-
Training
- Flow Cytometry Basic Training
-
Product-Based Training
- BD FACSDiscover™ S8 Cell Sorter Product Training
- Accuri C6 Plus Product-Based Training
- FACSAria Product Based Training
- FACSCanto Product-Based Training
- FACSLyric Product-Based Training
- FACSMelody Product-Based Training
- FACSymphony Product-Based Training
- HTS Product-Based Training
- LSRFortessa Product-Based Training
- Advanced Training
-
- BD FACSDiscover™ S8 Cell Sorter Product Training
- Accuri C6 Plus Product-Based Training
- FACSAria Product Based Training
- FACSCanto Product-Based Training
- FACSLyric Product-Based Training
- FACSMelody Product-Based Training
- FACSymphony Product-Based Training
- HTS Product-Based Training
- LSRFortessa Product-Based Training
- United States (English)
-
Change country/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?




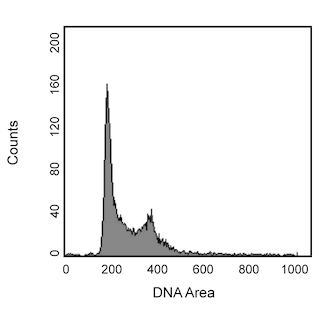
Flow cytometric analysis of Histone H3 (pS28) on C20 cells. C20 cells, a mouse T-helper lymphocytic cell line with cytotoxic activity, were treated with 1 µg/mL Colcemid (Sigma-Aldrich Cat. No. D7385; also known as Demecolcine or N-Deacetyl-N-methylcolchicine) for 4 hours at 37 °C to increase the population of mitotic cells. Cells were then fixed and permeabilized with 70% cold ethanol prior to staining with the Rat Anti-Histone H3 (pS28) antibody in conjunction with RNase/propidium iodide. Dot plots were derived from gated events based on light scattering characteristics for C20 cells. Flow cytometry was performed on a BD™ LSR II flow cytometry system.


BD Horizon™ V450 Rat Anti-Histone H3 (pS28)

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
Flow cytometry: Colcemid (Demecolcine) influences cells by depolymerizing microtubules and arresting the cell cycle (i.e spindles cannot form) at the metaphase checkpoint during mitosis, also known as the M-phase. Investigators may want to consider using Colcemid for purposes of increasing the frequency of cells found in the M-phase as identifying these cells while they cycle normally can be difficult due to low population frequencies. As Histone H3 is phosphorylated during the M-phase, the BD Horizon™ V450 Rat Anti-Histone H3 (pS28) antibody may be useful for helping identify these cells that are in the M-phase.
1. Wash cell suspension twice with 1X PBS.
2. Fix the cells by adding ice-cold 70% ethanol drop-wise while vortexing the cell suspension, then storing them for at least 4 hours at -20°C in the 70% ethanol.
3. Aliquot ~1 million fixed cells per tube for staining. Wash them twice with 1X PBS, then once with stain buffer.
4. Stain the cells with 5 μl BD Horizon™ V450 Rat Anti-Histone H3 (pS28) in 95 μl stain buffer for 20 minutes at room temperature, then wash them with stain buffer.
5. For optimum cell cycle analysis, the cells should be treated with RNase before staining with propidium iodide. Investigators may wish to stain the cells with 0.5 ml PI/RNase Staining Buffer (Cat. No. 550825) for 15 minutes at room temperature or alternatively, treat the stained cells with 50 μg RNase A (Sigma-Aldrich Cat. No. R5500) in 50 μl 1X PBS for 30 minutes at 37°C and without washing, stain DNA by adding 5 μg Propidium Iodide (Sigma-Aldrich Cat. No. P4170) in 450 μl staining buffer for at least 10 minutes at room temperature.
6. The cells are now ready for flow cytometric analysis.
BD™ CompBeads can be used as surrogates to assess fluorescence spillover (Compensation). When fluorochrome conjugated antibodies are bound to CompBeads, they have spectral properties very similar to cells. However, for some fluorochromes there can be small differences in spectral emissions compared to cells, resulting in spillover values that differ when compared to biological controls. It is strongly recommended that when using a reagent for the first time, users compare the spillover on cells and CompBead to ensure that BD Comp beads are appropriate for your specific cellular application.
Product Notices
- This reagent has been pre-diluted for use at the recommended Volume per Test. We typically use 1 × 10^6 cells in a 100-µl experimental sample (a test).
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
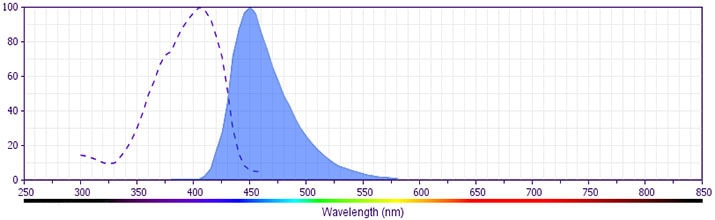
- BD Horizon V450 has a maximum absorption of 406 nm and maximum emission of 450 nm. Before staining with this reagent, please confirm that your flow cytometer is capable of exciting the fluorochrome and discriminating the resulting fluorescence.
- Pacific Blue™ is a trademark of Molecular Probes, Inc., Eugene, OR.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to http://regdocs.bd.com to access safety data sheets (SDS).
- Species cross-reactivity detected in product development may not have been confirmed on every format and/or application.
- This product is provided under an intellectual property license between Life Technologies Corporation and BD Businesses. The purchase of this product conveys to the buyer the non-transferable right to use the purchased amount of the product and components of the product in research conducted by the buyer (whether the buyer is an academic or for-profit entity). The buyer cannot sell or otherwise transfer (a) this product (b) its components or (c) materials made using this product or its components to a third party or otherwise use this product or its components or materials made using this product or its components for Commercial Purposes. Commercial Purposes means any activity by a party for consideration and may include, but is not limited to: (1) use of the product or its components in manufacturing; (2) use of the product or its components to provide a service, information, or data; (3) use of the product or its components for therapeutic, diagnostic or prophylactic purposes; or (4) resale of the product or its components, whether or not such product or its components are resold for use in research. For information on purchasing a license to this product for any other use, contact Life Technologies Corporation, Cell Analysis Business Unit Business Development, 29851 Willow Creek Road, Eugene, OR 97402, USA, Tel: (541) 465-8300. Fax: (541) 335-0504.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products

