-
Training
- Flow Cytometry Basic Training
-
Product-Based Training
- BD FACSDiscover™ S8 Cell Sorter Product Training
- Accuri C6 Plus Product-Based Training
- FACSAria Product Based Training
- FACSCanto Product-Based Training
- FACSLyric Product-Based Training
- FACSMelody Product-Based Training
- FACSymphony Product-Based Training
- HTS Product-Based Training
- LSRFortessa Product-Based Training
- Advanced Training
-
- BD FACSDiscover™ S8 Cell Sorter Product Training
- Accuri C6 Plus Product-Based Training
- FACSAria Product Based Training
- FACSCanto Product-Based Training
- FACSLyric Product-Based Training
- FACSMelody Product-Based Training
- FACSymphony Product-Based Training
- HTS Product-Based Training
- LSRFortessa Product-Based Training
- United States (English)
-
Change country/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?




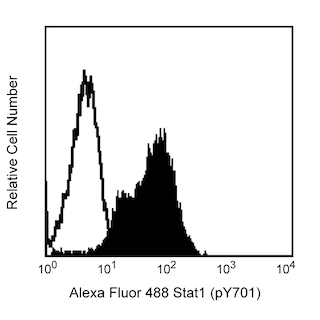
Analysis of ERK2 in human epithelioid carcinoma. HeLa S3 cells (ATCC CCL 2.2) were either transfected with ERK2 RNAi (open histogram) or untransfected (shaded histogram). The cells were fixed (BD Cytofix™ buffer, Cat. No. 554655) for 10 minutes at 37°C, then permeabilized (BD Phosflow™ Perm Buffer III, Cat. No. 558050) on ice for 30 minutes, and then stained with Alexa Fluor® 647 Mouse anti-ERK2 (Cat. No. 558526). Down-regulation of ERK2 expression is evident in the RNAi-transfected cells. Flow cytometry was performed on a BD FACSArray™ bioanalyzer system.


BD™ Phosflow Alexa Fluor® 647 Mouse anti-ERK2

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Product Notices
- This reagent has been pre-diluted for use at the recommended Volume per Test. We typically use 1 × 10^6 cells in a 100-µl experimental sample (a test).
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Alexa Fluor® 647 fluorochrome emission is collected at the same instrument settings as for allophycocyanin (APC).
- Alexa Fluor® is a registered trademark of Molecular Probes, Inc., Eugene, OR.
- The Alexa Fluor®, Pacific Blue™, and Cascade Blue® dye antibody conjugates in this product are sold under license from Molecular Probes, Inc. for research use only, excluding use in combination with microarrays, or as analyte specific reagents. The Alexa Fluor® dyes (except for Alexa Fluor® 430), Pacific Blue™ dye, and Cascade Blue® dye are covered by pending and issued patents.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products



The members of the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) family are components of a key signal transduction cascade that links events at the cell surface to responses in the nucleus. The signaling cascade is found in species as varied as yeast and humans, with many of the proteins being well conserved. In mammals the most widely studied members of the cascade are the Extracellular signal-Regulated Kinases, ERK1 (p44 MAPK) and ERK2 (p42 MAPK). ERK1 and ERK2 share 85% homology and are activated by extracellular signals such as growth factors, hormones, and phorbol esters. Activation occurs through a series of phosphorylations by kinases activating other kinases and eventually leading to phosphorylation of the ERKs. Growth factor stimulation leads to activation of Ras and Raf, leading to phosphorylation of MEK1 (MAPK/ERK kinase) which, in turn, activates the ERKs via dual phosphorylation. Once activated, the ERKs phosphorylate other cytoplasmic signaling molecules (protein kinases and phosphatases), cell-surface receptors, microtubule-associated proteins, and transcription factors in the nucleus. Thus, the active ERK has myriad downstream effectors that implicate it in the control of cell proliferation and differentiation, as well as regulation of the cytoskeleton. Furthermore, studies have shown that elevated ERK activity is associated with some cancers. The G263-7 recognizes ERK2. It does not cross-react with ERK1. Clone G263-7 was originally characterized in human (A431) and mouse (NIH/3T3) cells. A human ERK2 synthetic peptide was used as immunogen.
Development References (9)
-
Cobb MH, Boulton TG, Robbins DJ. Extracellular signal-regulated kinases: ERKs in progress. Cell Regul. 1991; 2:965-978. (Biology). View Reference
-
Davis RJ. The mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathway. J Biol Chem. 1993; 268(20):14553-14556. (Biology). View Reference
-
Fang JY, Richardson BC. The MAPK signalling pathways and colorectal cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2005; 6(5):322-327. (Biology). View Reference
-
Kim SC, Hahn JS, Min YH, Yoo NC, Ko YW, Lee WJ. Constitutive activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase in human acute leukemias: combined role of activation of MEK, hyperexpression of extracellular signal-regulated kinase, and downregulation of a phosphatase, PAC1. Blood. 1999; 93(11):3893-3899. (Biology). View Reference
-
Reiser V, Ammerer G, Ruis H. Nucleocytoplasmic traffic of MAP kinases. Gene Expr. 1999; 7(4-6):247-254. (Biology). View Reference
-
Sivaraman VS, Wang H, Nuovo GJ, Malbon CC. Hyperexpression of mitogen-activated protein kinase in human breast cancer. J Clin Invest. 1997; 99(7):1478-1483. (Biology). View Reference
-
Stupack DG, Cho SY, Klemke RL. Molecular signaling mechanisms of cell migration and invasion. Immunol Res. 2000; 21(2-3):83-88. (Biology). View Reference
-
Sweatt JD. The neuronal MAP kinase cascade: a biochemical signal integration system subserving synaptic plasticity and memory. J Neurochem. 2001; 76:1-10. (Biology).
-
Treisman R. Regulation of transcription by MAP kinase cascades. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1996; 8:205-215. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.