Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?



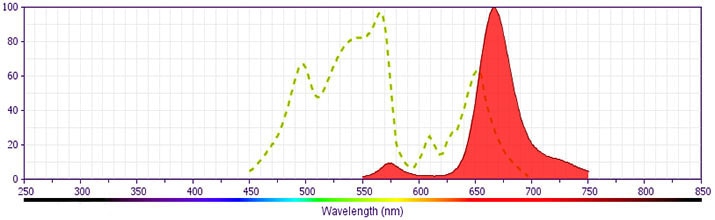
Flow cytometric analysis of CD152 expression on stimulated Human peripheral mononuclear cells. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were stimulated with Concanavalin A for 3 days, then stained with either PE-Cy™5 Mouse IgG2a, κ Isotype Control (Cat. No. 555575; dashed line histogram) or PE-Cy™5 Mouse Anti-Human CD152 (Cat. No. 555854/561717; solid line histogram). The fluorescence histograms were derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scattering characteristics of viable activated cells. Flow cytometry was performed on a BD FACScan™ system.

BD Pharmingen™ PE-Cy™5 Mouse Anti-Human CD152
Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
BD® CompBeads can be used as surrogates to assess fluorescence spillover (compensation). When fluorochrome conjugated antibodies are bound to BD® CompBeads, they have spectral properties very similar to cells. However, for some fluorochromes there can be small differences in spectral emissions compared to cells, resulting in spillover values that differ when compared to biological controls. It is strongly recommended that when using a reagent for the first time, users compare the spillover on cell and BD® CompBeads to ensure that BD® CompBeads are appropriate for your specific cellular application.
Product Notices
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- This reagent has been pre-diluted for use at the recommended Volume per Test. We typically use 1 × 10^6 cells in a 100-µl experimental sample (a test).
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- PE-Cy5 is optimized for use with a single argon ion laser emitting 488-nm light. Because of the broad absorption spectrum of the PE-Cy5 tandem fluorochrome, extra care must be taken when using dual-laser cytometers which may directly excite both PE and Cy5™.
- PE-Cy5 is a tandem fluorochrome composed of R-phycoerythrin (PE), which is excited by the 488 nm light of an Argon ion laser and serves as an energy donor, coupled to the cyanine dye Cy5, which acts as an energy acceptor and fluoresces at 670 nm. BD Biosciences Pharmingen has maximized the fluorochrome energy transfer in PE-Cy5, thus maximizing its fluorescence emission intensity, minimizing residual emission from PE, and minimizing lot-to-lot variation.
- Species cross-reactivity detected in product development may not have been confirmed on every format and/or application.
- Please observe the following precautions: Absorption of visible light can significantly alter the energy transfer occurring in any tandem fluorochrome conjugate; therefore, we recommend that special precautions be taken (such as wrapping vials, tubes, or racks in aluminum foil) to prevent exposure of conjugated reagents, including cells stained with those reagents, to room illumination.
- PE-Cy5 tandem fluorochromes have been reported to bind some classes of human macrophages and granulocytes via Fc receptors, and PE has been reported to bind to mouse B lymphocytes via Fc receptors. Preincubation of mouse leukocytes with Mouse BD Fc Block™ purified anti-mouse CD16/CD32 mAb 2.4G2 can reduce the non-specific binding of PE-Cy5-conjugated reagents to mouse B cells. However, PE-Cy5 conjugated reagents should not be used to stain splenocytes of SJL, NOD, and MRL mice as B lymphocytes and/or other leukocytes have been reported to non-specifically stain regardless of the use of Mouse BD Fc Block™ (the CD72c complex has been implicated for PE-Cy5 binding in these strains). Reagents conjugated to PE, PerCP, PerCP-Cy5.5, APC, and APC-Cy7 tandem fluorochrome can be used on leukocytes from these mouse strains.
- Please refer to http://regdocs.bd.com to access safety data sheets (SDS).
- Cy is a trademark of Global Life Sciences Solutions Germany GmbH or an affiliate doing business as Cytiva.