Histones are highly basic proteins that complex with DNA to form chromatin. Histone H3 is a ~15-kDa protein that is phosphorylated at serine 28 (S28), S10, and/or threonine 11 during mammalian cell mitosis and meiosis. The phosphorylation sites are located in the N-terminal tail, a region that is outside of the chromatin fiber and is thus accessible for interactions with agents that may regulate chromatin or specific gene activities. The phosphorylation states of the two serine sites during the cell cycle are highly regulated by Aurora B kinase and a PP1 phosphatase: S10 is in the phosphorylated state from late G2 phase to anaphase, while S28 is phosphorylated from prophase to anaphase. Furthermore, phosphorylation of histone H3 S28 may be mediated by other kinases in response to external stimuli. Evidence suggests that histone phosphorylation is involved in the regulation of chromosome condensation, cell division, and gene transcription.
The HTA28 monoclonal antibody reacts with histone H3 phosphorylated at S28 in its N-terminal tail. It does not recognize the unphosphorylated protein.
The antibody is conjugated to BD Horizon V450, which has been developed for use in multicolor flow cytometry experiments and is available exclusively from BD Biosciences. It is excited by the Violet laser Ex max of 406 nm and has an Em Max at 450 nm. Conjugates with BD Horizon V450 can be used in place of Pacific Blue™ conjugates.
Development References (9)
-
Carmena M, Earnshaw WC. The cellular geography of aurora kinases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003; 4:842-854. (Biology).
-
Cheung P, Allis CD, Sassone-Corsi P. Signaling to chromatin through histone modifications. Cell. 2000; 103:263-271. (Biology).
-
Choi HS, Choi BY, Cho Y-Y, Zhu F, Bode AM, Dong Z. Phosphorylation of Ser28 in histone H3 mediated by mixed lineage kinase-like mitogen-activated protein triple kinase α. J Biol Chem. 2005; 280(14):13545-13553. (Biology).
-
Dyson MH, Thomson S, Inagaki M, et al. MAP kinase-mediated phosphorylation of distinct pools of histone H3 at S10 or S28 via mitogen- and stress-activated kinase 1/2. J Cell Sci. 2005; 118(10):2247-2259. (Biology).
-
Furukawa K, Sugiyama S, Osouda S, et al. Barrier-to-autointegration factor plays crucial roles in cell cycle progression and nuclear organization in Drosophila. J Cell Sci. 2003; 116(18):3811-3823. (Biology).
-
Goto H, Tomono Y, Ajiro K, et al. Identification of a novel phosphorylation site on histone H3 coupled with mitotic chromosome condensation. J Biol Chem. 1999; 274(36):25543-25549. (Immunogen).
-
Hirata A, Inada K, Tsukamoto T, et al. Characterization of a monoclonal antibody, HTA28, recognizing a histone H3 phosphorylation site as a useful marker of M-phase cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 2004; 52(11):1503-1509. (Biology).
-
Nowak SJ, Corces VG. Phosphorylation of histone H3: a balancing act between chromosome condensation and transcriptional activation. Trends Genet. 2004; 20(4):214-220. (Biology).
-
Pascreau G, Arlot-Bonnemains Y, Prigent C. Phosphorylation of histone and histone-like proteins by aurora kinases during mitosis. Prog Cell Cycle Res. 2003; 5:369-374. (Biology).
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.