-
Your selected country is
Middle East / Africa
- Change country/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?
BD IMag™ Mouse NK Cell Separation Set - DM
(RUO)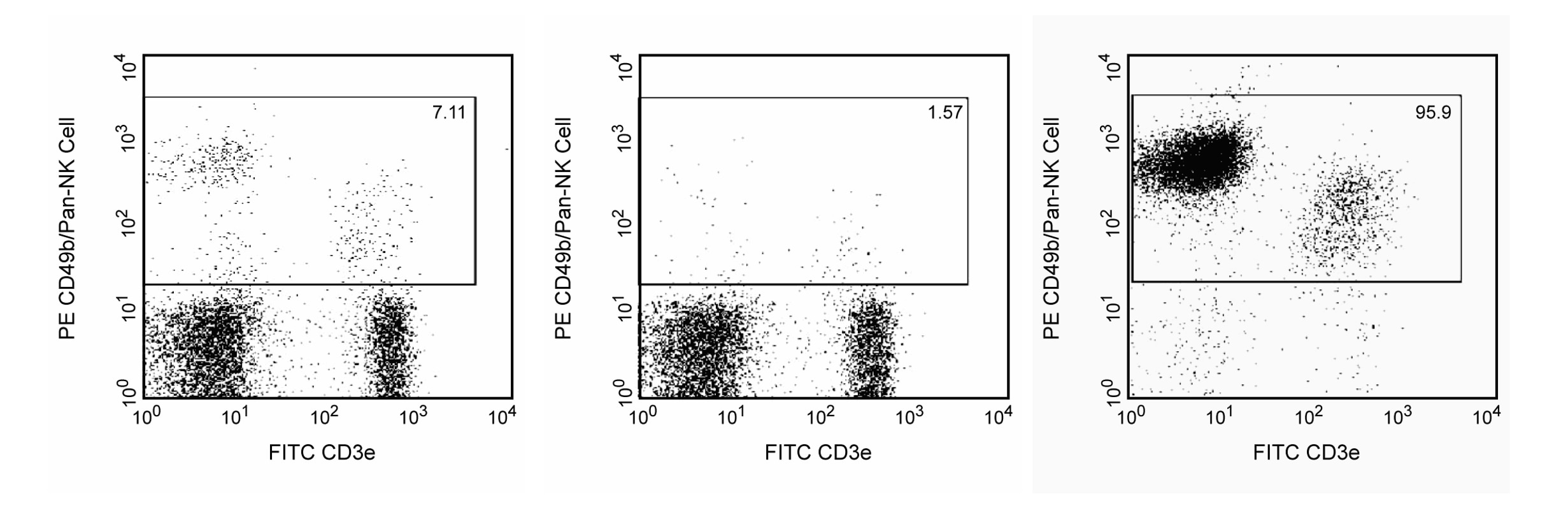



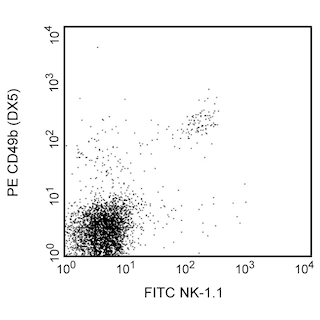
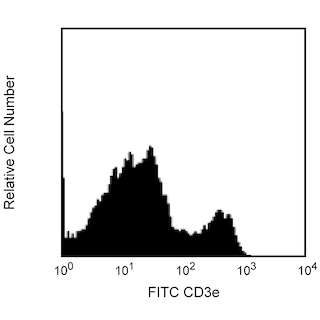
Positive selection of Mouse NK cells. BALB/c splenocytes were stained with PE Rat Anti-Mouse CD49b (Cat. No. 561066/553858) and FITC Hamster Anti-Mouse CD3ε (Cat. No 553061) monoclonal antibodies, and then labeled with BD IMag™ Anti-PE Particles 2 - DM (Cat. No. 558004). After labeling, the cells were separated using the BD IMag™ Cell Separation Magnet (Cat. No. 552311), and the negative (CD49b-) and positive (CD49b+) fractions were collected as described in the Magnetic Labeling and Separation Protocol. Please refer to the Positive Selection Flow Chart to identify the separated cell populations represented in this figure. Unseparated splenocytes (left panel), the negative fraction (middle panel), and the positive fraction (right panel) were analyzed by flow cytometry. Nonviable cells were eliminated from analysis by staining with Propidium Iodide Staining Solution (Cat. No.556463), and all viable leukocytes are displayed. The combined percentage of NK and NK-T cells (CD3e- CD49b[bright] and CD3e+ CD49b[dim], respectively) in each sample is given. Flow cytometry was performed on a BD FACSCalibur™ instrument.



