-
Training
- Flow Cytometry Basic Training
-
Product-Based Training
- BD FACSDiscover™ S8 Cell Sorter Product Training
- Accuri C6 Plus Product-Based Training
- FACSAria Product Based Training
- FACSCanto Product-Based Training
- FACSLyric Product-Based Training
- FACSMelody Product-Based Training
- FACSymphony Product-Based Training
- HTS Product-Based Training
- LSRFortessa Product-Based Training
- Advanced Training
-
- BD FACSDiscover™ S8 Cell Sorter Product Training
- Accuri C6 Plus Product-Based Training
- FACSAria Product Based Training
- FACSCanto Product-Based Training
- FACSLyric Product-Based Training
- FACSMelody Product-Based Training
- FACSymphony Product-Based Training
- HTS Product-Based Training
- LSRFortessa Product-Based Training
- United States (English)
-
Change country/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?


.png)

Analysis of PKCθ in lymphocytes. Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were either stimulated with 10 µM PMA (Sigma, Cat. No. P8139) for 24 hours at 37ºC (shaded histogram) or unstimulated (open histogram). The cells were fixed (BD Cytofix™ buffer, Cat. No. 554655) for 10 minutes, then permeabilized with BD Phosflow™ Perm Buffer III (Cat. No. 558050) on ice for at least 30 minutes, and then stained with APC Mouse anti-Human PKCθ (Cat. No. 560344). Lymphocytes were selected by scatter profile. The data demonstrates that the expression of PKCθ decreases when the lymphocytes are stimulated by PMA. Flow cytometry was performed on a BD FACSCalibur™ flow cytometry system. The specificity of mAb 27/PKCθ was confirmed by western blot analysis using unconjugated antibody at 4.0 μg/ml on lysates from control (lane 1) and PMA-treated (lane 2) PBMC. PKCθ is identified as a band of 79 kDa, which decreases in intensity in the treated cells.
.png)

BD™ Phosflow APC Mouse anti-Human PKCθ
.png)
Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
Any of the three BD Phosflow™ permeabilization buffers may be used.
Product Notices
- This reagent has been pre-diluted for use at the recommended Volume per Test. We typically use 1 × 10^6 cells in a 100-µl experimental sample (a test).
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
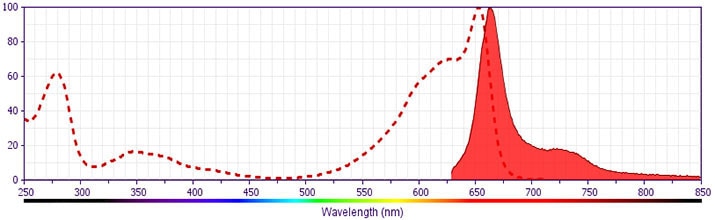
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- This APC-conjugated reagent can be used in any flow cytometer equipped with a dye, HeNe, or red diode laser.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products




The Protein Kinase C (PKC) family of homologous serine/threonine protein kinases is involved in a number of processes, such as growth, differentiation, and cytokine secretion. At least eleven isozymes have been described. These proteins are products of multiple genes and alternative splicing. Conventional PKC (cPKC) subfamily members (α, β, and γ isoforms) consists of a single polypeptide chain containing four conserved regions (C) and five variable regions (V). The N-terminal half containing C1, C2, V1, and V2 constitutes the regulatory domain and interacts with the PKC activators Ca2+, phospholipid, diacylglycerol, or phorbol ester. However, the the C2-like domains of novel PKC (nPKC) subfamily members (δ, ε, η, and θ isoforms) are Ca2+-independent. The atypical PKC (aPKC) subfamily members (ζ, ι, and λ isoforms) lack the C2 domain and are unique in that their activity is independent of diacylglycerols and phorbol esters. They also lack one repeat of the cysteine-rich sequences that are conserved in cPKC and nPKC members. The C-terminal region of PKC contains the catalytic domain. The PKC pathway represents a major signal transduction system that is activated following ligand-stimulation of transmembrane receptors by hormones, neurotransmitters, and growth factors. PKCθ transcripts are expressed in most tissues with the highest levels being found in hematopoietic tissues and cell lines, including T cells and thymocytes. PKCθ mRNA is readily detectable in skeletal muscle, lung and brain. However, PKCθ expression is not detected in several human carcinoma cell lines. Abundant expression of this PKC isozyme in hematopoietic cells suggest that it may have a role in growth and differentiation processes of these cells.
The 27/PKCθ monoclonal antibody recognizes the C2-like domain of human PKCθ, regardless of phosphorylation status.
Development References (3)
-
Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988; 334(6184):661-665. (Biology). View Reference
-
Parker PJ, Murray-Rust J. PKC at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2004; 117:131-132. (Biology). View Reference
-
Soderling TR. Protein kinases. Regulation by autoinhibitory domains. J Biol Chem. 1990; 265(4):1823-1826. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.