-
Reagents
- Flow Cytometry Reagents
-
Western Blotting and Molecular Reagents
- Immunoassay Reagents
-
Single-Cell Multiomics Reagents
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- BD® OMICS-One Protein Panels
- BD OMICS-One™ WTA Next Assay
-
Functional Assays
-
Microscopy and Imaging Reagents
-
Cell Preparation and Separation Reagents
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current location site or be switched to your location?
BD Transduction Laboratories™ Purified Mouse Anti-Vti1a
Clone 45/Vti1a (RUO)
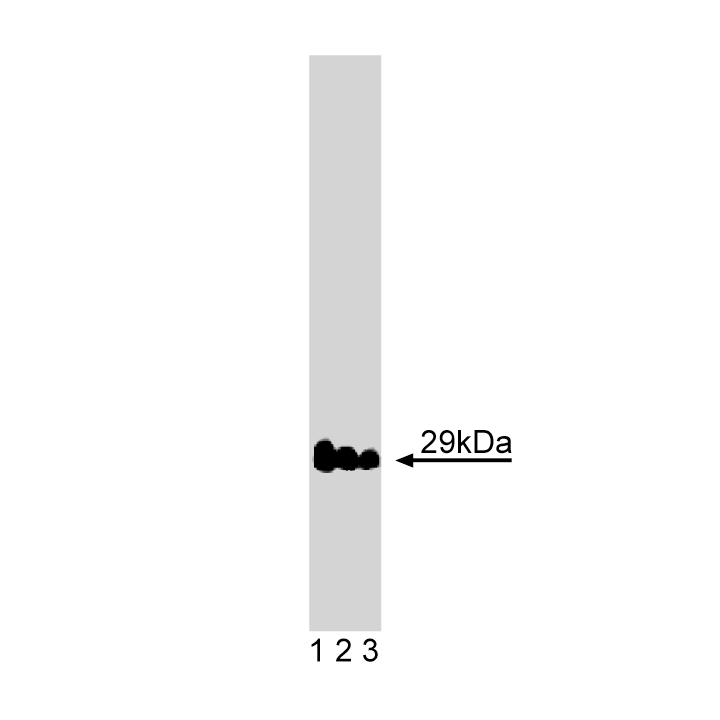



Western blot analysis of Vti1a on rat brain lysate. Lane 1: 1:2500, lane 2: 1:5000, lane 3: 1:10000 dilution of Vti1a.

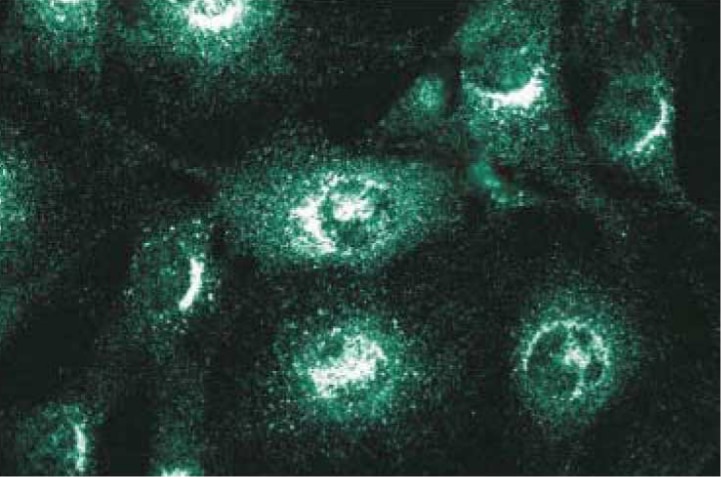
Immunofluorescence staining of NIH-3T3 cells.




Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
Companion Products


Eukaryotic protein trafficking involves the packaging of molecules into membranous vesicles that bud from a donor compartment, travel to a specific destination, fuse, and release their components into an acceptor compartment. Recognition between vesicle and acceptor membrane is mediated by the pairing of the integral membrane SNARE proteins. The stable interaction between vesicle proteins (v-SNAREs) and target proteins (t-SNAREs) juxtaposes the membranes and results in an activated docked state and/or membrane fusion. VTI1a and VTI1b are putative mammalian SNARE proteins identified by sequence comparison with yeast SNAREs. In line with their involvement in vesicle transport, these molecules are expressed in a wide range of mammalian tissues. Vti1a, a possible t-SNARE, contains a C-terminal hydrophobic domain and several regions that may form coiled-coil structures. It exists in distinct syntaxin 5- and syntaxin 6-containing SNARE complexes within the Golgi apparatus. Inhibition of Vti1a blocks transport of G proteins to the cell surface and results in their accumulation within the Golgi. Thus, Vti1a functions in protein transport within the secretory pathway.
Development References (5)
-
Advani RJ, Bae HR, Bock JB, et al. Seven novel mammalian SNARE proteins localize to distinct membrane compartments. J Biol Chem. 1998; 273(17):10317-10324. (Biology). View Reference
-
Chiu R, Novikov L, Mukherjee S, Shields D. A caspase cleavage fragment of p115 induces fragmentation of the Golgi apparatus and apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2002; 159(4):637-648. (Clone-specific: Western blot). View Reference
-
Mallard F, Tang BL, Galli T. Early/recycling endosomes-to-TGN transport involves two SNARE complexes and a Rab6 isoform. J Cell Biol. 2002; 156(4):653-664. (Clone-specific: Western blot). View Reference
-
Shorter J, Beard MB, Seemann J, Dirac-Svejstrup AB, Warren G. Sequential tethering of Golgins and catalysis of SNAREpin assembly by the vesicle-tethering protein p115. J Cell Biol. 2002; 157(1):45-62. (Clone-specific: Western blot). View Reference
-
Xu Y, Wong SH, Tang BL, Subramaniam VN, Zhang T, Hong W. A 29-kilodalton Golgi soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor (Vti1-rp2) implicated in protein trafficking in the secretory pathway. J Biol Chem. 1998; 273(34):21783-21789. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.