BD IMag™ Mouse NK Cell Separation Set - DM

BD IMag™ Mouse NK Cell Separation Set - DM

Mouse NK Cell Separation Set - DM
Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Description
The BD IMag™ Mouse NK Cell Separation Set - DM is optimized for the positive selection or depletion of NK and NK-T cells using the BD IMag™ Cell Separation Magnet. The PE rat anti-mouse CD49b antibody (clone DX5) recognizes CD49b, which has been reported to be expressed at high density on most NK cells and at low density on subsets of NK-T cells in many mouse strains (e.g., A/J, AKR, BALB/c, C3H/HeJ, C57BL/6, C57BL/10, C57BR, C57L, C58, CBA/Ca, CBA/J, DBA/1, DBA/2, NOD, SJL, SWR, 129/J). The BD IMag™ Anti-PE Particles 2 - DM are magnetic nanoparticles that have anti-PE monoclonal antibody covalently conjugated to their surfaces. This Separation Set has been optimized for use with the BD IMag™ Cell Separation Magnet and it contains sufficient reagents to label 2 x 10e9 leukocytes.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
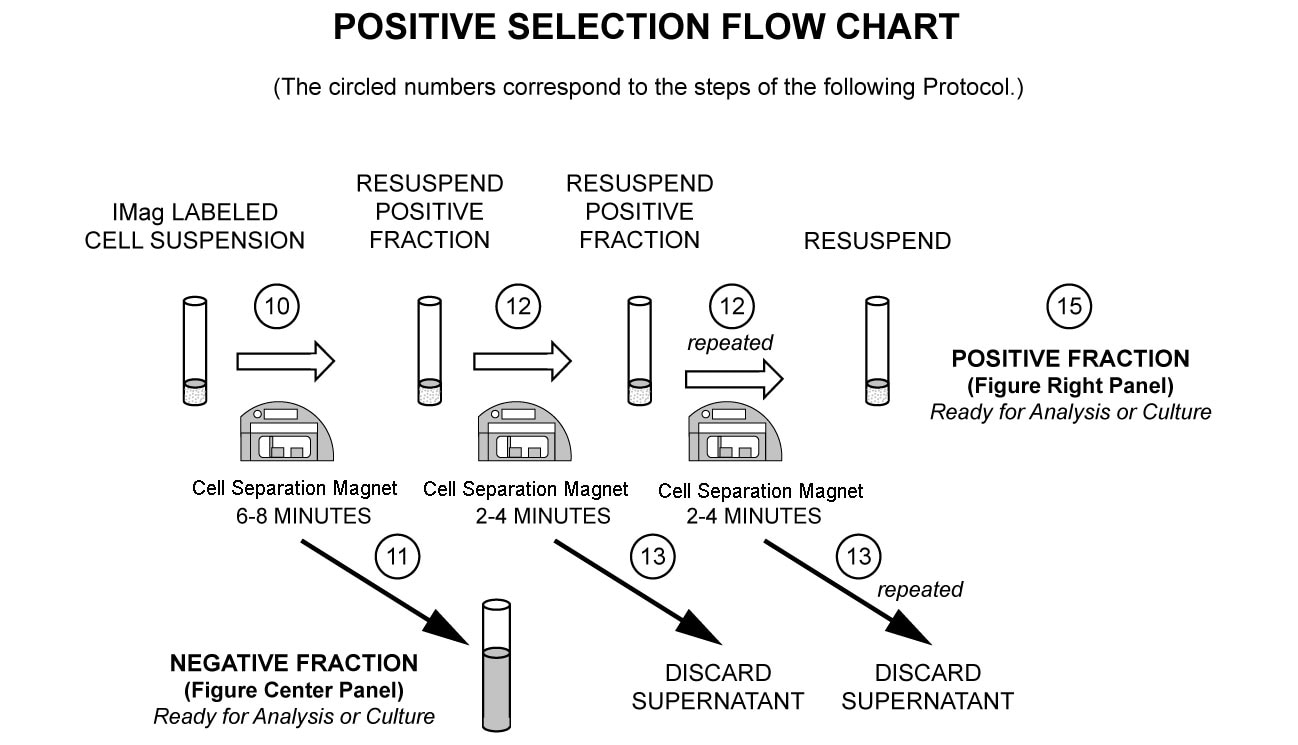
In summary, the PE rat anti-mouse CD49b antibody stains NK and NK-T cells. After washing away excess antibody, BD IMag™ Anti-PE Particles 2 - DM are added to the cell suspension and bind the cells bearing the PE-conjugated antibody. The tube containing this labeled cell suspension is then placed within the magnetic field of the BD IMag™ Cell Separation Magnet. Positive selection or depletion is then performed. Labeled cells migrate toward the magnet (positive fraction), leaving the unlabeled cells in suspension so they can be drawn off (depleted or negative fraction). The tube is then removed from the magnetic field for resuspension of the positive fraction. The selections are repeated twice to increase the purity of the positive fraction. For clarification of the procedure, the magnetic separation steps are diagrammed in the Positive Selection Flow Chart. The small size of the BD IMag™ particles allows the positive fraction to be further evaluated in downstream applications such as flow cytometry.
MAGNETIC LABELING AND SEPARATION PROTOCOL
1. Dilute BD IMag™ Buffer (10X) (Cat. No. 552362) 1:10 with sterile distilled water or prepare 1X BD IMag™ buffer by supplementing Phosphate Buffered Saline with 0.5% BSA, 2 mM EDTA, and 0.09% sodium azide. Place on ice.
2. Aseptically prepare a single-cell suspension from the peripheral lymphoid tissue of interest. Remove clumps of cells and/or debris by passing the suspended cells through a 70-µm nylon cell strainer. NK cells are fragile and therefore should be prepared in tissue culture medium [e.g., Dulbecco's Minimum Essential Medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and L-glutamine].
3. Count the cells. If the concentration is between 1 x 10e7 and 2 x 10e7 cells/ml, then proceed to Step 4. If cells are more dilute than 1 x 10e7 cells/ml, then spin down the cells and resuspend them in tissue culture medium at a concentration of 2 x 10e7 cells/ml.
4. Optional: Add BD Mouse Fc Block™ purified anti-mouse CD16/CD32 (Cat. No. 553141) at 0.25 µg per 1 x 10e6 cells, and incubate on ice for 15 minutes.*
5. Add the BD IMag™ PE Rat Anti-Mouse CD49b at 5 µl per 1 x 10e6 cells, and refrigerate for 15 minutes at 6-12°C.†
6. Wash the labeled cells with an excess volume of 1X BD IMag™ buffer, and carefully aspirate ALL the supernatant.
7. Vortex the BD IMag™ Anti-PE Particles 2 - DM thoroughly, and add 5 µl of particles for every 1 x 10e6 total cells.
8. Mix thoroughly. Refrigerate for 30 minutes at 6-12°C.†
9. Bring the labeling volume up to 2 to 8 x 10e7 cells/ml with 1X BD IMag™ buffer.
10. Immediately place the tube onto the Cell Separation Magnet and incubate for 6 to 8 minutes.
11. With the tube on the Cell Separation Magnet, carefully aspirate the supernatant. This supernatant is considered the Negative (or NK cell-depleted) Fraction.
12. Remove the tube from the Cell Separation Magnet, and add 1X BD IMag™ buffer to the same volume as in Step 9. Gently resuspend the cells by pipetting up and down, and return the tube to the Cell Separation Magnet for another 2 to 4 minutes. Longer inclubation time will increase the percentage of NK-T cells in the positive fraction.
13. With the tube on the Cell Separation Magnet, carefully remove the supernatant (wash fraction) and discard.
14. Repeat Steps 12 and 13.
15. After the final wash step, remove the tube from the Cell Separation Magnet. Resuspend the Positive Fraction in an appropriate buffer or culture medium, and proceed with desired downstream application(s), including flow cytometry.
NOTES:
* The use of BD Mouse Fc Block™ purified anti-mouse CD16/CD32 mAb 2.4G2 in step 4 can increase the purity and recovery of the NK cells by up to 5%. Please note that this results in enriched NK cells that may have purified anti-mouse CD16/CD32 mAb bound to their surface, which may affect the function of those NK cells.
† Avoid nonspecific labeling by working quickly and adhering to recommended incubation times.
Product Notices
- BD IMag™ particles are prepared from carboxy-functionalized magnetic particles which are manufactured by Skold Technology and are licensed under US patent number 7,169,618.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products



