) and 2D6 (Th1, lane 2) cells and from untreated human NK-92 (lane 3) and Jurkat (lane 4) cells and PBMC (lane 5) were electrophoresed (15 µg total cellular protein/lane), transferred to membranes and blotted with Purified Mouse anti-T-bet (Clone 4B10; Cat. No. 561262) antibody (2 µg/ml). T-bet is identified as a band of ~62 kDa in the mouse 2D6 (Th1), NK-92, and PBMC samples. MIDDLE RIGHT and RIGHT PANELS: T-bet staining of human tonsil. Following antigen retrieval with BD Retrievagen A buffer (Cat. no. 550524), the formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections were stained with either Purified Mouse anti-T-bet monoclonal antibody (Clone 4B10; Cat. No. 561262; Middle Right Panel) or Purified Mouse IgG1 κ Isotype Control (Cat. No. 550878; Right Panel), with Hematoxylin counterstaining. T-bet is detected in the nuclei of the T lymphocytes between the lymphoid follicles of the tonsil. Original magnification: 20×.


BD Pharmingen™ Purified Mouse anti-T-Bet

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Product Notices
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- This product may be covered by US Patent No. 7,365,169.
- Limited Use License: The buyer (a) shall not sell or otherwise transfer this product to any third party, (b) shall use this product only for its internal, non-clinical research use, (c) shall not use this product for Commercial Purposes without a commercial license from Harvard (and if the buyer is interested in a commercial license, it should contact Harvard’s Office of Technology Development at 1350 Massachusetts Avenue, Holyoke Center, Suite 727, Cambridge, MA 02138, 617-495-3067), (d) shall use this product in compliance with all applicable laws and regulations, including, without limitation, applicable human health and animal welfare laws and regulations, (e) may transfer information or materials made through the use of this product to a scientific collaborator only if such transfer is not for any Commercial Purpose and such collaborator agrees in writing not to transfer such materials to any third party and to use such transferred materials and/or information solely for internal, non-clinical research and not for Commercial Purposes, (f) acknowledges that this product has not been approved for use in humans by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration or any other regulatory body and may not be used in humans and (g) shall indemnify, defend and hold harmless Becton Dickinson and Company and Harvard from and against all damages, losses, expenses (including reasonable attorneys’ fees), claims, demands, suits and other actions in any way arising from the buyer’s use, storage or disposal of this product.
Companion Products


The 4B10 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to human and mouse T-bet. T-bet (T-box gene expressed in T cells) is a master regulatory transcription factor that is also known as TBX21 (T-box21) and TBLYM (T-box transcription factor, expressed in lymphocytes). Human (535 amino acids; 58.3 kDa predicted molecular mass) and mouse (530 amino acids; 57.7 kDa) T-bet proteins are encoded by the human TBX21 (chromosome 17) and mouse Tbx21 (chromosome 11) genes. The human and mouse T-bet protein amino acid sequences are 88% homologous. Human and mouse T-bet proteins share a highly conserved (98% homologous amino acid sequences) T-box protein domain that is centrally located and mediates binding to DNA. T-bet is expressed by and activates transcriptional activities within hematopoietic cells including stem cells, NK and NKT cells and subsets of thymocytes, primed/activated CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells and γδ T cells, B cells, and dendritic cells. Interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), interleukin-27 (IL-27), and IL-12 act on peripheral antigen-triggered (TCR-signaling) T cells to increase T-bet expression. With respect to T helper lymphocytes, T-bet directs the differentiation of naïve CD4+ precursor T cells to become Th1-like effector and memory cells. T-bet accomplishes this by activating Th1 genetic programs (including epigenetic modifications) while repressing opposing T helper subset programs. T-bet controls the upregulated expression of the Th1 signature cytokine, IFN-γ, the IL-12Rβ2 subunit and the Runx3 transcription factor and can repress the function of other transcriptional regulators, such as GATA-3 (master regulator of Th2 development) and the expression of other cytokines including IL-2, IL-4 and IL-5.
Development References (10)
-
Hibbert L, Pflanz S, De Waal Malefyt R, Kastelein RA. IL-27 and IFN-alpha signal via Stat1 and Stat3 and induce T-Bet and IL-12Rbeta2 in naive T cells. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2003; 23(9):513-522. (Biology). View Reference
-
Hwang ES, Hong JH, Glimcher LH. IL-2 production in developing Th1 cells is regulated by heterodimerization of RelA and T-bet and requires T-bet serine residue 508. J Exp Med. 2005; 202(9):1289-1300. (Clone-specific: Western blot). View Reference
-
Hwang ES, Szabo SJ, Schwartzberg PL, Glimcher LH. T helper cell fate specified by kinase-mediated interaction of T-bet with GATA-3. Science. 2005; 307(5780):430-433. (Clone-specific: Western blot). View Reference
-
Lugo-Villarino G, Maldonado-Lopez R, Possemato R, Penaranda C, Glimcher LH. T-bet is required for optimal production of IFN-gamma and antigen-specific T cell activation by dendritic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003; 100(13):7749-7754. (Biology). View Reference
-
Peng SL, Szabo SJ, Glimcher LH. T-bet regulates IgG class switching and pathogenic autoantibody production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002; 99(8):5545-5550. (Biology). View Reference
-
Peng SL. The T-box transcription factor T-bet in immunity and autoimmunity. Cell Mol Immunol. 2006; 3(2):87-95. (Biology). View Reference
-
Szabo SJ, Kim ST, Costa GL, Zhang X, Fathman CG, Glimcher LH. A novel transcription factor, T-bet, directs Th1 lineage commitment. Cell. 2000; 100(6):655-669. (Immunogen: Western blot). View Reference
-
Takeda A, Hamano S, Yamanaka A, et al. Cutting edge: role of IL-27/WSX-1 signaling for induction of T-bet through activation of STAT1 during initial Th1 commitment. J Immunol. 2003; 170(10):4886-4890. (Biology). View Reference
-
Townsend MJ, Weinmann AS, Matsuda JL, et al. T-bet regulates the terminal maturation and homeostasis of NK and Valpha14i NKT cells. Immunity. 2004; 20(4):477-494. (Biology). View Reference
-
Zhang WX, Yang SY. Cloning and characterization of a new member of the T-box gene family. Genomics. 2000; 70(1):41-48. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.