Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?
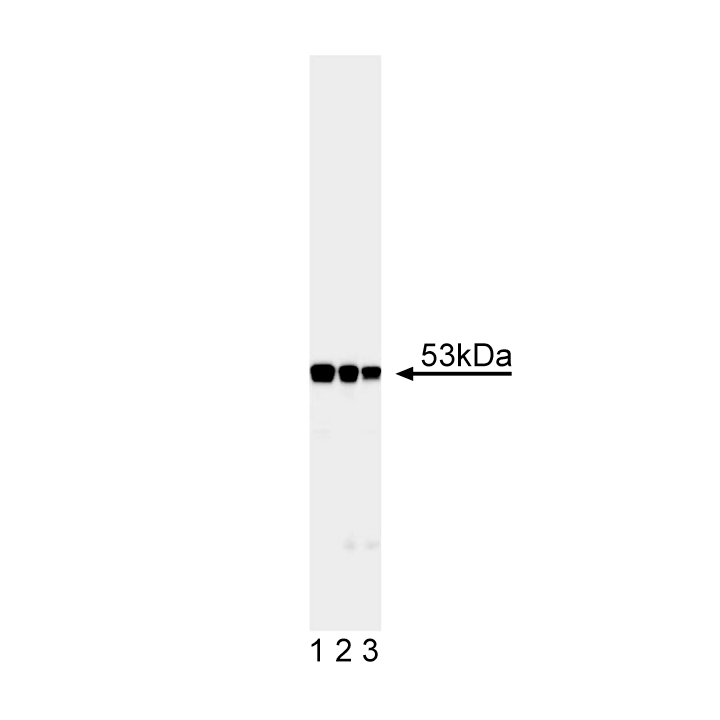



Western blot analysis of desmin. Mouse muscle lysate was probed with anti-desmin (clone RD301, Cat. No. 550626) at concentrations 0.25 (lane 1), 0.125 (lane 2), and 0.06 µg/ml (lane 3). Desmin is identified as a band of ~53 kDa.


BD Pharmingen™ Purified Mouse Anti-Desmin

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
Applications include western blot analysis and immunofluorescence microscopy on frozen sections although IF is not tested at BD Pharmingen. Mouse muscle lysate is recommended as a positive control.
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
Intermediate filaments (IF) are a subset of cytoskeletal proteins which function to give overall structural integrity to the plasma membrane as well as organize cells into specific tissues. IF proteins can be divided into six major types based upon the similarity in sequence. Desmin belongs to the type III category of IF proteins which are predominantly expressed in muscle cells including cardiac, skeletal and smooth muscle. Furthermore, the expression of desmin is regulated in a stage and tissue-specific manner, since it is induced during terminal differentiation of skeletal muscle cells. In skeletal cardiac muscle cells, desmin is localized in the Z-disk region and at the intercalated disk and acts to stabilize sarcomeres in stimulated muscle. Desmin migrates in SDS/PAGE as a 53 kDa protein.
Development References (5)
-
Broers JL, Carney DN, Klein Rot M, et al . Intermediate filament proteins in classic and variant types of small cell lung carcinoma cell lines: a biochemical and immunochemical analysis using a panel of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies. J Cell Sci. 1986; 83:37-60. (Immunogen). View Reference
-
Lodish HF. Molecular cell biology, 4th ed.. New York: W.H. Freeman; 2000:795-847.
-
Pieper FR, Schaart G, Krimpenfort PJ, et al. Transgenic expression of the muscle-specific intermediate filament protein desmin in nonmuscle cells. J Cell Biol. 1989; 108(3):1009-1024. (Clone-specific: Fluorescence microscopy, Western blot). View Reference
-
Raats JM, Pieper FR, Vree Egberts WT, Verrijp KN, Ramaekers FC, Bloemendal H. Assembly of amino-terminally deleted desmin in vimentin-free cells. J Cell Biol. 1990; 111(5):1971-1985. (Clone-specific: Fluorescence microscopy, Western blot). View Reference
-
Schaart G, Viebahn C, Langmann W, Ramaekers F. Desmin and titin expression in early postimplantation mouse embryos. Development. 1989; 107(3):585-596. (Clone-specific: Fluorescence microscopy, Western blot). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.