-
Your selected country is
Middle East / Africa
- Change country/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?






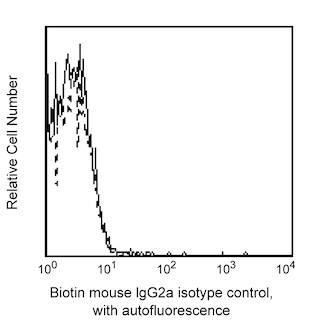
Flow cytometric analysis of glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor protein on GPI defective mutant cells. GPI defective mutant cells were stained with Biotin Mouse Anti-Human CD59 (Cat. No. 555762; solid line histogram) or Biotin Mouse IgG2a, κ Isotype Control (Cat. No. 555572; dashed line histogram), and PE Streptavidin (Cat. No. 554061). The fluorescence histograms were derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scattering characteristics of viable cells. Flow cytometry was performed on a BD FACScan™.

Flow cytometric analysis of glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor protein cells on K562 cells. K562 cells were stained with Biotin Mouse Anti-Human CD59 (Cat. No. 555762; solid line histogram) or Biotin Mouse IgG2a, κ Isotype Control (Cat. No. 555572; dashed line histogram) and PE Streptavidin (Cat. No. 554061). The fluorescence histograms were derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scattering characteristics of viable cells. Flow cytometry was performed on a BD FACScan™.


BD Pharmingen™ Biotin Mouse Anti-Human CD59

BD Pharmingen™ Biotin Mouse Anti-Human CD59

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Product Notices
- This reagent has been pre-diluted for use at the recommended Volume per Test. We typically use 1 × 10^6 cells in a 100-µl experimental sample (a test).
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Species cross-reactivity detected in product development may not have been confirmed on every format and/or application.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products


.png?imwidth=320)
The p282 (HI9) monoclonal antibody specifically binds to CD59, a 19 kDa glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored glycoprotein, expressed on hematopoietic and non-hematopoietic cells. Because of its interaction with complement activated products, CD59 has been termed membrane-attack-complex-inhibitory factor (MACIF), homologus restriction factor (HRF20), membrane inhibitor of reactive lysis (MIRL) and Protectin. It inhibits the cytolytic activity of the complement system by binding to C8 and C9, thereby blocking the assembly of the membrane attack complex. CD59 also participates in spontaneous T-cell/erythrocyte adhesion, interacts with CD2, and plays a role in T-cell activation.
Development References (8)
-
Barclay NA, Brown MH, Birkeland ML, et al, ed. The Leukocyte Antigen FactsBook. San Diego, CA: Academic Press; 1997.
-
Davies A, Lachmann PJ. Membrane defence against complement lysis: the structure and biological properties of CD59. Immunol Res. 1993; 12(3):258-275. (Biology). View Reference
-
Deckert M, Kubar J, Bernard A. CD58 and CD59 molecules exhibit potentializing effects in T cell adhesion and activation. J Immunol. 1992; 148(3):672-677. (Biology). View Reference
-
Deckert M, Kubar J, Zoccola D, et al. CD59 molecule: a second ligand for CD2 in T cell adhesion. Eur J Immunol. 1992; 22(11):2943-2947. (Biology). View Reference
-
Guesdon JL, Ternynck T, Avrameas S. The use of avidin-biotin interaction in immunoenzymatic techniques. J Histochem Cytochem. 1979; 27(8):1131-1139. (Biology). View Reference
-
Kishimoto T. Tadamitsu Kishimoto .. et al., ed. Leucocyte typing VI : white cell differentiation antigens : proceedings of the sixth international workshop and conference held in Kobe, Japan, 10-14 November 1996. New York: Garland Pub.; 1997.
-
Schlossman SF. Stuart F. Schlossman .. et al., ed. Leucocyte typing V : white cell differentiation antigens : proceedings of the fifth international workshop and conference held in Boston, USA, 3-7 November, 1993. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1995.
-
Whitlow MB, Iida K, Stefanova I, Bernard A, Nussenzweig V. H19, a surface membrane molecule involved in T-cell activation, inhibits channel formation by human complement. Cell Immunol. 1990; 126(1):176-184. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.