-
Your selected country is
Middle East / Africa
- Change country/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?
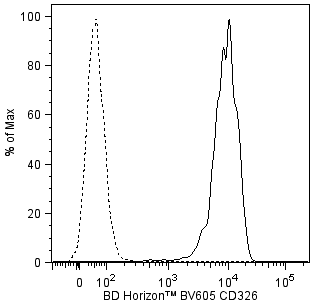



Flow cytometric analysis of CD326 expression on human SK-BR-3 cells. Human SK-BR-3 breast carcinoma cells (Cat. No. ATCC® HTB-30™) were stained with BD Horizon™ BV605 Mouse Anti-Human CD326 antibody (Cat. No. 563182; solid line histogram) or with a BD Horizon™ BV605 Mouse IgG1, κ Isotype Control (Cat. No. 562652; dashed line histogram). The fluorescence histograms were derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of viable cells. Flow cytometric analysis was performed using a BD™ LSR II Flow Cytometer System.


BD Horizon™ BV605 Mouse Anti-Human CD326

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Product Notices
- This reagent has been pre-diluted for use at the recommended Volume per Test. We typically use 1 × 10^6 cells in a 100-µl experimental sample (a test).
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- Please observe the following precautions: Absorption of visible light can significantly alter the energy transfer occurring in any tandem fluorochrome conjugate; therefore, we recommend that special precautions be taken (such as wrapping vials, tubes, or racks in aluminum foil) to prevent exposure of conjugated reagents, including cells stained with those reagents, to room illumination.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Although every effort is made to minimize the lot-to-lot variation in the efficiency of the fluorochrome energy transfer, differences in the residual emission from BD Horizon™ BV421 may be observed. Therefore, we recommend that individual compensation controls be performed for every BD Horizon™ BV605 conjugate.
- CF™ is a trademark of Biotium, Inc.
Companion Products



The EBA-1 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to human CD326. CD326 is an approximately 40 kDa type 1 transmembrane glycoprotein and adhesion molecule that mediates intercellular adhesive interactions. CD326 is also known as epithelial adhesion molecule (EpCAM), epithelial glycoprotein 2 (EGP-2), and epithelial surface antigen (ESA). The epithelial cells present in non-squamous epithelia and tumors derived from such cells show EpCAM expression. The normal epithelial cells reactive with anti-EpCAM antibodies are those present in the (lower) respiratory tract; the (lower) gastrointestinal tract; tubules in the kidney; the surface epithelium of the ovary; the exocrine and endocrine pancreas; secondary germ cells of telogenic hair follicles; and secretory tubules of sweat glands in the skin, whereas the epidermis is negative. In addition, all epithelial cells in the thyroid and epithelial cells in the thymus show EpCAM expression, while the outer cortex and Hassall's corpuscles have low expression. In the liver, only the bile ducts appear to be positive with anti-EpCAM antibodies. Non-squamous- carcinoma cells have high EpCAM expression; some squamous carcinoma cells. Tumors arising from non-epithelial cells, such as lymphoma, mesothelioma, neuroblastoma, and melanoma, do not express EpCAM.
This antibody is conjugated to BD Horizon BV605 which is part of the BD Horizon Brilliant™ Violet family of dyes. With an Ex Max of 407-nm and Em Max of 602-nm, BD Horizon BV605 can be excited by a violet laser and detected with a standard 610/20-nm filter set. BD Horizon BV605 is a tandem fluorochrome of BD Horizon BV421 and an acceptor dye with an Em max at 605-nm. Due to the excitation of the acceptor dye by the green (532 nm) and yellow-green (561 nm) lasers, there will be significant spillover into the PE and BD Horizon PE-CF594 detectors off the green or yellow-green lasers. BD Horizon BV605 conjugates are very bright, often exhibiting brightness equivalent to PE conjugates and can be used as a third color off of the violet laser.
For optimal and reproducible results, BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer should be used anytime two or more BD Horizon Brilliant dyes are used in the same experiment. Fluorescent dye interactions may cause staining artifacts which may affect data interpretation. The BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer was designed to minimize these interactions. More information can be found in the Technical Data Sheet of the BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer (Cat. No. 563794).
Development References (11)
-
Braun S, Pantel K, Müller P, et al. Cytokeratin-positive cells in the bone marrow and survival of patients with stage I, II, or III breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2000; 342:525-533. (Biology). View Reference
-
De Leij L, Helrich W, Stein R, Mattes MJ. SCLC-cluster-2 antibodies detect the pancarcinoma/epithelial glycoprotein EGP-2. Int J Cancer. 1994; 8:60-63. (Biology). View Reference
-
Diel IJ, Kaufmann M, Goerner R, Costa SD, Kaul S, Bastert G. Detection of tumor cells in bone marrow of patients with primary breast cancer: a prognostic factor for distant metastasis. J Clin Oncol. 1992; 10:1534-1539. (Biology). View Reference
-
Hardingham JE, Kotasek D, Farmer B, et al. Immunobead-PCR: a technique for the detection of circulating tumor cells using immunomagnetic beads and the polymerase chain reaction. Cancer Res. 1993; 53(15):3455-3458. (Biology). View Reference
-
Latza U, Niedobitek G, Schwarting R, Nekarda H, Stein H. Ber-EP4: new monoclonal antibody which distinguishes epithelia from mesothelial. J Clin Pathol. 1990; 43(3):213-219. (Biology). View Reference
-
Momburg F, Moldenhauer G, Hämmerling GJ, Möller P. Immunohistochemical study of the expression of a Mr 34,000 human epithelium-specific surface glycoprotein in normal and malignant tissues. Cancer Res. 1987; 47:2883-2891. (Biology). View Reference
-
Naume B, Borgen E, Beiske K, et al.. Immunomagnetic techniques for the enrichment and detection of isolated breast carcinoma cells in bone marrow and peripheral blood. J Hematother Stem Cell Res. 1997; 6:103-113. (Biology). View Reference
-
Patriarca C, Macchi RM, Marschner AK, Mellstedt H. Epithelial cell adhesion molecule expression (CD326) in cancer: a short review. Cancer Treat Rev. 2012; 38(1):68-75. (Biology). View Reference
-
Stahel RA, Gilks WR, Lehmann HP, Schenker T. Third International Workshop on Lung Tumor and Differentiation Antigens: overview of the results of the central data analysis. Int J Cancer. 1994; 8:6-26. (Biology). View Reference
-
Trzpis M, McLaughlin PM, de Leij LM, Harmsen MC. Epithelial cell adhesion molecule: more than a carcinoma marker and adhesion molecule. Am J Pathol. 2007; 171(2):386-395. (Biology). View Reference
-
Yemul S, Leon Ja, Pozniakoff T, Esser PD, Estabrook A. Radioimmunoimaging of human breast carcinoma xenografts in nude mouse model with 111In-labeled new monoclonal antibody EBA-1 and F(ab')2 fragments. Nucl Med Biol. 1993; 20:325-335. (Clone-specific). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.