- For U.S. patents that may apply, see bd.com/patents.
The BNI3 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to the human cytolytic T lymphocyte-associated antigen (CTLA-4), also known as CD152. CTLA-4 is transiently expressed on activated CD28+ T cells and binds to CD80 and CD86 present on antigen presenting cells (APC) with high avidity. This interaction appears to deliver a negative regulatory signal to the T cell. Recent reports indicate that CTLA-4 is also expressed on B cells when cultured with activated T cells, suggesting a role for CTLA-4 in the regulation of B-cell response. Immobilized BNI3 antibody enhances T-cell proliferation induced by antibody-mediated crosslinking of CD3 and CD28. Recent studies have shown that CD152 can be expressed by regulatory T (Treg) cells. After cellular fixation and permeabilization, the BNI3 antibody can stain intracellular CD152 expressed in T cells including Treg cells. Clone BNI3 was studied in the VI Leukocyte Typing Workshop.
Development References (10)
-
Cabezon R, Sintes J, Llinas L, Benitez-Ribas D. Analysis of HLDA9 mAbs on plasmacytoid dendritic cell. Immunol Lett. 2011; 134(2):167-173. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Castan J, Klauenberg U, Kalmar P, Fleischer B, Broker BM. Expression of CTLA-4 (CD152) on human medullary CD4+ thymocytes. Med Microbiol Immunol (Berl). 1998; 187(1):49-52. (Immunogen: Fluorescence microscopy, Immunocytochemistry, Immunofluorescence, Immunohistochemistry). View Reference
-
Castan J, Tenner-Racz K, Racz P, Fleischer B, Broker BM. Accumulation of CTLA-4 expressing T lymphocytes in the germinal centres of human lymphoid tissues. Immunology. 1997; 90(2):265-271. (Immunogen: ELISA, Fluorescence microscopy, Immunofluorescence, Immunohistochemistry). View Reference
-
Healy ZR, Murdoch DM. OMIP-036: Co-inhibitory receptor (immune checkpoint) expression analysis in human T cell subsets.. Cytometry A. 2016; 89(10):889-892. (Clone-specific: Intracellular Staining/Flow Cytometry). View Reference
-
Kuiper HM, Brouwer M, Linsley PS, van Lier RA. Activated T cells can induce high levels of CTLA-4 expression on B cells. J Immunol. 1995; 155(4):1776-1783. (Biology). View Reference
-
Lindsten T, Lee KP, Harris ES, et al. Characterization of CTLA-4 structure and expression on human T cells. J Immunol. 1993; 151(7):3489-3499. (Biology). View Reference
-
Morton PA, Fu XT, Stewart JA, et al. Differential effects of CTLA-4 substitutions on the binding of human CD80 (B7-1) and CD86 (B7-2). J Immunol. 1996; 156(3):1047-1054. (Biology). View Reference
-
Rabe H, Lundell AC, Andersson K, Adlerberth I, Wold AE, Rudin A. Higher proportions of circulating FOXP3+ and CTLA-4+ regulatory T cells are associated with lower fractions of memory CD4+ T cells in infants.. J Leukoc Biol. 2011; 90(6):1133-40. (Clone-specific: Intracellular Staining/Flow Cytometry). View Reference
-
Santegoets SJ, Dijkgraaf EM, Battaglia A, et al. Monitoring regulatory T cells in clinical samples: consensus on an essential marker set and gating strategy for regulatory T cell analysis by flow cytometry.. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2015; 64(10):1271-86. (Clone-specific: Intracellular Staining/Flow Cytometry). View Reference
-
Wang H, Shih CC, Waters JB, et al. CD152 (CTLA4) Workshop: Expression and function of CD152 on human T cells: A study using a mouse anti-human CD152 monoclonal antibody BNI3.1. In: Kishimoto T. Tadamitsu Kishimoto .. et al., ed. Leucocyte typing VI : white cell differentiation antigens : proceedings of the sixth international workshop and conference held in Kobe, Japan, 10-14 November 1996. New York: Garland Pub.; 1997:97-98.
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.