-
抗体試薬
- フローサイトメトリー用試薬
-
ウェスタンブロッティング抗体試薬
- イムノアッセイ試薬
-
シングルセル試薬
- BD® AbSeq Assay | シングルセル試薬
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits | シングルセル試薬
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit | シングルセル試薬
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits | シングルセル試薬
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit | シングルセル試薬
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Profiling Assays (VDJ Assays) | シングルセル試薬
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
-
細胞機能評価のための試薬
-
顕微鏡・イメージング用試薬
-
細胞調製・分離試薬
-
- BD® AbSeq Assay | シングルセル試薬
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits | シングルセル試薬
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit | シングルセル試薬
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits | シングルセル試薬
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit | シングルセル試薬
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Profiling Assays (VDJ Assays) | シングルセル試薬
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- Japan (Japanese)
-
Change country/language
Old Browser
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?




Multicolor flow cytometric analysis of CD28 expression on C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes. Splenic leucocytes were pre-incubated with Purified Rat Anti-Mouse CD16/CD32 antibody (Mouse BD Fc Block™) (Cat. No. 553141/553142). The cells were then stained simultaneously with FITC Rat Anti-Mouse CD4 (Cat. No. 553046/553047/561835) and FITC Rat Anti-Mouse CD8 (Cat. No. 553030/553031/561966) antibodies and with either BD Horizon™ BV421 Armenian Hamster IgG2, κ Isotype Control (Cat. No. 562629; Left Panel) or BD Horizon™ BV421 Hamster Anti-Mouse CD28 antibody (Cat. No. 562764; Right Panel). Two-color flow cytometric dot plots show the correlated expression patterns of CD28 (or Ig Isotype Control staining) versus CD4 and CD8 for gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of viable leucocytes. Flow cytometry was performed using a BD™ LSR II Flow Cytometer System.


BD Pharmingen™ BV421 Hamster Anti-Mouse CD28

Regulatory Statusの凡例
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation and Storage
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Although hamster immunoglobulin isotypes have not been well defined, BD Biosciences Pharmingen has grouped Armenian and Syrian hamster IgG monoclonal antibodies according to their reactivity with a panel of mouse anti-hamster IgG mAbs. A table of the hamster IgG groups, Reactivity of Mouse Anti-Hamster Ig mAbs, may be viewed at http://www.bdbiosciences.com/documents/hamster_chart_11x17.pdf.
- Brilliant Violet™ 421 is a trademark of Sirigen.
- Pacific Blue™ is a trademark of Molecular Probes, Inc., Eugene, OR.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
関連製品





