-
Training
- Flow Cytometry Basic Training
-
Product-Based Training
- BD FACSDiscover™ S8 Cell Sorter Product Training
- Accuri C6 Plus Product-Based Training
- FACSAria Product Based Training
- FACSCanto Product-Based Training
- FACSLyric Product-Based Training
- FACSMelody Product-Based Training
- FACSymphony Product-Based Training
- HTS Product-Based Training
- LSRFortessa Product-Based Training
- Advanced Training
-
- BD FACSDiscover™ S8 Cell Sorter Product Training
- Accuri C6 Plus Product-Based Training
- FACSAria Product Based Training
- FACSCanto Product-Based Training
- FACSLyric Product-Based Training
- FACSMelody Product-Based Training
- FACSymphony Product-Based Training
- HTS Product-Based Training
- LSRFortessa Product-Based Training
- United States (English)
-
Change country/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?




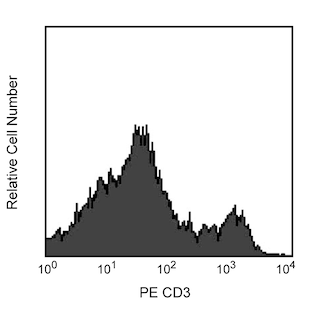
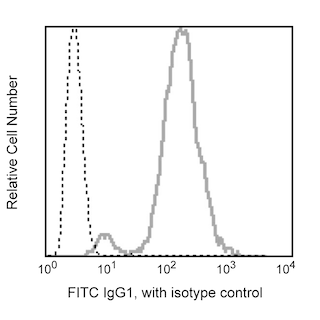
Flow cytometric analysis of αβ TCR expression in rat spleen and thymus. Lewis splenocytes were simultaneously stained with PE Mouse Anti-Rat CD3 (Cat. No. 554911, left panels) and Purified Mouse Anti-Rat αβ T-Cell Receptor (Cat. No. 554911; bottom left panel), followed by FITC Rat Anti-Mouse IgG1 (Cat. No. 553443, left panels). Lewis thymocytes were stained with Purified Mouse Anti-Rat αβ T-Cell Receptor (bottom right panel), followed by FITC Rat Anti-Mouse IgG1 (right panels). Fluorescent histograms and two-color contour plots were derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scattering characteristics of viable cells. Flow cytometry was performed on a BD FACScan™ flow cytometry system.


BD Pharmingen™ Purified Mouse Anti-Rat αβ T-Cell Receptor

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Sodium azide is a reversible inhibitor of oxidative metabolism; therefore, antibody preparations containing this preservative agent must not be used in cell cultures nor injected into animals. Sodium azide may be removed by washing stained cells or plate-bound antibody or dialyzing soluble antibody in sodium azide-free buffer. Since endotoxin may also affect the results of functional studies, we recommend the NA/LE (No Azide/Low Endotoxin) antibody format, if available, for in vitro and in vivo use.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products



