Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?
BD Pharmingen™ APC Annexin V
(RUO)

.png)

APC Annexin V: A tool for identifying cells that are undergoing apoptosis. Jurkat T cells were left untreated (left panel) or treated for 4 hours (right panel) with 6 µM camptothecin. Cells were incubated with APC Annexin V and analyzed by flow cytometry. Untreated cells were primarily APC Annexin V negative, indicating that they were viable and not undergoing apoptosis. After a 4 hour treatment with camptothecin, there were two populations of cells: cells undergoing apoptosis (APC Annexin V positive), and cells that were viable and not undergoing apoptosis (APC Annexin V negative).
.png)

BD Pharmingen™ APC Annexin V
.png)
Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
APC Annexin V is a sensitive probe for identifying apoptotic cells, binding to negatively charged phospholipid surfaces (Kd of ~5 x 10e2) with a higher affinity for phosphatidylserine (PS) than most other phospholipids. APC Annexin V binding is calcium dependent and defined calcium and salt concentrations are required for optimal staining as described in the APC Annexin V Staining Protocol. Investigators should note that APC Annexin V flow cytometric analysis on adherent cell types (e.g HeLa, NIH 3T3, etc.) is not routinely tested as specific membrane damage may occur during cell detachment or harvesting. Methods for utilizing Annexin V for flow cytometry on adherent cell types, however, have been previously reported (Casiola-Rosen et al. and van Engelend et al.).
INDUCTION OF APOPTOSIS BY CAMPTOTHECIN
The following protocol is provided as an illustration on how APC Annexin V may be used on a cell line (Jurkat).
Materials
1. Prepare Camptothecin stock solution (Sigma-Aldrich Cat.No. C-9911): 1 mM in DMSO.
2. Jurkat T cells (ATCC TIB-152).
Procedure
1. Add Camptothecin (final conc. 4-6 µM) to 1 x 10e6 Jurkat cells.
2. Incubate the cells for 4-6 hr at 37°C.
3. Proceed with the APC Annexin V Staining Protocol to measure apoptosis.
APC ANNEXIN V STAINING PROTOCOL
Reagents
1. APC Annexin V: Included. Use 5 µl per test.
2. 7-Amino-Actinomycin D (7-AAD): Not included. 7-AAD (Cat.No. 559925) is a convenient, ready-to-use nucleic acid dye with fluorescence detectable in the far red range of the spectrum. Use 5 µl per test.
3. 10X Binding Buffer: Not Included. 0.1 M Hepes (pH 7.4) 1.4 M NaCl, 25 mM CaCl2. Store at 4°C. Alternatively, catalog number 556454 may be purchased.
Staining
1. Wash cells twice with cold PBS and then resuspend cells in 1X Binding Buffer at a concentration of 1 x 10e6 cells/ml.
2. Transfer 100 µl of the solution (1 x 10e5 cells) to a 5 ml culture tube.
3. Add 5 µl of APC Annexin V (for one and two color analysis) and 5 µl of 7-AAD (for two color analysis only).
4. Gently vortex the cells and incubate for 15 min at RT (25°C) in the dark.
5. Add 400 µl of 1X Binding Buffer to each tube. Analyze by flow cytometry within 1 hr.
SUGGESTED CONTROLS FOR SETTING UP FLOW CYTOMETRY
The following controls are used to set up compensation and quadrants:
1. Unstained cells.
2. Cells stained with APC Annexin V alone (no 7-AAD).
3. Cells stained with 7-AAD alone (no APC Annexin V).
Other Staining Controls
A cell line that can be easily induced to undergo apoptosis should be used to obtain positive control staining with APC Annexin V and/or APC Annexin V and 7-AAD. It is important to note that the basal level of apoptosis and necrosis varies considerably within a population. Thus, even in the absence of induced apoptosis, most cell populations will contain a minor percentage of cells that are positive for apoptosis (APC Annexin V positive, 7-AAD negative or APC Annexin V positive, 7-AAD positive).
The untreated population is used to define the basal level of apoptotic and dead cells. The percentage of cells that have been induced to undergo apoptosis is then determined by subtracting the percentage of apoptotic cells in the untreated population from percentage of apoptotic cells in the treated population. Since cell death is the eventual outcome of cells undergoing apoptosis, cells in the late stages of apoptosis will have a damaged membrane and stain positive for 7-AAD as well as for APC Annexin V. Thus, the assay does not distinguish between cells that have already undergone an apoptotic cell death and those that have died as a result of necrotic pathway, because in either case the dead cells will stain with both APC Annexin V and 7-AAD.
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
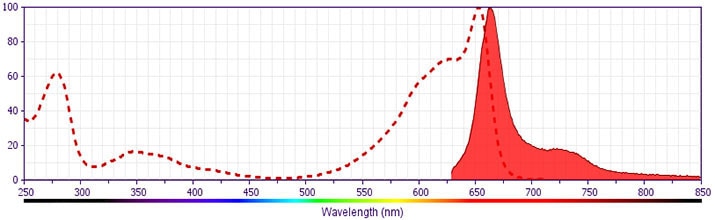
- This APC-conjugated reagent can be used in any flow cytometer equipped with a dye, HeNe, or red diode laser.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
Companion Products


