-
抗体試薬
- フローサイトメトリー用試薬
-
ウェスタンブロッティング抗体試薬
- イムノアッセイ試薬
-
シングルセル試薬
- BD® AbSeq Assay | シングルセル試薬
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits | シングルセル試薬
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit | シングルセル試薬
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits | シングルセル試薬
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit | シングルセル試薬
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Profiling Assays (VDJ Assays) | シングルセル試薬
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
-
細胞機能評価のための試薬
-
顕微鏡・イメージング用試薬
-
細胞調製・分離試薬
-
- BD® AbSeq Assay | シングルセル試薬
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits | シングルセル試薬
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit | シングルセル試薬
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits | シングルセル試薬
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit | シングルセル試薬
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Profiling Assays (VDJ Assays) | シングルセル試薬
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- Japan (Japanese)
-
Change country/language
Old Browser
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?


PE-Cy™7 Mouse Anti-Human CD16
Regulatory Statusの凡例
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation and Storage
The monoclonal antibody is supplied as 100 μg purified immunoglobulin in 2.0 mL (50 μg/mL) of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). The FITC conjugate is supplied as 250 μg in 2.0 mL (125 μg/mL) of PBS. The PE conjugate is supplied as 50 μg in 2.0 mL (25 μg/mL) of PBS. The PE-Cy7 conjugate is supplied as 50 μg in 0.5 mL (100 μg/mL) of PBS. PBS contains gelatin and 0.1% sodium azide.
Store vials at 2° to 8°C. Conjugated forms should not be frozen and should be protected from prolonged exposure to light. Each reagent is stable for the period shown on the bottle label when stored as directed.
CD16 (Leu-11a), clone NKP15, is derived from hybridization of mouse P3-X63-Ag8 myeloma cells with spleen cells from BALB/c mice immunized with large granular lymphocytes. CD16 (Leu-11b), clone GO22, is derived from hybridization of mouse P3-X63 myeloma cells with spleen cells from BALB/c mice immunized with granulocytes. CD16 (Leu-11c), clone B73.1, is derived from hybridization of mouse P3-X63-Ag8.653 myeloma cells with spleen cells from BALB/c mice immunized with NK lymphocytes. CD16 antibodies recognize an Mr 50- to 65-kilodalton (kd) antigen present on human natural killer (NK) lymphocytes that is the IgG Fc receptor III.
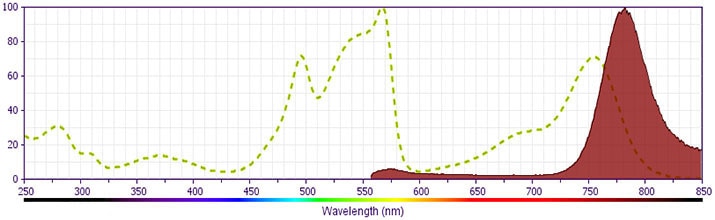
Development References (13)
-
Campbell JJ, Qin S, Unutmaz D, et al. Unique subpopulations of CD56+ NK and NK-T peripheral blood lymphocytes identified by chemokine receptor expression repertoire. J Immunol. 2001; 166(11):6477-6482. (Biology). View Reference
-
Cooper MA, Fehniger TA, Caligiuri MA. The biology of human natural killer–cell subsets. Trends Immunol. 2001; 22(11):633-640. (Biology). View Reference
-
Galandrini R, Tassi I, Mattia G, et al. SH2-containing inositol phosphatase (SHIP-1) transiently translocates to raft domains and modulates CD16-mediated cytotoxicity in human NK cells. Blood. 2001; 100(13):4581-4589. (Biology). View Reference
-
Gerosa F, Baldani-Guerra B, Nisii C, Marchesini V, Carra G, Trinchieri G. Reciprocal activating interaction between natural killer cells and dendritic cells. J Exp Med. 2002; 195(3):327-333. (Biology). View Reference
-
Lanier LL, Kipps TJ, Phillips JH. Functional properties of a unique subset of cytotoxic CD3+ T lymphocytes that express Fc receptors for IgG (CD16/Leu-11 antigen). J Exp Med. 1985; 162(6):2089-2106. (Biology). View Reference
-
Lanier LL, Le AM, Civin CI, Loken MR, Phillips JH. The relationship of CD16 (Leu-11) and Leu-19 (NKH-1) antigen expression on human peripheral blood NK cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986; 136(12):4480-4486. (Biology). View Reference
-
Lanier LL, Le AM, Phillips JH, Warner NL, Babcock GF. Subpopulations of human natural killer cells defined by expression of the Leu-7 (HNK-1) and Leu-11 (NK-15) antigens. J Immunol. 1983; 131(4):1789-1796. (Biology). View Reference
-
Perussia B, Acuto O, Terhorst C, et al. Human natural killer cells analyzed by B73-1, a monoclonal antibody blocking Fc receptor functions, II: studies of B73-1 antibody-antigen interaction on the lymphocyte membrane. J Immunol. 1983; 130:2142-2148. (Biology).
-
Perussia B, Starr S, Abraham S, Fanning V, Trinchieri G. Human natural killer cells analyzed by B73.1, a monoclonal antibody blocking Fc receptor functions. I. Characterization of the lymphocyte subset reactive with B73.1. J Immunol. 1983; 130(5):2133-2141. (Biology). View Reference
-
Perussia B, Trinchieri G, Jackson A, et al. The Fc receptor for IgG on human natural killer cells: phenotypic, functional, and comparative studies with monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1984; 133(1):180-189. (Biology). View Reference
-
Phillips JH, Babcock GF. A monoclonal antibody reactive against purified human natural killer cells and granuocytes. Immunol Letters. 1983; 6:143. (Biology).
-
Schmidt RE. Non-lineage/natural killer section report: new and previously defined clusters. In: Knapp W. W. Knapp .. et al., ed. Leucocyte typing IV : white cell differentiation antigens. Oxford New York: Oxford University Press; 1989:517-542.
-
Thompson J, Goeken N, Brown S, Rhodes J. Phenotypic definition of human monocyte/macrophage subpopulations by monoclonal antibodies, II: Distinction of non-T, non-B natural killer cells (NK) from antigen-presenting stimulating cells in the mixed lymphocyte response (MLR) Presented at the American Association for Clinical Histocompatibility Testing. (Biology).
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Although not required, these products are manufactured in accordance with Good Manufacturing Practices.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.