| Description | EntrezGene ID |
|---|---|
| PE Rat Anti-Mouse CD49b | N/A |
| Anti-PE Particles 2 - DM | N/A |
Development References (5)
-
Arase H, Saito T, Phillips JH, Lanier LL. Cutting edge: the mouse NK cell-associated antigen recognized by DX5 monoclonal antibody is CD49b (alpha 2 integrin, very late antigen-2). J Immunol. 2001; 167(3):1141-1144. (Biology). View Reference
-
Gadue P, Stein PL. NK T cell precursors exhibit differential cytokine regulation and require Itk for efficient maturation. J Immunol. 2002; 169(5):2397-2406. (Biology). View Reference
-
Karnbach C, Daws MR, Niemi EC, Nakamura MC. Immune rejection of a large sarcoma following cyclophosphamide and IL-12 treatment requires both NK and NK T cells and is associated with the induction of a novel NK T cell population. J Immunol. 2001; 167(5):2569-2576. (Biology). View Reference
-
Lee IF, Qin H, Trudeau J, Dutz J, Tan R. Regulation of autoimmune diabetes by complete Freund's adjuvant is mediated by NK cells. J Immunol. 2004; 172(2):937-942. (Biology). View Reference
-
Ortaldo JR, Winkler-Pickett R, Mason AT, Mason LH. The Ly-49 family: regulation of cytotoxicity and cytokine production in murine CD3+ cells. J Immunol. 1998; 160(1):1158-1165. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.