Old Browser
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?


PE Mouse Anti-Human IL-1α
Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Store vials at 2°C–8°C. Conjugated forms should not be frozen. Protect from exposure to light. Each reagent is stable until the expiration date shown on the bottle label when stored as directed.
The Anti-Hu–IL-1α antibody, clone AS5, is derived from fusion of P3X63Ag8 myeloma cells with splenocytes from BALB/c mice immunized with recombinant human IL-1α. The Anti-Human Interleukin-1α (Anti-Hu–IL-1α) antibody recognizes a 13- to 18-kilodalton (kDa) polypeptide.
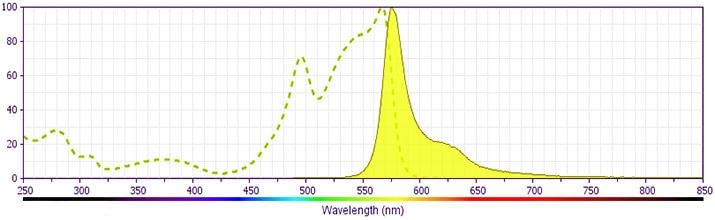
Development References (14)
-
Centers for Disease Control. Update: universal precautions for prevention of transmission of human immunodeficiency virus, hepatitis B virus, and other bloodborne pathogens in healthcare settings. MMWR. 1988; 37:377-388. (Biology).
-
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2005. (Biology).
-
Conlon PJ, Grabstein KH, Alpert A, et al. Localization of human mononuclear cell interleukin 1. J Immunol. 1987; 139:98-102. (Biology).
-
Dinarello CA. Biology of interleukin 1. FASEB J. 1988; 2:108-115. (Biology).
-
Dinarello CA. Interleukin-1 and interleukin-1 antagonism. Blood. 1991; 77(8):1627-1652. (Biology). View Reference
-
Fini ME, Strissel KJ, Girard MT, Mays JW, Rinehart WB. Interleukin 1αmediates collegenase synthesis stimulated by Phorbol 12-Myristate 13-Acetate. J Bio Chem. 1994; 269:11291-11298. (Biology).
-
Giri JG, Lomedico PT, Mizel SB. Studies on the synthesis and secretion of interleukin 1. I. A 33,000 molecular weight precursor for interleukin 1. J Immunol. 1985; 134(1):343-349. (Biology). View Reference
-
Mantovani A, Dejana E. Cytokines as communication signals between leukocytes and endothelial cells.. Immunol Today. 1989; 10(11):370-5. (Biology). View Reference
-
Matsushima K, Yodoi J, Tagaya Y, Oppenheim JJ. Downregulation of interleukin-1 receptor expression by IL-1 and fate of internalized125 I-labeled IL-1 β in a human large granular lymphocyte cell line. J Immunol. 1986; 137:3183-3188. (Biology).
-
Mizel SB. The interleukins. FASEB J. 1989; 32379-2388. (Biology).
-
Saklatvala J. Tumour necrosis factor α stimulates resorption and inhibits synthesis of proteoglycan in cartilage. Science. 1986; 322:547-549. (Biology).
-
Slack J, McMahan CJ, Waugh S. et al. Independent binding of interleukin-1 α and interleukin-1 β to type I and type II interleukin 1 receptors. J Bio Chem. 1993; 268:2513-2524. (Biology).
-
Van Zee KJ, DeForge LE, Fischer E, et al. IL-8 in septic shock, endotoxemia and after IL-1 administration. J Immunol. 1991; 146:3478-3482. (Biology).
-
West-Mays JA, Strissel KJ, Sadow PM, Fini ME. Competence for collegenase gene expression by tissue fibroblasts requires activation of an interleukin 1α autocrine loop. Prod Natl Acad Sci. 1995; 92:6768-6772. (Biology).
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Although not required, these products are manufactured in accordance with Good Manufacturing Practices.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.