.png?imwidth=320)
The 37.51 antibody reacts with CD28, which is expressed on most thymocytes, at low density on nearly all CD4+ and CD8+ peripheral T cells, and at even lower density on NK cells. The expression of CD28, in splenocytes and thymocytes, has been reported to increase after activation. CD28 transcripts are found in mast cells, and cell-surface expression of CD28 is induced upon maturation or activation of mast cells. It has been reported that CD28 is not expressed on some populations of intraepithelial T lymphocytes. CD28 is a costimulatory receptor; its ligands include CD80 (B7-1) and CD86 (B7-2). The 37.51 mAb augments proliferation and cytokine production by activated T and NK cells and can provide a costimulatory signal for CTL induction. There is considerable evidence that CD28 is a costimulatory receptor involved in many, but not all, T cell-dependent immune responses.
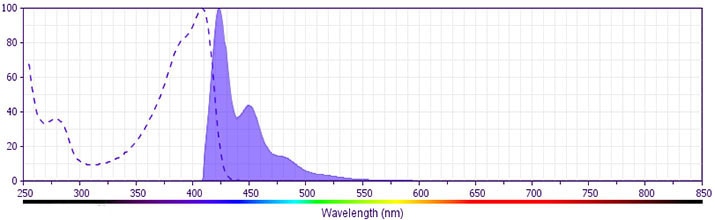
The antibody was conjugated to BD Horizon™ BV421 which is part of the BD Horizon™ Brilliant Violet™ family of dyes. With an Ex Max of 407-nm and Em Max at 421-nm, BD Horizon™ BV421 can be excited by the violet laser and detected in the standard Pacific Blue™ filter set (eg, 450/50-nm filter). BD Horizon™ BV421 conjugates are very bright, often exhibiting a 10 fold improvement in brightness compared to Pacific Blue™ conjugates.
Development References (16)
-
Bluestone JA. New perspectives of CD28-B7-mediated T cell costimulation. Immunity. 1995; 2(6):555-559. (Biology: Apoptosis). View Reference
-
Cibotti R, Punt JA, Dash KS, Sharrow SO, Singer A. Surface molecules that drive T cell development in vitro in the absence of thymic epithelium and in the absence of lineage-specific signals. Immunity. 1997; 6(3):245-255. (Clone-specific: (Co)-stimulation, Stimulation). View Reference
-
Gelfanov V, Lai YG, Gelfanova V, Dong JY, Su JP, Liao NS. Differential requirement of CD28 costimulation for activation of murine CD8+ intestinal intraepithelial lymphocyte subsets and lymph node cells. J Immunol. 1995; 155(1):76-82. (Clone-specific: (Co)-stimulation, Flow cytometry, Stimulation). View Reference
-
Gross JA, Callas E, Allison JP. Identification and distribution of the costimulatory receptor CD28 in the mouse. J Immunol. 1992; 149(2):380-388. (Immunogen: (Co)-stimulation, Flow cytometry, Immunoprecipitation, Stimulation). View Reference
-
Harding FA, Allison JP. CD28-B7 interactions allow the induction of CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes in the absence of exogenous help. J Exp Med. 1993; 177(6):1791-1796. (Clone-specific: (Co)-stimulation, Inhibition, Stimulation). View Reference
-
Harding FA, McArthur JG, Gross JA, Raulet DH, Allison JP. CD28-mediated signalling co-stimulates murine T cells and prevents induction of anergy in T-cell clones. Nature. 1992; 356(6370):607-609. (Clone-specific: (Co)-stimulation, Stimulation). View Reference
-
June CH, Bluestone JA, Nadler LM, Thompson CB. The B7 and CD28 receptor families. Immunol Today. 1994; 15(7):321-331. (Biology). View Reference
-
Krummel MF, Allison JP. CD28 and CTLA-4 have opposing effects on the response of T cells to stimulation. J Exp Med. 1995; 182(2):459-465. (Clone-specific: (Co)-stimulation, Stimulation). View Reference
-
Lepesant H, Pierres M, Naquet P. Deficient antigen presentation by thymic epithelial cells reveals differential induction of T cell clone effector functions by CD28-mediated costimulation. Cell Immunol. 1995; 161(2):279-287. (Clone-specific: (Co)-stimulation, Stimulation). View Reference
-
Marietta EV, Weis JJ, Weis JH. CD28 expression by mouse mast cells is modulated by lipopolysaccharide and outer surface protein A lipoprotein from Borrelia burgdorferi. J Immunol. 1997; 159(6):2840-2848. (Clone-specific: (Co)-stimulation, Flow cytometry, Stimulation). View Reference
-
Nandi D, Gross JA, Allison JP. CD28-mediated costimulation is necessary for optimal proliferation of murine NK cells. J Immunol. 1994; 152(7):3361-3369. (Clone-specific: (Co)-stimulation, Flow cytometry, Stimulation). View Reference
-
Nishio M, Spielman J, Lee RK, Nelson DL, Podack ER. CD80 (B7.1) and CD54 (intracellular adhesion molecule-1) induce target cell susceptibility to promiscuous cytotoxic T cell lysis. J Immunol. 1996; 157(10):4347-4353. (Biology). View Reference
-
Ong CJ, Lim AS, Teh HS. CD28-induced cytokine production and proliferation by thymocytes are differentially regulated by the p59fyn tyrosine kinase. J Immunol. 1997; 159(5):2169-2176. (Clone-specific: (Co)-stimulation, Stimulation). View Reference
-
Rakasz E, Hagen M, Sandor M, Lynch RG. Gamma delta T cells of the murine vagina: T cell response in vivo in the absence of the expression of CD2 and CD28 molecules. Int Immunol. 1997; 9(1):161-167. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Shahinian A, Pfeffer K, Lee KP, et al. Differential T cell costimulatory requirements in CD28-deficient mice. Science. 1993; 261(5121):609-612. (Biology). View Reference
-
Wells AD, Gudmundsdottir H, Turka LA. Following the fate of individual T cells throughout activation and clonal expansion. Signals from T cell receptor and CD28 differentially regulate the induction and duration of a proliferative response. J Clin Invest. 1997; 100(12):3173-3183. (Clone-specific: (Co)-stimulation, Stimulation). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.