Apoptosis is a normal physiologic process which occurs during embryonic development as well as in maintenence of tissue homeostasis. The apoptotic program is characterized by certain morphologic features, including loss of plasma membrane asymmetry and attachment, condensation of the cytoplasm and nucleus, and internucleosomal cleavage of DNA. Loss of plasma membrane is one of the earliest features. In apoptotic cells, the membrane phospholipid phosphatidylserine (PS) is translocated from the inner to the outer leaflet of the plasma membrane, thereby exposing PS to the external cellular environment. Annexin V is a 35-36 kDa Ca2+ dependent phospholipid-binding protein that has a high affinity for PS, and binds to cells with exposed PS. Annexin V may be conjugated to fluorochromes including APC. This format retains its high affinity for PS and thus serves as a sensitive probe for flow cytometric analysis of cells that are undergoing apoptosis. Since externalization of PS occurs in the earlier stages of apoptosis, APC Annexin V staining can identify apoptosis at an earlier stage than assays based on nuclear changes such as DNA fragmentation.
APC Annexin V staining precedes the loss of membrane integrity which accompanies the latest stages of cell death resulting from either apoptotic or necrotic processes. Therefore, staining with APC Annexin V is typically used in conjunction with a vital dye such as propidium iodide (PI) or 7-Amino-Actinomycin (7-AAD) to allow the investigator to identify early apoptotic cells (7-AAD negative, APC Annexin V positive). Viable cells with intact membranes exclude 7-AAD, whereas the membranes of dead and damaged cells are permeable to 7-AAD. For example, cells that are considered viable are both APC Annexin V and 7-AAD negative while cells that are in early apoptosis are APC Annexin V positive and 7-AAD negative, while cells that are in late apoptosis or already dead are both APC Annexin V and 7-AAD positive. This assay does not distinguish between cells that have undergone apoptotic death versus those that have died as a result of a necrotic pathway because in either case, the dead cells will stain with both APC Annexin V and 7-AAD. However, when apoptosis is measured over time, cells can be often tracked from APC Annexin V and 7-AAD negative (viable, or no measurable apoptosis), to APC Annexin V positive and 7-AAD negative (early apoptosis, membrane integrity is present) and finally to APC Annexin V and 7-AAD positive (end stage apoptosis and death). The movement of cells through these three stages suggests apoptosis. In contrast, a single observation indicating that cells are both APC Annexin V and 7-AAD positive, in of itself, reveals less information about the process by which the cells underwent their demise.
APC Annexin V is routinely tested by flow cytometric analysis. Other applications were tested at BD Biosciences Pharmingen during antibody development only or reported in the literature.
Development References (8)
-
Andree HA, Reutelingsperger CP, Hauptmann R, Hemker HC, Hermens WT, Willems GM. Binding of vascular anticoagulant alpha (VAC alpha) to planar phospholipid bilayers. J Biol Chem. 1990; 265(9):4923-4928. (Biology). View Reference
-
Casciola-Rosen L, Rosen A, Petri M, Schlissel M. Surface blebs on apoptotic cells are sites of enhanced procoagulant activity: implications for coagulation events and antigenic spread in systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996; 93(4):1624-1629. (Methodology: Apoptosis, Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Homburg CH, de Haas M, von dem Borne AE, Verhoeven AJ, Reutelingsperger CP, Roos D. Human neutrophils lose their surface Fc gamma RIII and acquire Annexin V binding sites during apoptosis in vitro. Blood. 1995; 85(2):532-540. (Biology). View Reference
-
Koopman G, Reutelingsperger CP, Kuijten GA, Keehnen RM, Pals ST, van Oers MH. Annexin V for flow cytometric detection of phosphatidylserine expression on B cells undergoing apoptosis. Blood. 1994; 84(5):1415-1420. (Methodology: Apoptosis, Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Martin SJ, Reutelingsperger CP, McGahon AJ, et al. Early redistribution of plasma membrane phosphatidylserine is a general feature of apoptosis regardless of the initiating stimulus: inhibition by overexpression of Bcl-2 and Abl. J Exp Med. 1995; 182(5):1545-1556. (Biology). View Reference
-
Raynal P, Pollard HB. Annexins: the problem of assessing the biological role for a gene family of multifunctional calcium- and phospholipid-binding proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994; 1197(1):63-93. (Biology). View Reference
-
Vermes I, Haanen C, Steffens-Nakken H, Reutelingsperger C. A novel assay for apoptosis. Flow cytometric detection of phosphatidylserine expression on early apoptotic cells using fluorescein labelled Annexin V. J Immunol Methods. 1995; 184(1):39-51. (Methodology: Apoptosis, Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
van Engeland M, Ramaekers FC, Schutte B, Reutelingsperger CP. A novel assay to measure loss of plasma membrane asymmetry during apoptosis of adherent cells in culture. Cytometry. 1996; 24(2):131-139. (Methodology: Apoptosis, Flow cytometry). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.