.png?imwidth=320)
The R73 monoclonal antibody specifically recognizes the αβ T-cell Receptor (TCR) found on most peripheral T lymphocytes, intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes, and thymocytes. It does not react with γδ TCR-bearing cells. Cross-linked R73 mAb induces T-cell activation and differentiation. In vivo treatment with mAb R73 can suppress immune function of peripheral αβ TCR-expressing T cells, and reduce the severity of experimental autoimmune, transplant rejection, and graft-versus-host responses.
Development References (14)
-
Brenan M, Rees DJ. Sequence analysis of rat integrin alpha E1 and alpha E2 subunits: tissue expression reveals phenotypic similarities between intraepithelial lymphocytes and dendritic cells in lymph. Eur J Immunol. 1997; 27(11):3070-3079. (Clone-specific: Western blot). View Reference
-
Fangmann J, Schwinzer R, Wonigeit K. Unusual phenotype of intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes in the rat: predominance of T cell receptor alpha/beta+/CD2- cells and high expression of the RT6 alloantigen. Eur J Immunol. 1991; 21(3):753-760. (Biology). View Reference
-
Gaede K, Nazet M, Bosse D, Hunig, Heesemann J. Treatment of arthritis in Lewis rats by a monoclonal antibody against alpha beta T cell receptor: differential sensitivity of Yersinia-induced arthritis versus adjuvant arthritis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1995; 77(3):339-348. (Clone-specific: Depletion, Immunohistochemistry). View Reference
-
Hasegawa T, Tanaka T, Yoshikai Y. The appearance and role of gamma delta T cells in the peritoneal cavity and liver during primary infection with Listeria monocytogenes in rats. Int Immunol. 1992; 4(10):1129-1136. (Clone-specific: Depletion). View Reference
-
Heidecke CD, Hancock WW, Jakobs F, et al. alpha/beta-T cell receptor-directed therapy in rat cardiac allograft recipients. Treatment prior to alloantigen exposure prevents sensitization and abrogates accelerated rejection. Transplantation. 1995; 59(1):78-84. (Clone-specific: Depletion, Immunohistochemistry). View Reference
-
Heidecke CD, Hancock WW, Westerholt S, et al. alpha/beta-T cell receptor-directed therapy in rat allograft recipients. Long-term survival of cardiac allografts after pretreatment with R73 mAb is associated with upregulation of Th2-type cytokines. Transplantation. 1996; 61(6):948-956. (Clone-specific: Depletion, Immunohistochemistry). View Reference
-
Hunig T, Wallny HJ, Hartley JK, Lawetzky A, Tiefenthaler G. A monoclonal antibody to a constant determinant of the rat T cell antigen receptor that induces T cell activation. Differential reactivity with subsets of immature and mature T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1989; 169(1):73-86. (Immunogen: (Co)-stimulation, Immunohistochemistry, Immunoprecipitation). View Reference
-
Jung S, Kramer S, Schluesener HJ, Hunig T, Toyka K, Hartung HP. Prevention and therapy of experimental autoimmune neuritis by an antibody against T cell receptors-alpha/beta. J Immunol. 1992; 148(12):3768-3775. (Clone-specific: Depletion). View Reference
-
Kiely PD, Thiru S, Oliveira DB. Inflammatory polyarthritis induced by mercuric chloride in the Brown Norway rat. Lab Invest. 1995; 73(2):284-293. (Clone-specific: Depletion). View Reference
-
Mitnacht R, Tacke M, Hunig T. Expression of cell interaction molecules by immature rat thymocytes during passage through the CD4+8+ compartment: developmental regulation and induction by T cell receptor engagement of CD2, CD5, CD28, CD11a, CD44 and CD53. Eur J Immunol. 1995; 25(2):328-332. (Clone-specific: (Co)-stimulation). View Reference
-
Pieters RH, Punt P, Bol M, van Dijken JM, Seinen W, Penninks AH. The thymus atrophy inducing organotin compound DBTC stimulates TcR alpha beta-CD3 signalling in immature rat thymocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995; 214(2):552-558. (Clone-specific: (Co)-stimulation, Depletion, Immunohistochemistry). View Reference
-
Wang M, Qu X, Stepkowski SM, Chou TC, Kahan BD. Beneficial effect of graft perfusion with anti-T cell receptor monoclonal antibodies on survival of small bowel allografts in rat recipients treated with brequinar alone or in combination with cyclosporine and sirolimus. Transplantation. 1996; 61(3):458-464. (Clone-specific: Depletion). View Reference
-
Yoshino S, Cleland LG, Mayrhofer G, Brown RR, Schwab JH. Prevention of chronic erosive streptococcal cell wall-induced arthritis in rats by treatment with a monoclonal antibody against the T cell antigen receptor alpha beta. J Immunol. 1991; 146(12):4187-4189. (Clone-specific: Depletion). View Reference
-
Yoshino S, Cleland LG. Depletion of alpha/beta T cells by a monoclonal antibody against the alpha/beta T cell receptor suppresses established adjuvant arthritis, but not established collagen-induced arthritis in rats. J Exp Med. 1992; 175(4):907-915. (Clone-specific: Depletion, Immunohistochemistry). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.